Dexin Liao
Towards A Unified Conformer Structure: from ASR to ASV Task
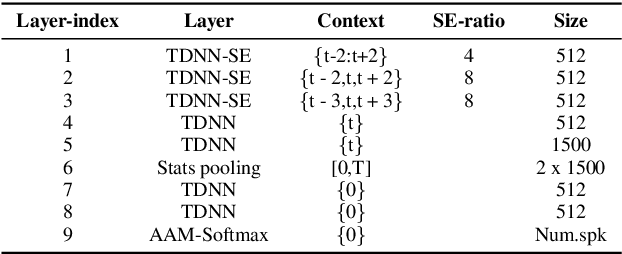
Nov 14, 2022Abstract:Transformer has achieved extraordinary performance in Natural Language Processing and Computer Vision tasks thanks to its powerful self-attention mechanism, and its variant Conformer has become a state-of-the-art architecture in the field of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). However, the main-stream architecture for Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) is convolutional Neural Networks, and there is still much room for research on the Conformer based ASV. In this paper, firstly, we modify the Conformer architecture from ASR to ASV with very minor changes. Length-Scaled Attention (LSA) method and Sharpness-Aware Minimizationis (SAM) are adopted to improve model generalization. Experiments conducted on VoxCeleb and CN-Celeb show that our Conformer based ASV achieves competitive performance compared with the popular ECAPA-TDNN. Secondly, inspired by the transfer learning strategy, ASV Conformer is natural to be initialized from the pretrained ASR model. Via parameter transferring, self-attention mechanism could better focus on the relationship between sequence features, brings about 11% relative improvement in EER on test set of VoxCeleb and CN-Celeb, which reveals the potential of Conformer to unify ASV and ASR task. Finally, we provide a runtime in ASV-Subtools to evaluate its inference speed in production scenario. Our code is released at https://github.com/Snowdar/asv-subtools/tree/master/doc/papers/conformer.md.
An Integrated Framework for Two-pass Personalized Voice Trigger
Jun 30, 2021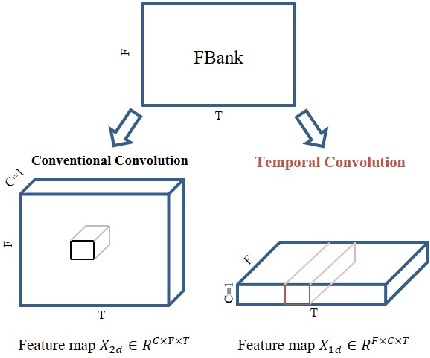
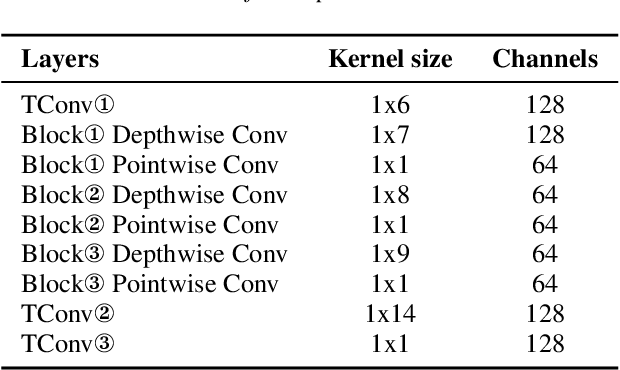
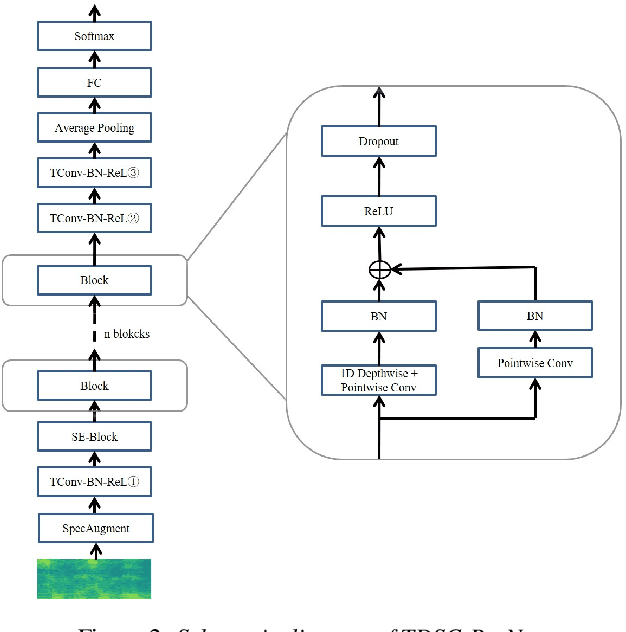
Abstract:In this paper, we present the XMUSPEECH system for Task 1 of 2020 Personalized Voice Trigger Challenge (PVTC2020). Task 1 is a joint wake-up word detection with speaker verification on close talking data. The whole system consists of a keyword spotting (KWS) sub-system and a speaker verification (SV) sub-system. For the KWS system, we applied a Temporal Depthwise Separable Convolution Residual Network (TDSC-ResNet) to improve the system's performance. For the SV system, we proposed a multi-task learning network, where phonetic branch is trained with the character label of the utterance, and speaker branch is trained with the label of the speaker. Phonetic branch is optimized with connectionist temporal classification (CTC) loss, which is treated as an auxiliary module for speaker branch. Experiments show that our system gets significant improvements compared with baseline system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge