Deniz Najafi
Lightator: An Optical Near-Sensor Accelerator with Compressive Acquisition Enabling Versatile Image Processing
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a high-performance and energy-efficient optical near-sensor accelerator for vision applications, called Lightator. Harnessing the promising efficiency offered by photonic devices, Lightator features innovative compressive acquisition of input frames and fine-grained convolution operations for low-power and versatile image processing at the edge for the first time. This will substantially diminish the energy consumption and latency of conversion, transmission, and processing within the established cloud-centric architecture as well as recently designed edge accelerators. Our device-to-architecture simulation results show that with favorable accuracy, Lightator achieves 84.4 Kilo FPS/W and reduces power consumption by a factor of ~24x and 73x on average compared with existing photonic accelerators and GPU baseline.
OISA: Architecting an Optical In-Sensor Accelerator for Efficient Visual Computing
Nov 30, 2023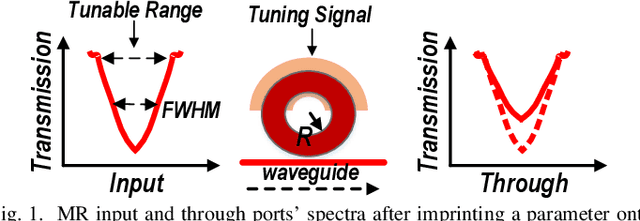
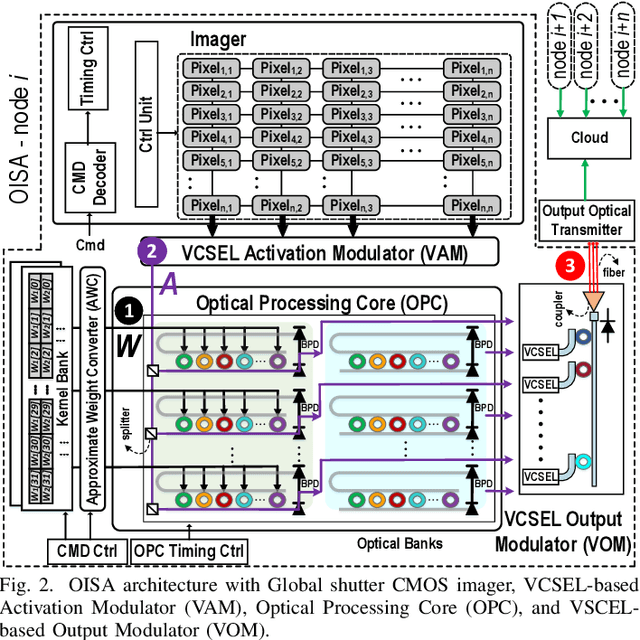
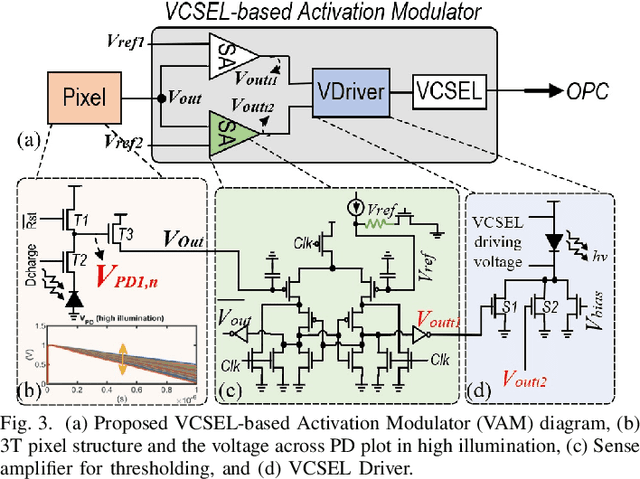
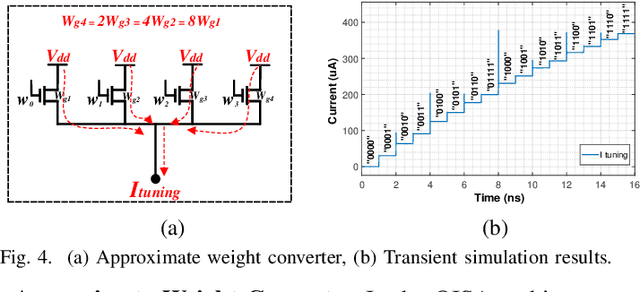
Abstract:Targeting vision applications at the edge, in this work, we systematically explore and propose a high-performance and energy-efficient Optical In-Sensor Accelerator architecture called OISA for the first time. Taking advantage of the promising efficiency of photonic devices, the OISA intrinsically implements a coarse-grained convolution operation on the input frames in an innovative minimum-conversion fashion in low-bit-width neural networks. Such a design remarkably reduces the power consumption of data conversion, transmission, and processing in the conventional cloud-centric architecture as well as recently-presented edge accelerators. Our device-to-architecture simulation results on various image data-sets demonstrate acceptable accuracy while OISA achieves 6.68 TOp/s/W efficiency. OISA reduces power consumption by a factor of 7.9 and 18.4 on average compared with existing electronic in-/near-sensor and ASIC accelerators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge