David Schneider-Joseph
Data movement limits to frontier model training
Nov 02, 2024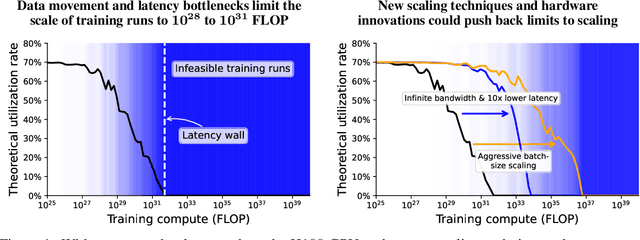
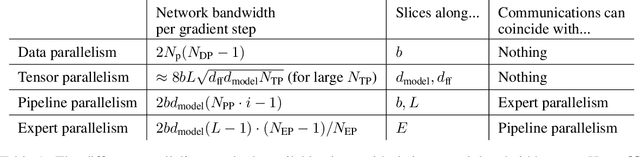
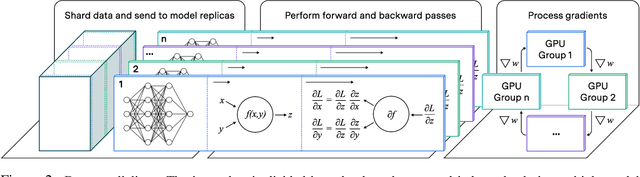

Abstract:We present a theoretical model of distributed training, and use it to analyze how far dense and sparse training runs can be scaled. Under our baseline assumptions, given a three month training duration, data movement bottlenecks begin to significantly lower hardware utilization for training runs exceeding about $10^{28}$ FLOP, two orders of magnitude above the largest training run to date, \textbf{suggesting the arrival of fundamental barriers to scaling in three years} given recent rates of growth. A training run exceeding about $10^{31}$ FLOP is infeasible even at low utilization. However, more aggressive batch size scaling and/or shorter and fatter model shapes, if achievable, have the potential to permit much larger training runs.
LEACE: Perfect linear concept erasure in closed form
Jun 23, 2023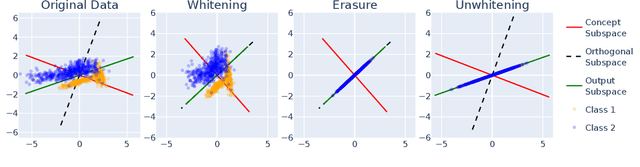
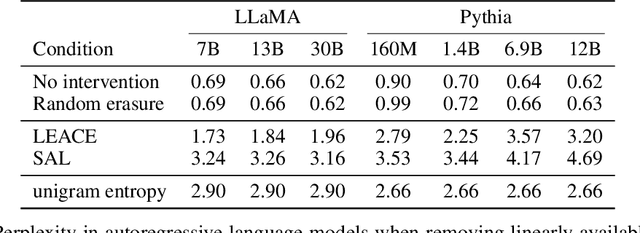
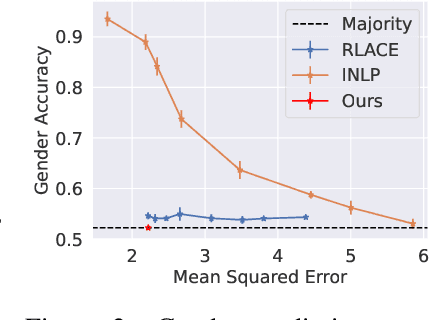
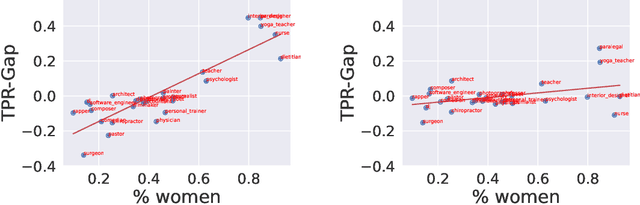
Abstract:Concept erasure aims to remove specified features from a representation. It can improve fairness (e.g. preventing a classifier from using gender or race) and interpretability (e.g. removing a concept to observe changes in model behavior). We introduce LEAst-squares Concept Erasure (LEACE), a closed-form method which provably prevents all linear classifiers from detecting a concept while changing the representation as little as possible, as measured by a broad class of norms. We apply LEACE to large language models with a novel procedure called "concept scrubbing," which erases target concept information from every layer in the network. We demonstrate our method on two tasks: measuring the reliance of language models on part-of-speech information, and reducing gender bias in BERT embeddings. Code is available at https://github.com/EleutherAI/concept-erasure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge