David Novo
ADAC
Approximations in Deep Learning
Dec 08, 2022Abstract:The design and implementation of Deep Learning (DL) models is currently receiving a lot of attention from both industrials and academics. However, the computational workload associated with DL is often out of reach for low-power embedded devices and is still costly when run on datacenters. By relaxing the need for fully precise operations, Approximate Computing (AxC) substantially improves performance and energy efficiency. DL is extremely relevant in this context, since playing with the accuracy needed to do adequate computations will significantly enhance performance, while keeping the quality of results in a user-constrained range. This chapter will explore how AxC can improve the performance and energy efficiency of hardware accelerators in DL applications during inference and training.
Sibyl: Adaptive and Extensible Data Placement in Hybrid Storage Systems Using Online Reinforcement Learning
May 15, 2022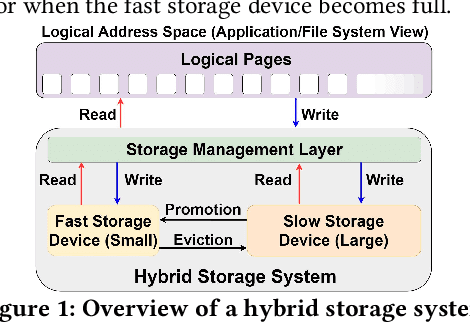

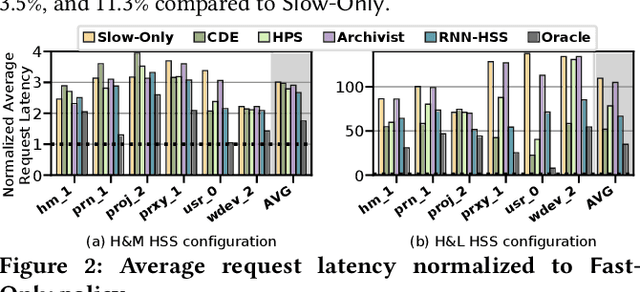
Abstract:Hybrid storage systems (HSS) use multiple different storage devices to provide high and scalable storage capacity at high performance. Recent research proposes various techniques that aim to accurately identify performance-critical data to place it in a "best-fit" storage device. Unfortunately, most of these techniques are rigid, which (1) limits their adaptivity to perform well for a wide range of workloads and storage device configurations, and (2) makes it difficult for designers to extend these techniques to different storage system configurations (e.g., with a different number or different types of storage devices) than the configuration they are designed for. We introduce Sibyl, the first technique that uses reinforcement learning for data placement in hybrid storage systems. Sibyl observes different features of the running workload as well as the storage devices to make system-aware data placement decisions. For every decision it makes, Sibyl receives a reward from the system that it uses to evaluate the long-term performance impact of its decision and continuously optimizes its data placement policy online. We implement Sibyl on real systems with various HSS configurations. Our results show that Sibyl provides 21.6%/19.9% performance improvement in a performance-oriented/cost-oriented HSS configuration compared to the best previous data placement technique. Our evaluation using an HSS configuration with three different storage devices shows that Sibyl outperforms the state-of-the-art data placement policy by 23.9%-48.2%, while significantly reducing the system architect's burden in designing a data placement mechanism that can simultaneously incorporate three storage devices. We show that Sibyl achieves 80% of the performance of an oracle policy that has complete knowledge of future access patterns while incurring a very modest storage overhead of only 124.4 KiB.
Fast Exploration of Weight Sharing Opportunities for CNN Compression
Feb 02, 2021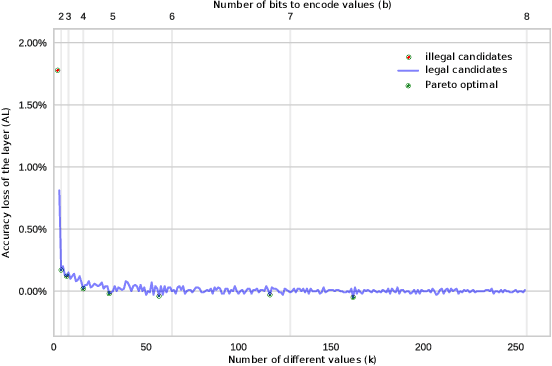
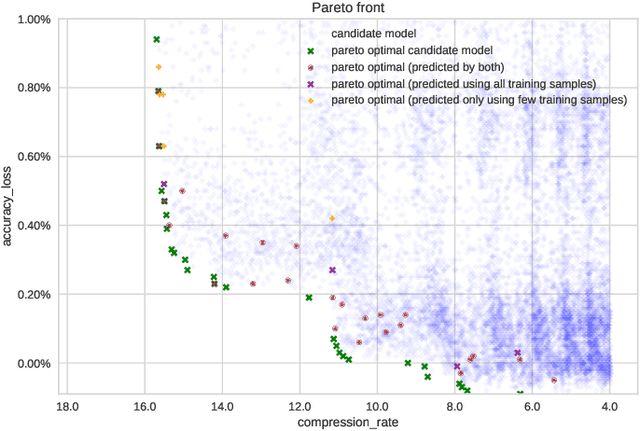
Abstract:The computational workload involved in Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) is typically out of reach for low-power embedded devices. There are a large number of approximation techniques to address this problem. These methods have hyper-parameters that need to be optimized for each CNNs using design space exploration (DSE). The goal of this work is to demonstrate that the DSE phase time can easily explode for state of the art CNN. We thus propose the use of an optimized exploration process to drastically reduce the exploration time without sacrificing the quality of the output.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge