David John Gagne II
Improving Medium Range Severe Weather Prediction through Transformer Post-processing of AI Weather Forecasts
May 16, 2025Abstract:Improving the skill of medium-range (1-8 day) severe weather prediction is crucial for mitigating societal impacts. This study introduces a novel approach leveraging decoder-only transformer networks to post-process AI-based weather forecasts, specifically from the Pangu-Weather model, for improved severe weather guidance. Unlike traditional post-processing methods that use a dense neural network to predict the probability of severe weather using discrete forecast samples, our method treats forecast lead times as sequential ``tokens'', enabling the transformer to learn complex temporal relationships within the evolving atmospheric state. We compare this approach against post-processing of the Global Forecast System (GFS) using both a traditional dense neural network and our transformer, as well as configurations that exclude convective parameters to fairly evaluate the impact of using the Pangu-Weather AI model. Results demonstrate that the transformer-based post-processing significantly enhances forecast skill compared to dense neural networks. Furthermore, AI-driven forecasts, particularly Pangu-Weather initialized from high resolution analysis, exhibit superior performance to GFS in the medium-range, even without explicit convective parameters. Our approach offers improved accuracy, and reliability, which also provides interpretability through feature attribution analysis, advancing medium-range severe weather prediction capabilities.
Community Research Earth Digital Intelligence Twin (CREDIT)
Nov 09, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) for numerical weather prediction (NWP) have significantly transformed atmospheric modeling. AI NWP models outperform traditional physics-based systems, such as the Integrated Forecast System (IFS), across several global metrics while requiring fewer computational resources. However, existing AI NWP models face limitations related to training datasets and timestep choices, often resulting in artifacts that reduce model performance. To address these challenges, we introduce the Community Research Earth Digital Intelligence Twin (CREDIT) framework, developed at NSF NCAR. CREDIT provides a flexible, scalable, and user-friendly platform for training and deploying AI-based atmospheric models on high-performance computing systems. It offers an end-to-end pipeline for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation, democratizing access to advanced AI NWP capabilities. We demonstrate CREDIT's potential through WXFormer, a novel deterministic vision transformer designed to predict atmospheric states autoregressively, addressing common AI NWP issues like compounding error growth with techniques such as spectral normalization, padding, and multi-step training. Additionally, to illustrate CREDIT's flexibility and state-of-the-art model comparisons, we train the FUXI architecture within this framework. Our findings show that both FUXI and WXFormer, trained on six-hourly ERA5 hybrid sigma-pressure levels, generally outperform IFS HRES in 10-day forecasts, offering potential improvements in efficiency and forecast accuracy. CREDIT's modular design enables researchers to explore various models, datasets, and training configurations, fostering innovation within the scientific community.
Improving ensemble extreme precipitation forecasts using generative artificial intelligence
Jul 05, 2024Abstract:An ensemble post-processing method is developed to improve the probabilistic forecasts of extreme precipitation events across the conterminous United States (CONUS). The method combines a 3-D Vision Transformer (ViT) for bias correction with a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM), a generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) method, to post-process 6-hourly precipitation ensemble forecasts and produce an enlarged generative ensemble that contains spatiotemporally consistent precipitation trajectories. These trajectories are expected to improve the characterization of extreme precipitation events and offer skillful multi-day accumulated and 6-hourly precipitation guidance. The method is tested using the Global Ensemble Forecast System (GEFS) precipitation forecasts out to day 6 and is verified against the Climate-Calibrated Precipitation Analysis (CCPA) data. Verification results indicate that the method generated skillful ensemble members with improved Continuous Ranked Probabilistic Skill Scores (CRPSSs) and Brier Skill Scores (BSSs) over the raw operational GEFS and a multivariate statistical post-processing baseline. It showed skillful and reliable probabilities for events at extreme precipitation thresholds. Explainability studies were further conducted, which revealed the decision-making process of the method and confirmed its effectiveness on ensemble member generation. This work introduces a novel, generative-AI-based approach to address the limitation of small numerical ensembles and the need for larger ensembles to identify extreme precipitation events.
Physically Explainable Deep Learning for Convective Initiation Nowcasting Using GOES-16 Satellite Observations
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Convection initiation (CI) nowcasting remains a challenging problem for both numerical weather prediction models and existing nowcasting algorithms. In this study, object-based probabilistic deep learning models are developed to predict CI based on multichannel infrared GOES-R satellite observations. The data come from patches surrounding potential CI events identified in Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor Doppler weather radar products over the Great Plains region from June and July 2020 and June 2021. An objective radar-based approach is used to identify these events. The deep learning models significantly outperform the classical logistic model at lead times up to 1 hour, especially on the false alarm ratio. Through case studies, the deep learning model exhibits the dependence on the characteristics of clouds and moisture at multiple levels. Model explanation further reveals the model's decision-making process with different baselines. The explanation results highlight the importance of moisture and cloud features at different levels depending on the choice of baseline. Our study demonstrates the advantage of using different baselines in further understanding model behavior and gaining scientific insights.
Generative ensemble deep learning severe weather prediction from a deterministic convection-allowing model
Oct 09, 2023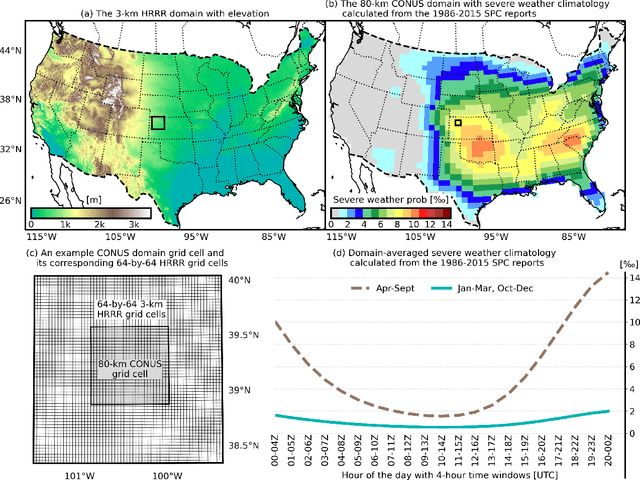
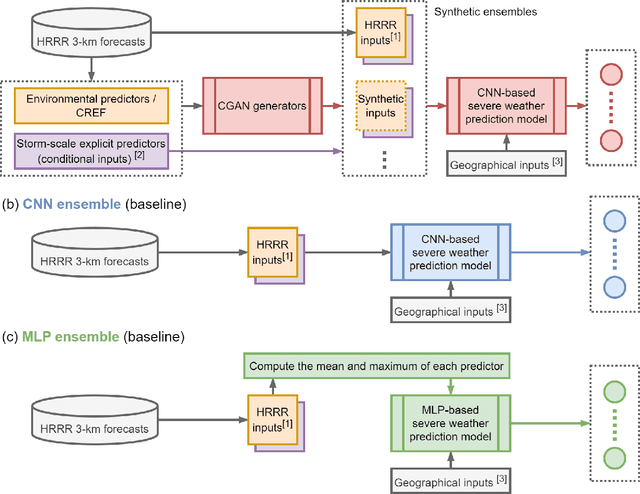
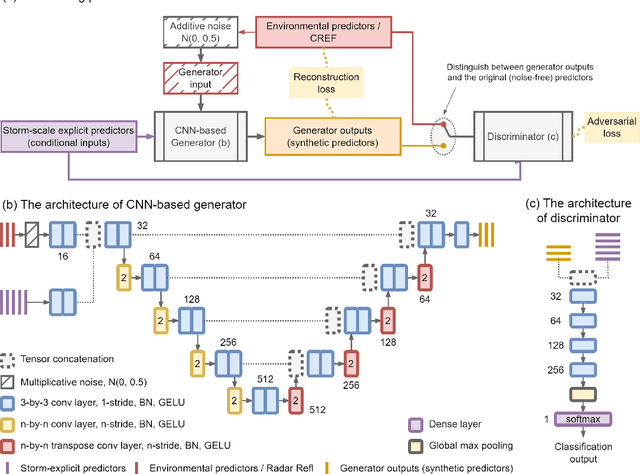
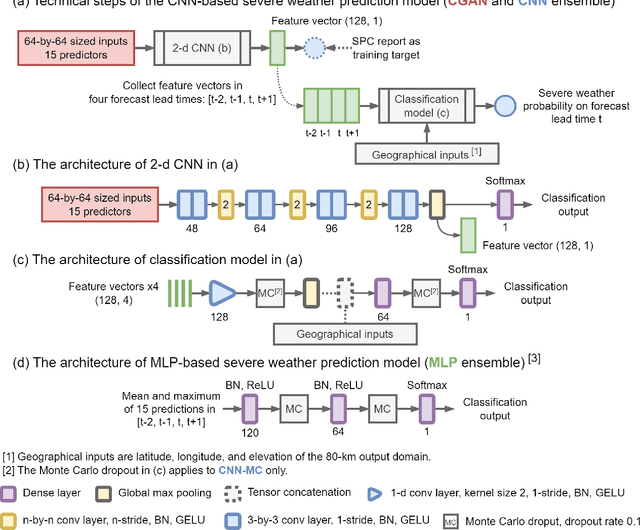
Abstract:An ensemble post-processing method is developed for the probabilistic prediction of severe weather (tornadoes, hail, and wind gusts) over the conterminous United States (CONUS). The method combines conditional generative adversarial networks (CGANs), a type of deep generative model, with a convolutional neural network (CNN) to post-process convection-allowing model (CAM) forecasts. The CGANs are designed to create synthetic ensemble members from deterministic CAM forecasts, and their outputs are processed by the CNN to estimate the probability of severe weather. The method is tested using High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) 1--24 hr forecasts as inputs and Storm Prediction Center (SPC) severe weather reports as targets. The method produced skillful predictions with up to 20% Brier Skill Score (BSS) increases compared to other neural-network-based reference methods using a testing dataset of HRRR forecasts in 2021. For the evaluation of uncertainty quantification, the method is overconfident but produces meaningful ensemble spreads that can distinguish good and bad forecasts. The quality of CGAN outputs is also evaluated. Results show that the CGAN outputs behave similarly to a numerical ensemble; they preserved the inter-variable correlations and the contribution of influential predictors as in the original HRRR forecasts. This work provides a novel approach to post-process CAM output using neural networks that can be applied to severe weather prediction.
Evidential Deep Learning: Enhancing Predictive Uncertainty Estimation for Earth System Science Applications
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:Robust quantification of predictive uncertainty is critical for understanding factors that drive weather and climate outcomes. Ensembles provide predictive uncertainty estimates and can be decomposed physically, but both physics and machine learning ensembles are computationally expensive. Parametric deep learning can estimate uncertainty with one model by predicting the parameters of a probability distribution but do not account for epistemic uncertainty.. Evidential deep learning, a technique that extends parametric deep learning to higher-order distributions, can account for both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty with one model. This study compares the uncertainty derived from evidential neural networks to those obtained from ensembles. Through applications of classification of winter precipitation type and regression of surface layer fluxes, we show evidential deep learning models attaining predictive accuracy rivaling standard methods, while robustly quantifying both sources of uncertainty. We evaluate the uncertainty in terms of how well the predictions are calibrated and how well the uncertainty correlates with prediction error. Analyses of uncertainty in the context of the inputs reveal sensitivities to underlying meteorological processes, facilitating interpretation of the models. The conceptual simplicity, interpretability, and computational efficiency of evidential neural networks make them highly extensible, offering a promising approach for reliable and practical uncertainty quantification in Earth system science modeling. In order to encourage broader adoption of evidential deep learning in Earth System Science, we have developed a new Python package, MILES-GUESS (https://github.com/ai2es/miles-guess), that enables users to train and evaluate both evidential and ensemble deep learning.
The Need for Ethical, Responsible, and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence for Environmental Sciences
Dec 15, 2021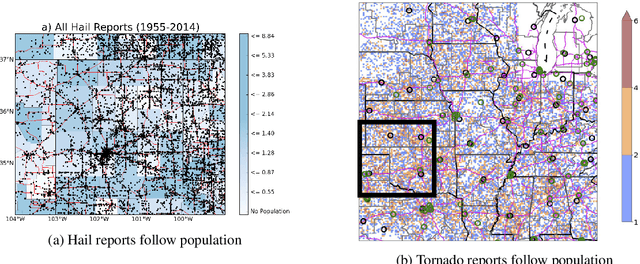
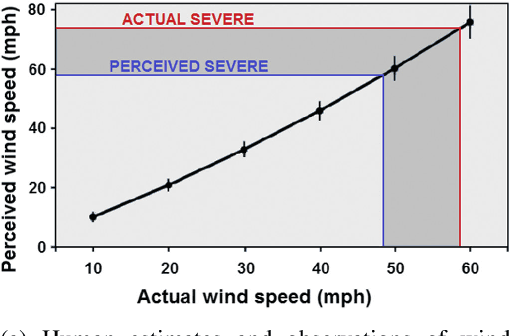
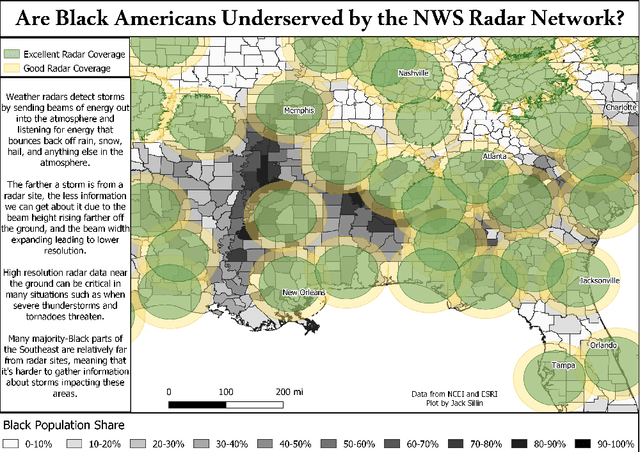
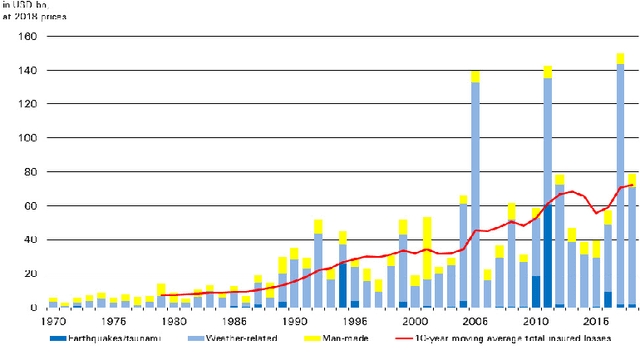
Abstract:Given the growing use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) methods across all aspects of environmental sciences, it is imperative that we initiate a discussion about the ethical and responsible use of AI. In fact, much can be learned from other domains where AI was introduced, often with the best of intentions, yet often led to unintended societal consequences, such as hard coding racial bias in the criminal justice system or increasing economic inequality through the financial system. A common misconception is that the environmental sciences are immune to such unintended consequences when AI is being used, as most data come from observations, and AI algorithms are based on mathematical formulas, which are often seen as objective. In this article, we argue the opposite can be the case. Using specific examples, we demonstrate many ways in which the use of AI can introduce similar consequences in the environmental sciences. This article will stimulate discussion and research efforts in this direction. As a community, we should avoid repeating any foreseeable mistakes made in other domains through the introduction of AI. In fact, with proper precautions, AI can be a great tool to help {\it reduce} climate and environmental injustice. We primarily focus on weather and climate examples but the conclusions apply broadly across the environmental sciences.
Machine Learning for Stochastic Parameterization: Generative Adversarial Networks in the Lorenz '96 Model
Sep 10, 2019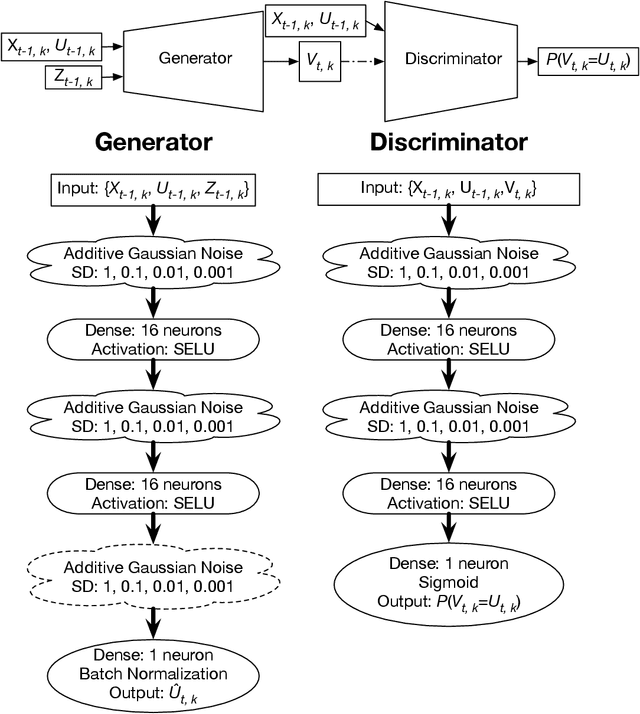
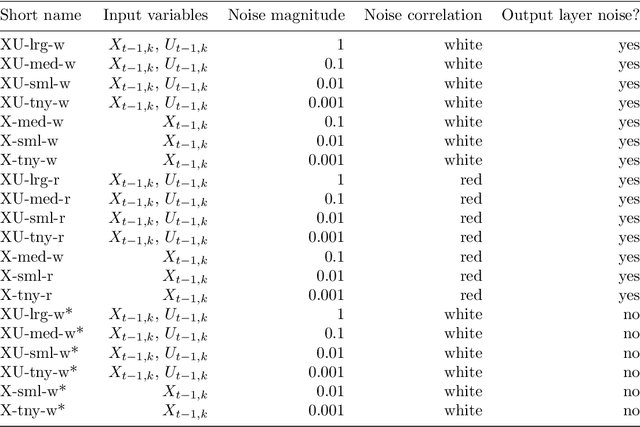

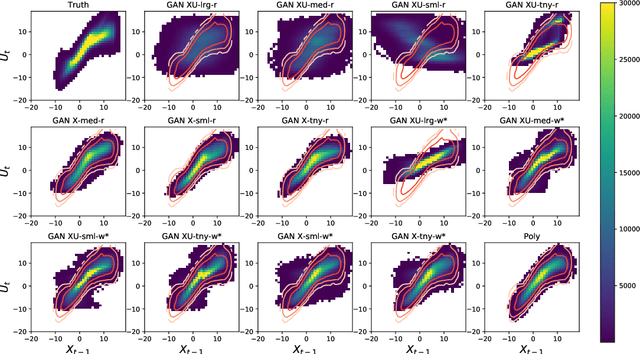
Abstract:Stochastic parameterizations account for uncertainty in the representation of unresolved sub-grid processes by sampling from the distribution of possible sub-grid forcings. Some existing stochastic parameterizations utilize data-driven approaches to characterize uncertainty, but these approaches require significant structural assumptions that can limit their scalability. Machine learning models, including neural networks, are able to represent a wide range of distributions and build optimized mappings between a large number of inputs and sub-grid forcings. Recent research on machine learning parameterizations has focused only on deterministic parameterizations. In this study, we develop a stochastic parameterization using the generative adversarial network (GAN) machine learning framework. The GAN stochastic parameterization is trained and evaluated on output from the Lorenz '96 model, which is a common baseline model for evaluating both parameterization and data assimilation techniques. We evaluate different ways of characterizing the input noise for the model and perform model runs with the GAN parameterization at weather and climate timescales. Some of the GAN configurations perform better than a baseline bespoke parameterization at both timescales, and the networks closely reproduce the spatio-temporal correlations and regimes of the Lorenz '96 system. We also find that in general those models which produce skillful forecasts are also associated with the best climate simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge