David Álvarez
Supervised learning for improving the accuracy of robot-mounted 3D camera applied to human gait analysis
Jul 03, 2022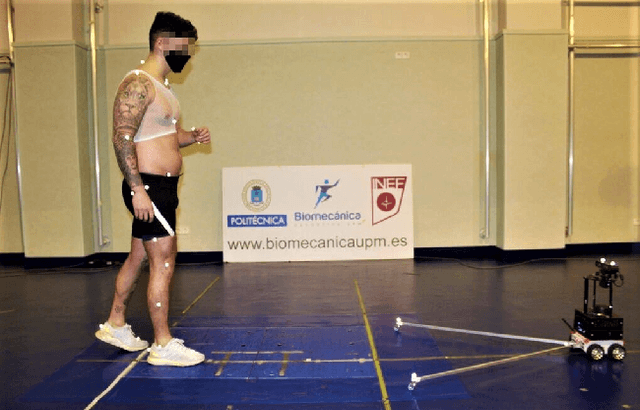


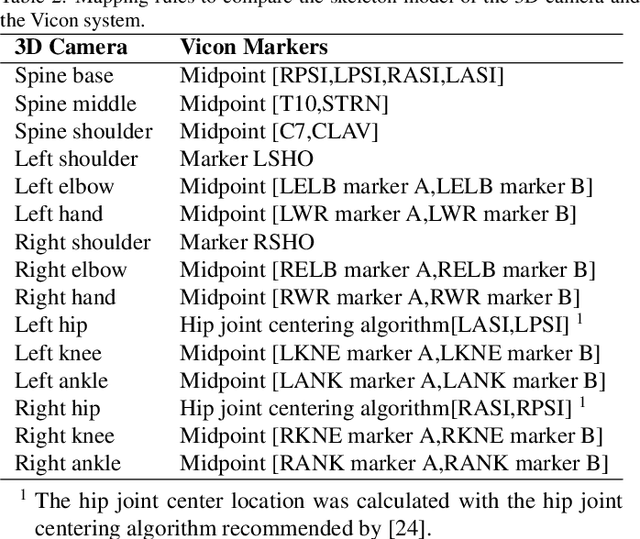
Abstract:The use of 3D cameras for gait analysis has been highly questioned due to the low accuracy they have demonstrated in the past. The objective of the study presented in this paper is to improve the accuracy of the estimations made by robot-mounted 3D cameras in human gait analysis by applying a supervised learning stage. The 3D camera was mounted in a mobile robot to obtain a longer walking distance. This study shows an improvement in detection of kinematic gait signals and gait descriptors by post-processing the raw estimations of the camera using artificial neural networks trained with the data obtained from a certified Vicon system. To achieve this, 37 healthy participants were recruited and data of 207 gait sequences were collected using an Orbbec Astra 3D camera. There are two basic possible approaches for training: using kinematic gait signals and using gait descriptors. The former seeks to improve the waveforms of kinematic gait signals by reducing the error and increasing the correlation with respect to the Vicon system. The second is a more direct approach, focusing on training the artificial neural networks using gait descriptors directly. The accuracy of the 3D camera was measured before and after training. In both training approaches, an improvement was observed. Kinematic gait signals showed lower errors and higher correlations with respect to the ground truth. The accuracy of the system to detect gait descriptors also showed a substantial improvement, mostly for kinematic descriptors rather than spatio-temporal. When comparing both training approaches, it was not possible to define which was the absolute best. Therefore, we believe that the selection of the training approach will depend on the purpose of the study to be conducted. This study reveals the great potential of 3D cameras and encourages the research community to continue exploring their use in gait analysis.
Input complexity and out-of-distribution detection with likelihood-based generative models
Sep 25, 2019
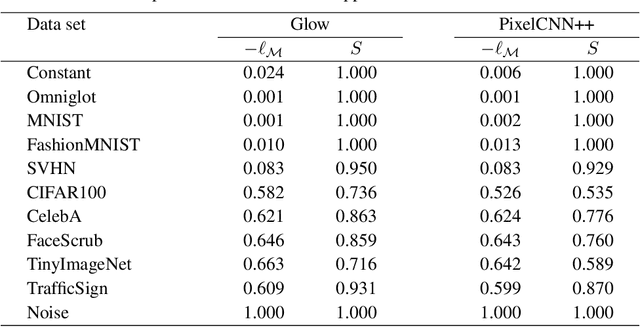

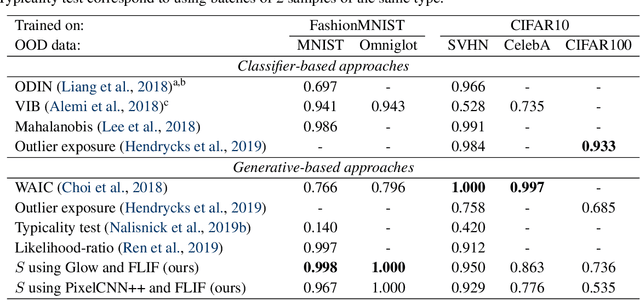
Abstract:Likelihood-based generative models are a promising resource to detect out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs which could compromise the robustness or reliability of a machine learning system. However, likelihoods derived from such models have been shown to be problematic for detecting certain types of inputs that significantly differ from training data. In this paper, we pose that this problem is due to the excessive influence that input complexity has in generative models' likelihoods. We report a set of experiments supporting this hypothesis, and use an estimate of input complexity to derive an efficient and parameter-free OOD score, which can be seen as a likelihood-ratio test akin to Bayesian model comparison. We find such score to perform comparably to, or even better than, existing OOD detection approaches under a wide range of data sets, models, and complexity estimates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge