Daniel Gareev
Local and Global Decoding in Text Generation
Oct 14, 2024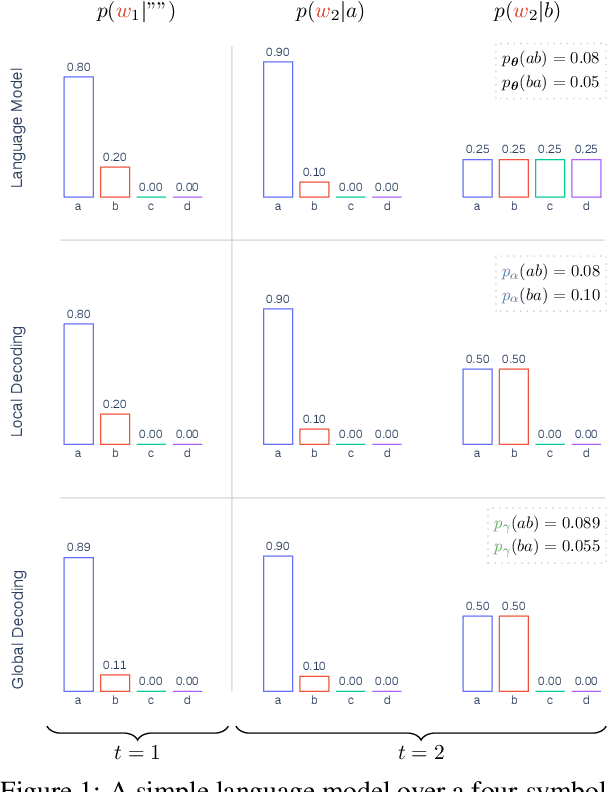
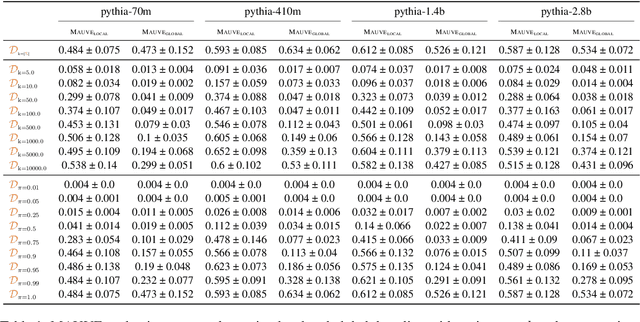

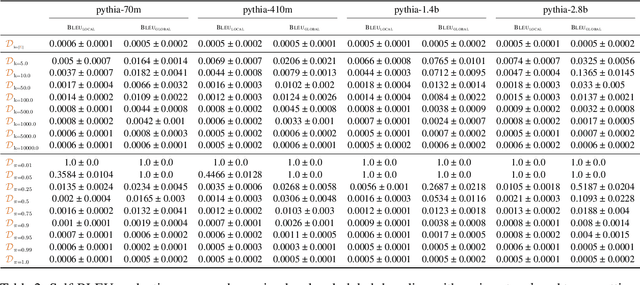
Abstract:Text generation, a key component in applications such as dialogue systems, relies on decoding algorithms that sample strings from a language model distribution. Traditional methods, such as top-$k$ and top-$\pi$, apply local normalisation to the model's output distribution, which can distort it. In this paper, we investigate the effect of this distortion by introducing globally-normalised versions of these decoding methods. Additionally, we propose an independent Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to approximate sampling from globally-normalised distributions without explicitly computing them. Our empirical analysis compares the performance of local and global normalisation across two decoding algorithms (top-$k$ and top-$\pi$) with various hyperparameters, using Pythia language models. Results show that, in most configurations, global decoding performs worse than the local decoding version of the same algorithms -- despite preserving the distribution's integrity. Our results suggest that distortion is an important feature of local decoding algorithms.
Hyperparameter Optimization for Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful approach for tackling complex problems. The recent introduction of multi-objective reinforcement learning (MORL) has further expanded the scope of RL by enabling agents to make trade-offs among multiple objectives. This advancement not only has broadened the range of problems that can be tackled but also created numerous opportunities for exploration and advancement. Yet, the effectiveness of RL agents heavily relies on appropriately setting their hyperparameters. In practice, this task often proves to be challenging, leading to unsuccessful deployments of these techniques in various instances. Hence, prior research has explored hyperparameter optimization in RL to address this concern. This paper presents an initial investigation into the challenge of hyperparameter optimization specifically for MORL. We formalize the problem, highlight its distinctive challenges, and propose a systematic methodology to address it. The proposed methodology is applied to a well-known environment using a state-of-the-art MORL algorithm, and preliminary results are reported. Our findings indicate that the proposed methodology can effectively provide hyperparameter configurations that significantly enhance the performance of MORL agents. Furthermore, this study identifies various future research opportunities to further advance the field of hyperparameter optimization for MORL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge