Craig Jin
Simi-SFX: A similarity-based conditioning method for controllable sound effect synthesis
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:Generating sound effects with controllable variations is a challenging task, traditionally addressed using sophisticated physical models that require in-depth knowledge of signal processing parameters and algorithms. In the era of generative and large language models, text has emerged as a common, human-interpretable interface for controlling sound synthesis. However, the discrete and qualitative nature of language tokens makes it difficult to capture subtle timbral variations across different sounds. In this research, we propose a novel similarity-based conditioning method for sound synthesis, leveraging differentiable digital signal processing (DDSP). This approach combines the use of latent space for learning and controlling audio timbre with an intuitive guiding vector, normalized within the range [0,1], to encode categorical acoustic information. By utilizing pre-trained audio representation models, our method achieves expressive and fine-grained timbre control. To benchmark our approach, we introduce two sound effect datasets--Footstep-set and Impact-set--designed to evaluate both controllability and sound quality. Regression analysis demonstrates that the proposed similarity score effectively controls timbre variations and enables creative applications such as timbre interpolation between discrete classes. Our work provides a robust and versatile framework for sound effect synthesis, bridging the gap between traditional signal processing and modern machine learning techniques.
A Scene Representation for Online Spatial Sonification
Dec 07, 2024Abstract:Robotic perception is emerging as a crucial technology for navigation aids, particularly benefiting individuals with visual impairments through sonification. This paper presents a novel mapping framework that accurately represents spatial geometry for sonification, transforming physical spaces into auditory experiences. By leveraging depth sensors, we convert incrementally built 3D scenes into a compact 360-degree representation based on angular and distance information, aligning with human auditory perception. Our proposed mapping framework utilises a sensor-centric structure, maintaining 2D circular or 3D cylindrical representations, and employs the VDB-GPDF for efficient online mapping. We introduce two sonification modes-circular ranging and circular ranging of objects-along with real-time user control over auditory filters. Incorporating binaural room impulse responses, our framework provides perceptually robust auditory feedback. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate superior performance in accuracy, coverage, and timing compared to existing approaches, with effective handling of dynamic objects. The accompanying video showcases the practical application of spatial sonification in room-like environments.
ICGAN: An implicit conditioning method for interpretable feature control of neural audio synthesis
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:Neural audio synthesis methods can achieve high-fidelity and realistic sound generation by utilizing deep generative models. Such models typically rely on external labels which are often discrete as conditioning information to achieve guided sound generation. However, it remains difficult to control the subtle changes in sounds without appropriate and descriptive labels, especially given a limited dataset. This paper proposes an implicit conditioning method for neural audio synthesis using generative adversarial networks that allows for interpretable control of the acoustic features of synthesized sounds. Our technique creates a continuous conditioning space that enables timbre manipulation without relying on explicit labels. We further introduce an evaluation metric to explore controllability and demonstrate that our approach is effective in enabling a degree of controlled variation of different synthesized sound effects for in-domain and cross-domain sounds.
HRTF Interpolation using a Spherical Neural Process Meta-Learner
Oct 20, 2023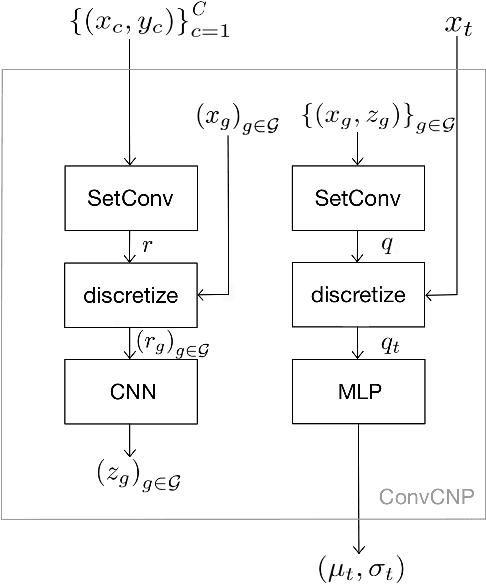
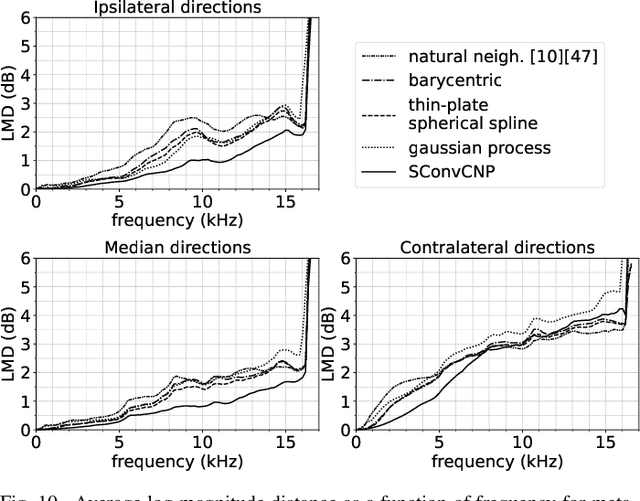
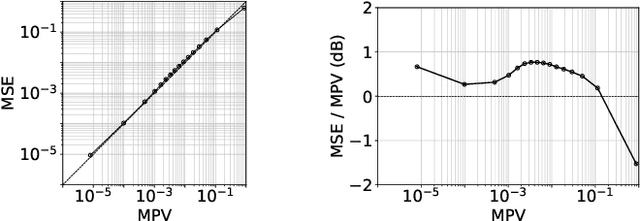
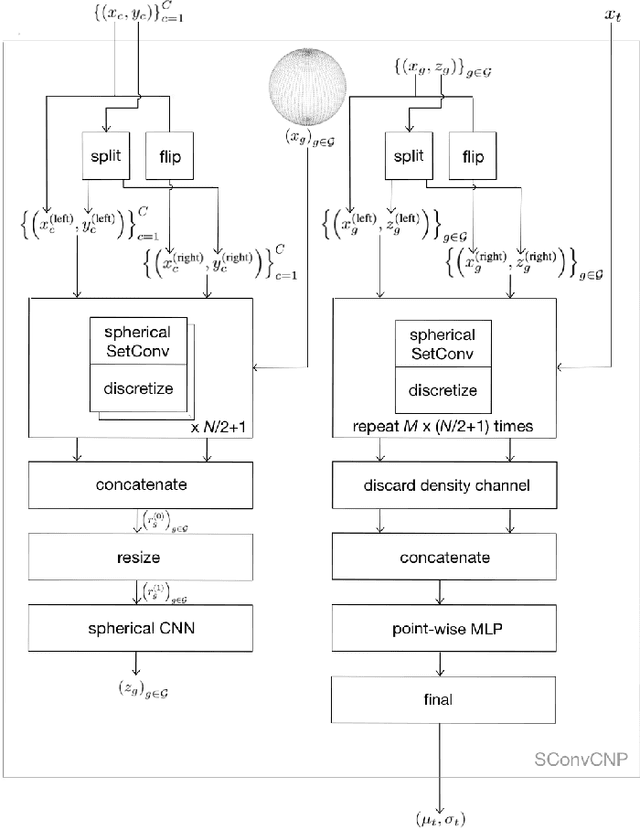
Abstract:Several individualization methods have recently been proposed to estimate a subject's Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF) using convenient input modalities such as anthropometric measurements or pinnae photographs. There exists a need for adaptively correcting the estimation error committed by such methods using a few data point samples from the subject's HRTF, acquired using acoustic measurements or perceptual feedback. To this end, we introduce a Convolutional Conditional Neural Process meta-learner specialized in HRTF error interpolation. In particular, the model includes a Spherical Convolutional Neural Network component to accommodate the spherical geometry of HRTF data. It also exploits potential symmetries between the HRTF's left and right channels about the median axis. In this work, we evaluate the proposed model's performance purely on time-aligned spectrum interpolation grounds under a simplified setup where a generic population-mean HRTF forms the initial estimates prior to corrections instead of individualized ones. The trained model achieves up to 3 dB relative error reduction compared to state-of-the-art interpolation methods despite being trained using only 85 subjects. This improvement translates up to nearly a halving of the data point count required to achieve comparable accuracy, in particular from 50 to 28 points to reach an average of -20 dB relative error per interpolated feature. Moreover, we show that the trained model provides well-calibrated uncertainty estimates. Accordingly, such estimates can inform the sequential decision problem of acquiring as few correcting HRTF data points as needed to meet a desired level of HRTF individualization accuracy.
DDSP-SFX: Acoustically-guided sound effects generation with differentiable digital signal processing
Sep 14, 2023



Abstract:Controlling the variations of sound effects using neural audio synthesis models has been a difficult task. Differentiable digital signal processing (DDSP) provides a lightweight solution that achieves high-quality sound synthesis while enabling deterministic acoustic attribute control by incorporating pre-processed audio features and digital synthesizers. In this research, we introduce DDSP-SFX, a model based on the DDSP architecture capable of synthesizing high-quality sound effects while enabling users to control the timbre variations easily. We propose a transient modelling technique with higher objective evaluation scores and subjective ratings over impulsive signals (footsteps, gunshots). We propose a simple method that achieves timbre variation control while also allowing deterministic attribute control. We further qualitatively show the timbre transfer performance using voice as the guiding sound.
Improving spatial cues for hearables using a parameterized binaural CDR estimator
Jul 17, 2022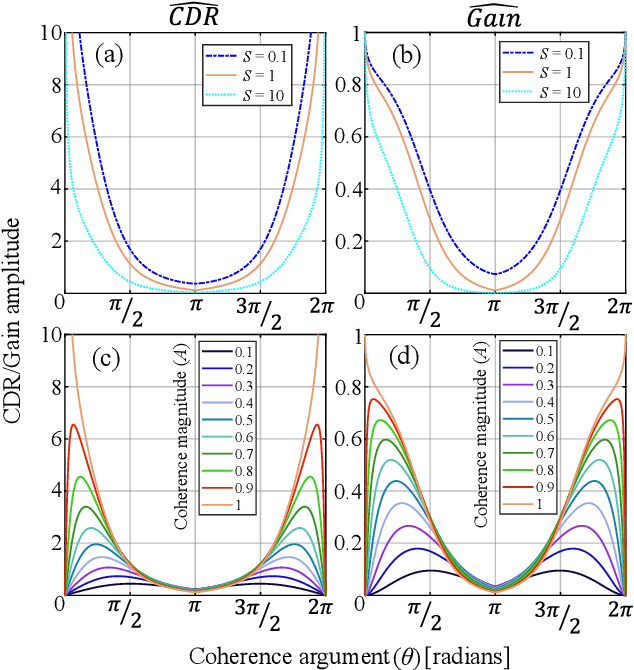
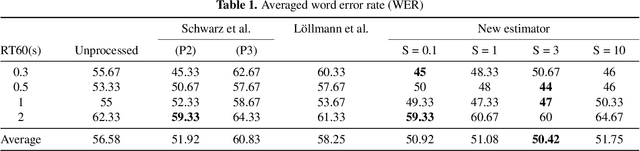
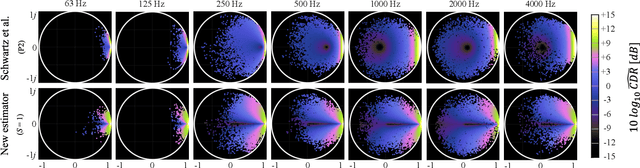
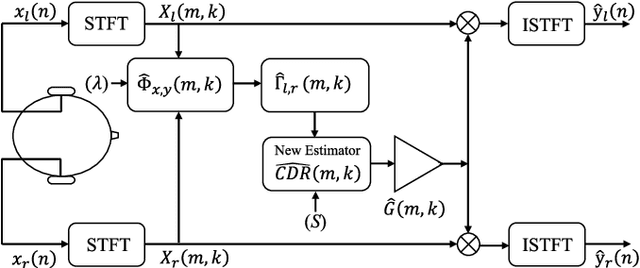
Abstract:We investigate a speech enhancement method based on the binaural coherence-to-diffuse power ratio (CDR), which preserves auditory spatial cues for maskers and a broadside target. Conventional CDR estimators typically rely on a mathematical coherence model of the desired signal and/or diffuse noise field in their formulation, which may influence their accuracy in natural environments. This work proposes a new robust and parameterized directional binaural CDR estimator. The estimator is calculated in the time-frequency domain and is based on a geometrical interpretation of the spatial coherence function between the binaural microphone signals. The binaural performance of the new CDR estimator is compared with three state-of-the-art CDR estimators in cocktail-party-like environments and has shown improvements in terms of several objective speech quality metrics such as PESQ and SRMR. We also discuss the benefits of the parameterizable CDR estimator for varying sound environments and briefly reflect on several informal subjective evaluations using a low-latency real-time framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge