Chunlin Zhong
OwlCap: Harmonizing Motion-Detail for Video Captioning via HMD-270K and Caption Set Equivalence Reward
Aug 27, 2025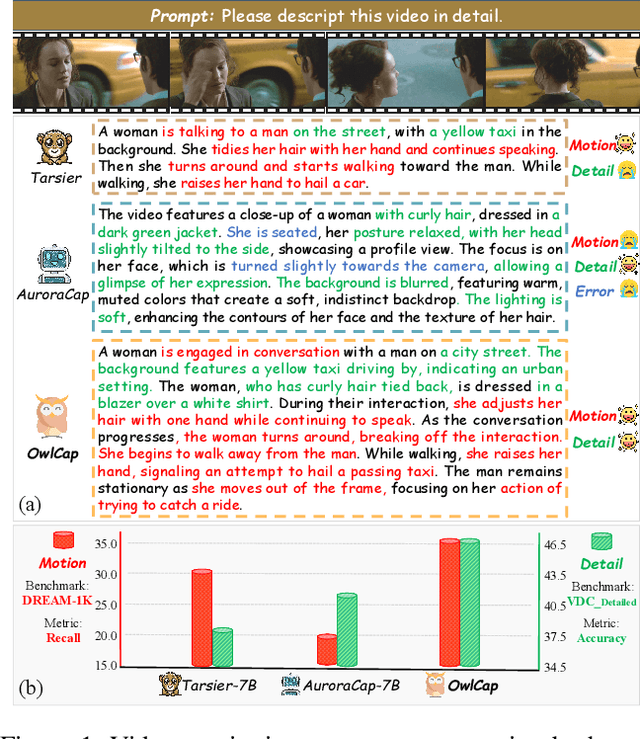
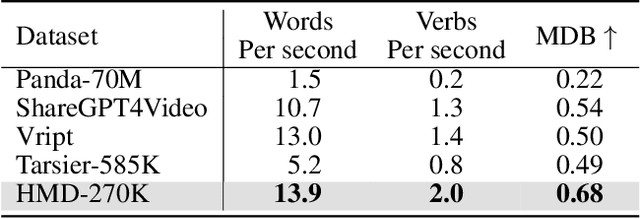
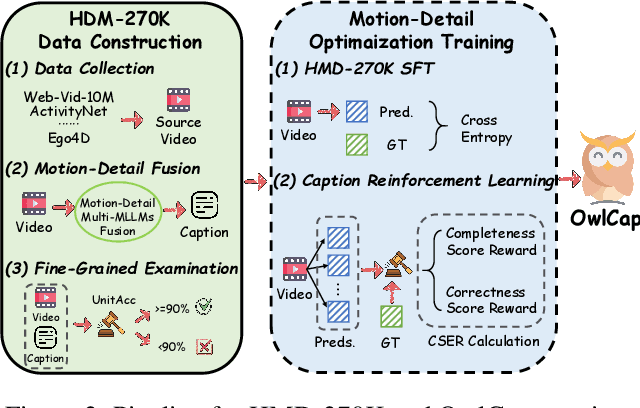
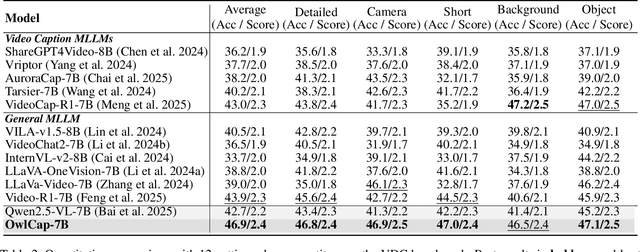
Abstract:Video captioning aims to generate comprehensive and coherent descriptions of the video content, contributing to the advancement of both video understanding and generation. However, existing methods often suffer from motion-detail imbalance, as models tend to overemphasize one aspect while neglecting the other. This imbalance results in incomplete captions, which in turn leads to a lack of consistency in video understanding and generation. To address this issue, we propose solutions from two aspects: 1) Data aspect: We constructed the Harmonizing Motion-Detail 270K (HMD-270K) dataset through a two-stage pipeline: Motion-Detail Fusion (MDF) and Fine-Grained Examination (FGE). 2) Optimization aspect: We introduce the Caption Set Equivalence Reward (CSER) based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). CSER enhances completeness and accuracy in capturing both motion and details through unit-to-set matching and bidirectional validation. Based on the HMD-270K supervised fine-tuning and GRPO post-training with CSER, we developed OwlCap, a powerful video captioning multi-modal large language model (MLLM) with motion-detail balance. Experimental results demonstrate that OwlCap achieves significant improvements compared to baseline models on two benchmarks: the detail-focused VDC (+4.2 Acc) and the motion-focused DREAM-1K (+4.6 F1). The HMD-270K dataset and OwlCap model will be publicly released to facilitate video captioning research community advancements.
PathVG: A New Benchmark and Dataset for Pathology Visual Grounding
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of computational pathology, many AI-assisted diagnostic tasks have emerged. Cellular nuclei segmentation can segment various types of cells for downstream analysis, but it relies on predefined categories and lacks flexibility. Moreover, pathology visual question answering can perform image-level understanding but lacks region-level detection capability. To address this, we propose a new benchmark called Pathology Visual Grounding (PathVG), which aims to detect regions based on expressions with different attributes. To evaluate PathVG, we create a new dataset named RefPath which contains 27,610 images with 33,500 language-grounded boxes. Compared to visual grounding in other domains, PathVG presents pathological images at multi-scale and contains expressions with pathological knowledge. In the experimental study, we found that the biggest challenge was the implicit information underlying the pathological expressions. Based on this, we proposed Pathology Knowledge-enhanced Network (PKNet) as the baseline model for PathVG. PKNet leverages the knowledge-enhancement capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to convert pathological terms with implicit information into explicit visual features, and fuses knowledge features with expression features through the designed Knowledge Fusion Module (KFM). The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the PathVG benchmark.
Unconstrained Salient and Camouflaged Object Detection
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Visual Salient Object Detection (SOD) and Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) are two interrelated yet distinct tasks. Both tasks model the human visual system's ability to perceive the presence of objects. The traditional SOD datasets and methods are designed for scenes where only salient objects are present, similarly, COD datasets and methods are designed for scenes where only camouflaged objects are present. However, scenes where both salient and camouflaged objects coexist, or where neither is present, are not considered. This simplifies the existing research on SOD and COD. In this paper, to explore a more generalized approach to SOD and COD, we introduce a benchmark called Unconstrained Salient and Camouflaged Object Detection (USCOD), which supports the simultaneous detection of salient and camouflaged objects in unconstrained scenes, regardless of their presence. Towards this, we construct a large-scale dataset, CS12K, that encompasses a variety of scenes, including four distinct types: only salient objects, only camouflaged objects, both, and neither. In our benchmark experiments, we identify a major challenge in USCOD: distinguishing between salient and camouflaged objects within the same scene. To address this challenge, we propose USCNet, a baseline model for USCOD that decouples the learning of attribute distinction from mask reconstruction. The model incorporates an APG module, which learns both sample-generic and sample-specific features to enhance the attribute differentiation between salient and camouflaged objects. Furthermore, to evaluate models' ability to distinguish between salient and camouflaged objects, we design a metric called Camouflage-Saliency Confusion Score (CSCS). The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the newly introduced USCOD task. The code and dataset will be publicly available.
CoLA: Conditional Dropout and Language-driven Robust Dual-modal Salient Object Detection
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:The depth/thermal information is beneficial for detecting salient object with conventional RGB images. However, in dual-modal salient object detection (SOD) model, the robustness against noisy inputs and modality missing is crucial but rarely studied. To tackle this problem, we introduce \textbf{Co}nditional Dropout and \textbf{LA}nguage-driven(\textbf{CoLA}) framework comprising two core components. 1) Language-driven Quality Assessment (LQA): Leveraging a pretrained vision-language model with a prompt learner, the LQA recalibrates image contributions without requiring additional quality annotations. This approach effectively mitigates the impact of noisy inputs. 2) Conditional Dropout (CD): A learning method to strengthen the model's adaptability in scenarios with missing modalities, while preserving its performance under complete modalities. The CD serves as a plug-in training scheme that treats modality-missing as conditions, strengthening the overall robustness of various dual-modal SOD models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art dual-modal SOD models, under both modality-complete and modality-missing conditions. We will release source code upon acceptance.
Synthetic Data in AI: Challenges, Applications, and Ethical Implications
Jan 03, 2024Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence, the creation and utilization of synthetic datasets have become increasingly significant. This report delves into the multifaceted aspects of synthetic data, particularly emphasizing the challenges and potential biases these datasets may harbor. It explores the methodologies behind synthetic data generation, spanning traditional statistical models to advanced deep learning techniques, and examines their applications across diverse domains. The report also critically addresses the ethical considerations and legal implications associated with synthetic datasets, highlighting the urgent need for mechanisms to ensure fairness, mitigate biases, and uphold ethical standards in AI development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge