Christoph Mandl
SciDef: Automating Definition Extraction from Academic Literature with Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Definitions are the foundation for any scientific work, but with a significant increase in publication numbers, gathering definitions relevant to any keyword has become challenging. We therefore introduce SciDef, an LLM-based pipeline for automated definition extraction. We test SciDef on DefExtra & DefSim, novel datasets of human-extracted definitions and definition-pairs' similarity, respectively. Evaluating 16 language models across prompting strategies, we demonstrate that multi-step and DSPy-optimized prompting improve extraction performance. To evaluate extraction, we test various metrics and show that an NLI-based method yields the most reliable results. We show that LLMs are largely able to extract definitions from scientific literature (86.4% of definitions from our test-set); yet future work should focus not just on finding definitions, but on identifying relevant ones, as models tend to over-generate them. Code & datasets are available at https://github.com/Media-Bias-Group/SciDef.
The Promises and Pitfalls of LLM Annotations in Dataset Labeling: a Case Study on Media Bias Detection
Nov 17, 2024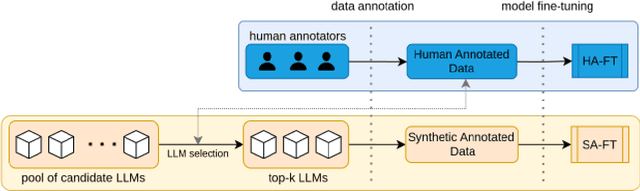
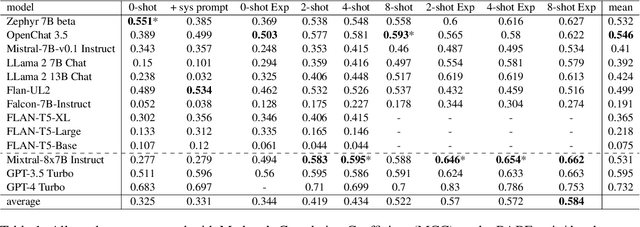
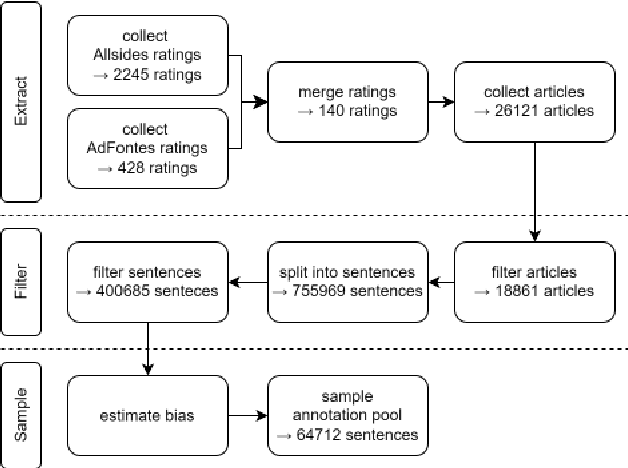
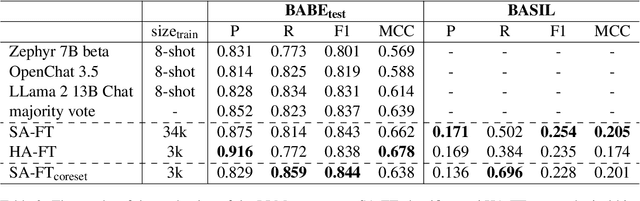
Abstract:High annotation costs from hiring or crowdsourcing complicate the creation of large, high-quality datasets needed for training reliable text classifiers. Recent research suggests using Large Language Models (LLMs) to automate the annotation process, reducing these costs while maintaining data quality. LLMs have shown promising results in annotating downstream tasks like hate speech detection and political framing. Building on the success in these areas, this study investigates whether LLMs are viable for annotating the complex task of media bias detection and whether a downstream media bias classifier can be trained on such data. We create annolexical, the first large-scale dataset for media bias classification with over 48000 synthetically annotated examples. Our classifier, fine-tuned on this dataset, surpasses all of the annotator LLMs by 5-9 percent in Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) and performs close to or outperforms the model trained on human-labeled data when evaluated on two media bias benchmark datasets (BABE and BASIL). This study demonstrates how our approach significantly reduces the cost of dataset creation in the media bias domain and, by extension, the development of classifiers, while our subsequent behavioral stress-testing reveals some of its current limitations and trade-offs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge