Christof Albert Bertram
Deep Learning model predicts the c-Kit-11 mutational status of canine cutaneous mast cell tumors by HE stained histological slides
Jan 02, 2024
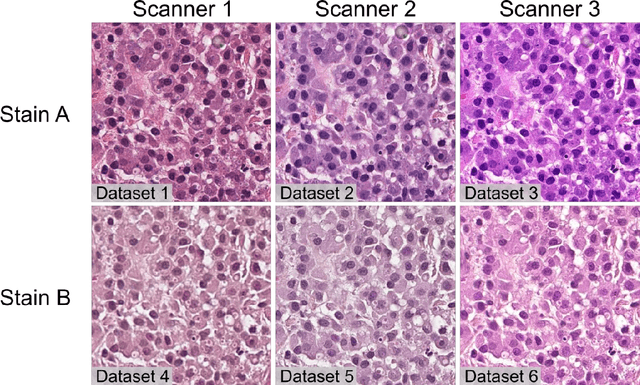
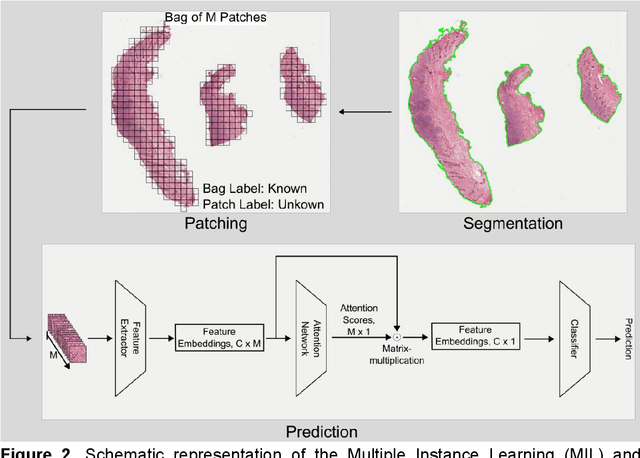
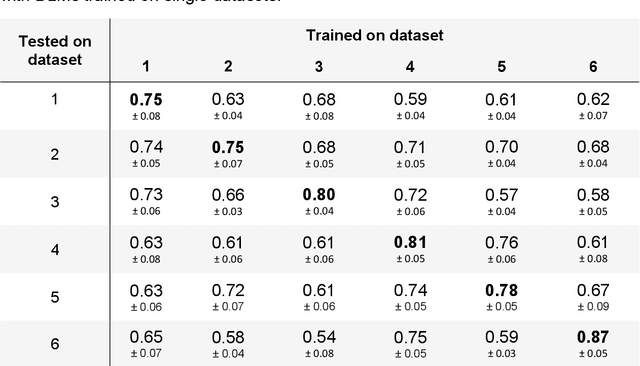
Abstract:Numerous prognostic factors are currently assessed histopathologically in biopsies of canine mast cell tumors to evaluate clinical behavior. In addition, PCR analysis of the c-Kit exon 11 mutational status is often performed to evaluate the potential success of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. This project aimed at training deep learning models (DLMs) to identify the c-Kit-11 mutational status of MCTs solely based on morphology without additional molecular analysis. HE slides of 195 mutated and 173 non-mutated tumors were stained consecutively in two different laboratories and scanned with three different slide scanners. This resulted in six different datasets (stain-scanner variations) of whole slide images. DLMs were trained with single and mixed datasets and their performances was assessed under scanner and staining domain shifts. The DLMs correctly classified HE slides according to their c-Kit 11 mutation status in, on average, 87% of cases for the best-suited stain-scanner variant. A relevant performance drop could be observed when the stain-scanner combination of the training and test dataset differed. Multi-variant datasets improved the average accuracy but did not reach the maximum accuracy of algorithms trained and tested on the same stain-scanner variant. In summary, DLM-assisted morphological examination of MCTs can predict c-Kit-exon 11 mutational status of MCTs with high accuracy. However, the recognition performance is impeded by a change of scanner or staining protocol. Larger data sets with higher numbers of scans originating from different laboratories and scanners may lead to more robust DLMs to identify c-Kit mutations in HE slides.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge