Christian Ritter
Deep Lagrangian Networks: Using Physics as Model Prior for Deep Learning
Jul 10, 2019



Abstract:Deep learning has achieved astonishing results on many tasks with large amounts of data and generalization within the proximity of training data. For many important real-world applications, these requirements are unfeasible and additional prior knowledge on the task domain is required to overcome the resulting problems. In particular, learning physics models for model-based control requires robust extrapolation from fewer samples - often collected online in real-time - and model errors may lead to drastic damages of the system. Directly incorporating physical insight has enabled us to obtain a novel deep model learning approach that extrapolates well while requiring fewer samples. As a first example, we propose Deep Lagrangian Networks (DeLaN) as a deep network structure upon which Lagrangian Mechanics have been imposed. DeLaN can learn the equations of motion of a mechanical system (i.e., system dynamics) with a deep network efficiently while ensuring physical plausibility. The resulting DeLaN network performs very well at robot tracking control. The proposed method did not only outperform previous model learning approaches at learning speed but exhibits substantially improved and more robust extrapolation to novel trajectories and learns online in real-time
Visual-Interactive Similarity Search for Complex Objects by Example of Soccer Player Analysis
Mar 09, 2017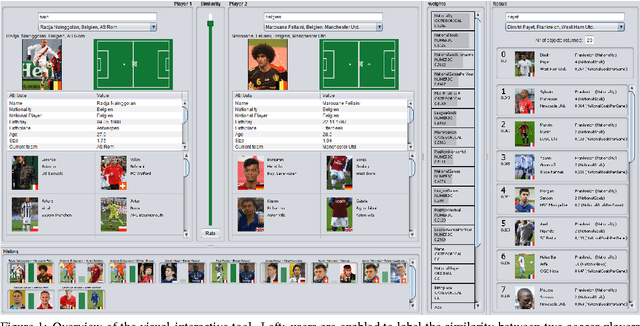
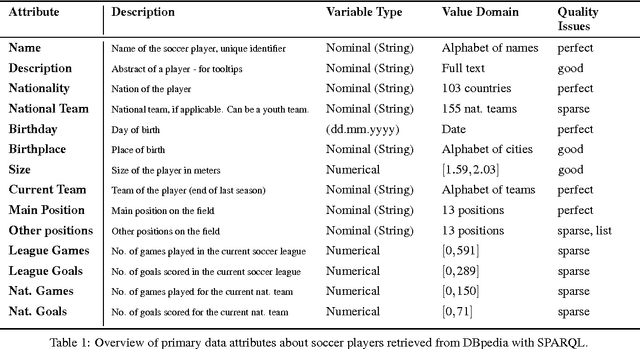
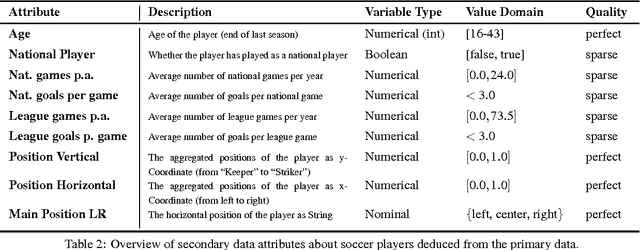
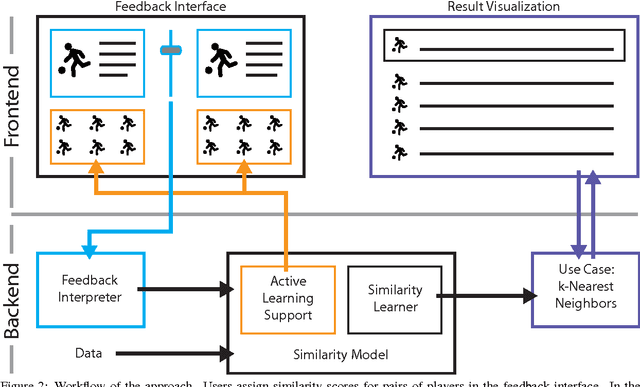
Abstract:The definition of similarity is a key prerequisite when analyzing complex data types in data mining, information retrieval, or machine learning. However, the meaningful definition is often hampered by the complexity of data objects and particularly by different notions of subjective similarity latent in targeted user groups. Taking the example of soccer players, we present a visual-interactive system that learns users' mental models of similarity. In a visual-interactive interface, users are able to label pairs of soccer players with respect to their subjective notion of similarity. Our proposed similarity model automatically learns the respective concept of similarity using an active learning strategy. A visual-interactive retrieval technique is provided to validate the model and to execute downstream retrieval tasks for soccer player analysis. The applicability of the approach is demonstrated in different evaluation strategies, including usage scenarions and cross-validation tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge