Chris Co
Expert Evaluation of LLM World Models: A High-$T_c$ Superconductivity Case Study
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) show great promise as a powerful tool for scientific literature exploration. However, their effectiveness in providing scientifically accurate and comprehensive answers to complex questions within specialized domains remains an active area of research. Using the field of high-temperature cuprates as an exemplar, we evaluate the ability of LLM systems to understand the literature at the level of an expert. We construct an expert-curated database of 1,726 scientific papers that covers the history of the field, and a set of 67 expert-formulated questions that probe deep understanding of the literature. We then evaluate six different LLM-based systems for answering these questions, including both commercially available closed models and a custom retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system capable of retrieving images alongside text. Experts then evaluate the answers of these systems against a rubric that assesses balanced perspectives, factual comprehensiveness, succinctness, and evidentiary support. Among the six systems two using RAG on curated literature outperformed existing closed models across key metrics, particularly in providing comprehensive and well-supported answers. We discuss promising aspects of LLM performances as well as critical short-comings of all the models. The set of expert-formulated questions and the rubric will be valuable for assessing expert level performance of LLM based reasoning systems.
Speech recognition for medical conversations
Jun 20, 2018
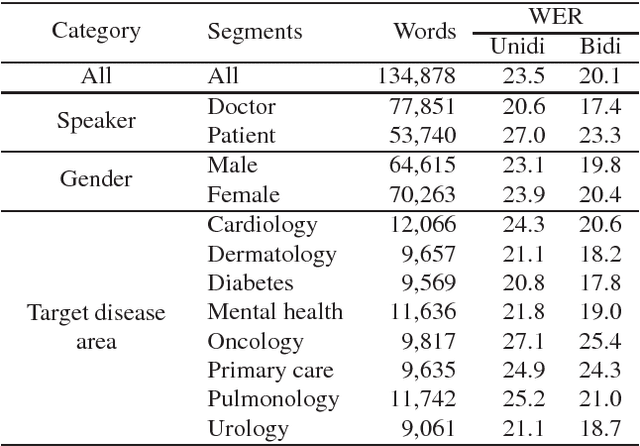
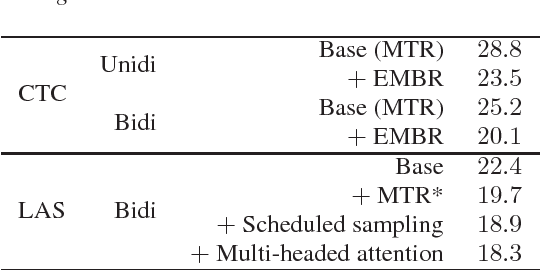
Abstract:In this work we explored building automatic speech recognition models for transcribing doctor patient conversation. We collected a large scale dataset of clinical conversations ($14,000$ hr), designed the task to represent the real word scenario, and explored several alignment approaches to iteratively improve data quality. We explored both CTC and LAS systems for building speech recognition models. The LAS was more resilient to noisy data and CTC required more data clean up. A detailed analysis is provided for understanding the performance for clinical tasks. Our analysis showed the speech recognition models performed well on important medical utterances, while errors occurred in causal conversations. Overall we believe the resulting models can provide reasonable quality in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge