Choon Hwai Yap
Real-Time Pulsatile Flow Prediction for Realistic, Diverse Intracranial Aneurysm Morphologies using a Graph Transformer and Steady-Flow Data Augmentation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Extensive studies suggested that fluid mechanical markers of intracranial aneurysms (IAs) derived from Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) can indicate disease progression risks, but to date this has not been translated clinically. This is because CFD requires specialized expertise and is time-consuming and low throughput, making it difficult to support clinical trials. A deep learning model that maps IA morphology to biomechanical markers can address this, enabling physicians to obtain these markers in real time without performing CFD. Here, we show that a Graph Transformer model that incorporates temporal information, which is supervised by large CFD data, can accurately predict Wall Shear Stress (WSS) across the cardiac cycle from IA surface meshes. The model effectively captures the temporal variations of the WSS pattern, achieving a Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) of up to 0.981 and a maximum-based relative L2 error of 2.8%. Ablation studies and SOTA comparison confirmed its optimality. Further, as pulsatile CFD data is computationally expensive to generate and sample sizes are limited, we engaged a strategy of injecting a large amount of steady-state CFD data, which are extremely low-cost to generate, as augmentation. This approach enhances network performance substantially when pulsatile CFD data sample size is small. Our study provides a proof of concept that temporal sequences cardiovascular fluid mechanical parameters can be computed in real time using a deep learning model from the geometric mesh, and this is achievable even with small pulsatile CFD sample size. Our approach is likely applicable to other cardiovascular scenarios.
Two-Stage Generative Model for Intracranial Aneurysm Meshes with Morphological Marker Conditioning
May 15, 2025Abstract:A generative model for the mesh geometry of intracranial aneurysms (IA) is crucial for training networks to predict blood flow forces in real time, which is a key factor affecting disease progression. This need is necessitated by the absence of a large IA image datasets. Existing shape generation methods struggle to capture realistic IA features and ignore the relationship between IA pouches and parent vessels, limiting physiological realism and their generation cannot be controlled to have specific morphological measurements. We propose AneuG, a two-stage Variational Autoencoder (VAE)-based IA mesh generator. In the first stage, AneuG generates low-dimensional Graph Harmonic Deformation (GHD) tokens to encode and reconstruct aneurysm pouch shapes, constrained to morphing energy statistics truths. GHD enables more accurate shape encoding than alternatives. In the second stage, AneuG generates parent vessels conditioned on GHD tokens, by generating vascular centreline and propagating the cross-section. AneuG's IA shape generation can further be conditioned to have specific clinically relevant morphological measurements. This is useful for studies to understand shape variations represented by clinical measurements, and for flow simulation studies to understand effects of specific clinical shape parameters on fluid dynamics. Source code and implementation details are available at https://github.com/anonymousaneug/AneuG.
Topology-Preserving Loss for Accurate and Anatomically Consistent Cardiac Mesh Reconstruction
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Accurate cardiac mesh reconstruction from volumetric data is essential for personalized cardiac modeling and clinical analysis. However, existing deformation-based approaches are prone to topological inconsistencies, particularly membrane penetration, which undermines the anatomical plausibility of the reconstructed mesh. To address this issue, we introduce Topology-Preserving Mesh Loss (TPM Loss), a novel loss function that explicitly enforces topological constraints during mesh deformation. By identifying topology-violating points, TPM Loss ensures spatially consistent reconstructions. Extensive experiments on CT and MRI datasets show that TPM Loss reduces topology violations by up to 93.1% while maintaining high segmentation accuracy (DSC: 89.1%-92.9%) and improving mesh fidelity (Chamfer Distance reduction up to 0.26 mm). These results demonstrate that TPM Loss effectively prevents membrane penetration and significantly improves cardiac mesh quality, enabling more accurate and anatomically consistent cardiac reconstructions.
Motion-enhancement to Echocardiography Segmentation via Inserting a Temporal Attention Module: An Efficient, Adaptable, and Scalable Approach
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Cardiac anatomy segmentation is essential for clinical assessment of cardiac function and disease diagnosis to inform treatment and intervention. In performing segmentation, deep learning (DL) algorithms improved accuracy significantly compared to traditional image processing approaches. More recently, studies showed that enhancing DL segmentation with motion information can further improve it. A range of methods for injecting motion information has been proposed, but many of them increase the dimensionality of input images (which is computationally expensive) or have not used an optimal method to insert motion information, such as non-DL registration, non-attention-based networks or single-headed attention. Here, we present a novel, computation-efficient alternative where a novel, scalable temporal attention module (TAM) extracts temporal feature interactions multiple times and where TAM has a multi-headed, KQV projection cross-attention architecture. The module can be seamlessly integrated into a wide range of existing CNN- or Transformer-based networks, providing novel flexibility for inclusion in future implementations. Extensive evaluations on different cardiac datasets, 2D echocardiography (CAMUS), and 3D echocardiography (MITEA) demonstrate the model's effectiveness when integrated into well-established backbone networks like UNet, FCN8s, UNetR, SwinUNetR, and the recent I2UNet. We further find that the optimized TAM-enhanced FCN8s network performs well compared to contemporary alternatives. Our results confirm TAM's robustness, scalability, and generalizability across diverse datasets and backbones.
Multiple Physics-Informed Neural Network for Biomedical Tube Flows
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:Fluid dynamics computations for tube-like geometries are important for biomedical evaluation of vascular and airway fluid dynamics. Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) have recently emerged as a good alternative to traditional computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methods. The vanilla PINN, however, requires much longer training time than the traditional CFD methods for each specific flow scenario and thus does not justify its mainstream use. Here, we explore the use of the multi-case PINN approach for calculating biomedical tube flows, where varied geometry cases are parameterized and pre-trained on the PINN, such that results for unseen geometries can be obtained in real time. Our objective is to identify network architecture, tube-specific, and regularization strategies that can optimize this, via experiments on a series of idealized 2D stenotic tube flows.
Multi-scale, Data-driven and Anatomically Constrained Deep Learning Image Registration for Adult and Fetal Echocardiography
Sep 11, 2023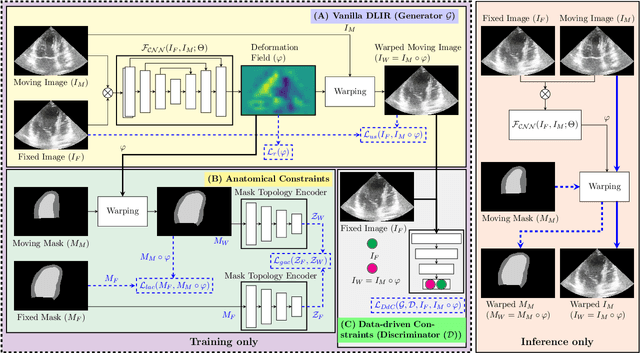
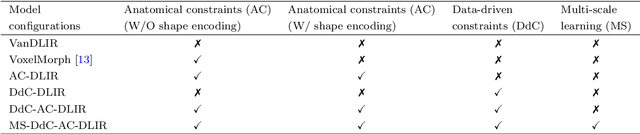
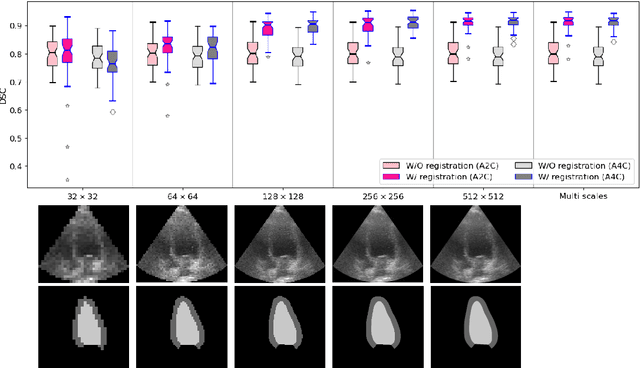
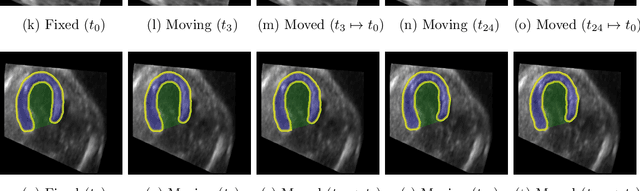
Abstract:Temporal echocardiography image registration is a basis for clinical quantifications such as cardiac motion estimation, myocardial strain assessments, and stroke volume quantifications. In past studies, deep learning image registration (DLIR) has shown promising results and is consistently accurate and precise, requiring less computational time. We propose that a greater focus on the warped moving image's anatomic plausibility and image quality can support robust DLIR performance. Further, past implementations have focused on adult echocardiography, and there is an absence of DLIR implementations for fetal echocardiography. We propose a framework that combines three strategies for DLIR in both fetal and adult echo: (1) an anatomic shape-encoded loss to preserve physiological myocardial and left ventricular anatomical topologies in warped images; (2) a data-driven loss that is trained adversarially to preserve good image texture features in warped images; and (3) a multi-scale training scheme of a data-driven and anatomically constrained algorithm to improve accuracy. Our tests show that good anatomical topology and image textures are strongly linked to shape-encoded and data-driven adversarial losses. They improve different aspects of registration performance in a non-overlapping way, justifying their combination. Despite fundamental distinctions between adult and fetal echo images, we show that these strategies can provide excellent registration results in both adult and fetal echocardiography using the publicly available CAMUS adult echo dataset and our private multi-demographic fetal echo dataset. Our approach outperforms traditional non-DL gold standard registration approaches, including Optical Flow and Elastix. Registration improvements could be translated to more accurate and precise clinical quantification of cardiac ejection fraction, demonstrating a potential for translation.
Skin Lesion Analysis: A State-of-the-Art Survey, Systematic Review, and Future Trends
Aug 25, 2022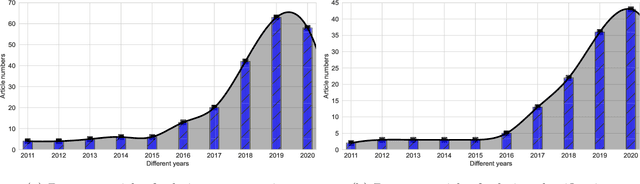
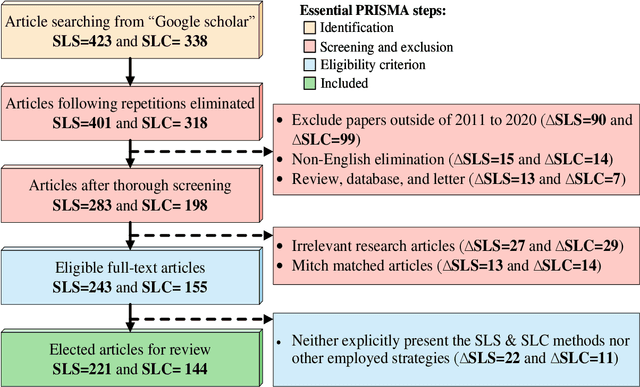
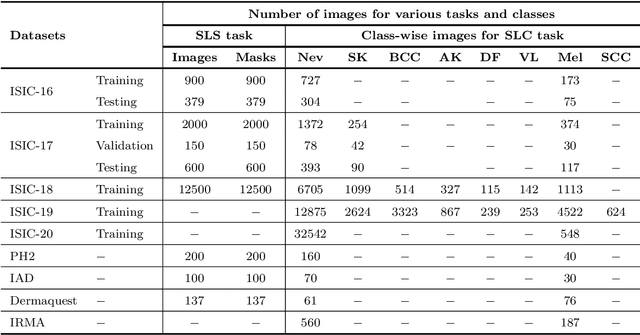
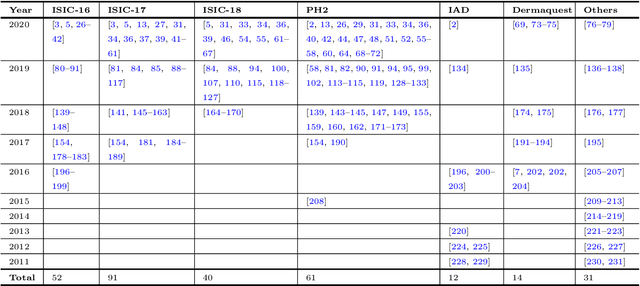
Abstract:The Computer-aided Diagnosis (CAD) system for skin lesion analysis is an emerging field of research that has the potential to relieve the burden and cost of skin cancer screening. Researchers have recently indicated increasing interest in developing such CAD systems, with the intention of providing a user-friendly tool to dermatologists in order to reduce the challenges that are raised by manual inspection. The purpose of this article is to provide a complete literature review of cutting-edge CAD techniques published between 2011 and 2020. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) method was used to identify a total of 365 publications, 221 for skin lesion segmentation and 144 for skin lesion classification. These articles are analyzed and summarized in a number of different ways so that we can contribute vital information about the methods for the evolution of CAD systems. These ways include: relevant and essential definitions and theories, input data (datasets utilization, preprocessing, augmentations, and fixing imbalance problems), method configuration (techniques, architectures, module frameworks, and losses), training tactics (hyperparameter settings), and evaluation criteria (metrics). We also intend to investigate a variety of performance-enhancing methods, including ensemble and post-processing. In addition, in this survey, we highlight the primary problems associated with evaluating skin lesion segmentation and classification systems using minimal datasets, as well as the potential solutions to these plights. In conclusion, enlightening findings, recommendations, and trends are discussed for the purpose of future research surveillance in related fields of interest. It is foreseen that it will guide researchers of all levels, from beginners to experts, in the process of developing an automated and robust CAD system for skin lesion analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge