Chengyun Song
KAN See In the Dark
Sep 05, 2024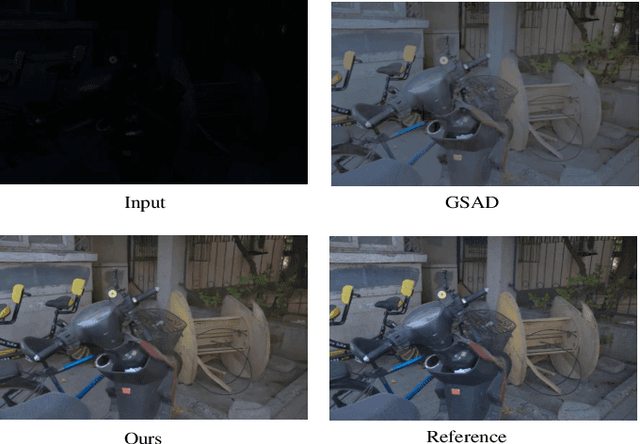
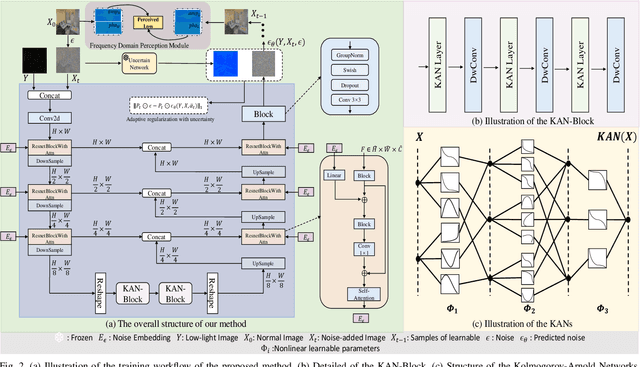

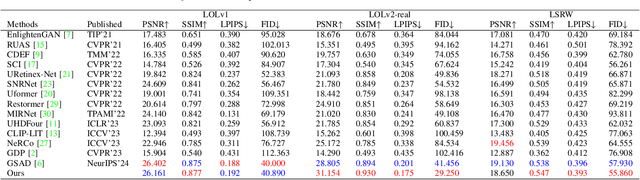
Abstract:Existing low-light image enhancement methods are difficult to fit the complex nonlinear relationship between normal and low-light images due to uneven illumination and noise effects. The recently proposed Kolmogorov-Arnold networks (KANs) feature spline-based convolutional layers and learnable activation functions, which can effectively capture nonlinear dependencies. In this paper, we design a KAN-Block based on KANs and innovatively apply it to low-light image enhancement. This method effectively alleviates the limitations of current methods constrained by linear network structures and lack of interpretability, further demonstrating the potential of KANs in low-level vision tasks. Given the poor perception of current low-light image enhancement methods and the stochastic nature of the inverse diffusion process, we further introduce frequency-domain perception for visually oriented enhancement. Extensive experiments demonstrate the competitive performance of our method on benchmark datasets. The code will be available at: https://github.com/AXNing/KSID}{https://github.com/AXNing/KSID.
Zero-LED: Zero-Reference Lighting Estimation Diffusion Model for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion model-based low-light image enhancement methods rely heavily on paired training data, leading to limited extensive application. Meanwhile, existing unsupervised methods lack effective bridging capabilities for unknown degradation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel zero-reference lighting estimation diffusion model for low-light image enhancement called Zero-LED. It utilizes the stable convergence ability of diffusion models to bridge the gap between low-light domains and real normal-light domains and successfully alleviates the dependence on pairwise training data via zero-reference learning. Specifically, we first design the initial optimization network to preprocess the input image and implement bidirectional constraints between the diffusion model and the initial optimization network through multiple objective functions. Subsequently, the degradation factors of the real-world scene are optimized iteratively to achieve effective light enhancement. In addition, we explore a frequency-domain based and semantically guided appearance reconstruction module that encourages feature alignment of the recovered image at a fine-grained level and satisfies subjective expectations. Finally, extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our approach to other state-of-the-art methods and more significant generalization capabilities. We will open the source code upon acceptance of the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge