Chengxiang Jin
Unveiling Latent Information in Transaction Hashes: Hypergraph Learning for Ethereum Ponzi Scheme Detection
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:With the widespread adoption of Ethereum, financial frauds such as Ponzi schemes have become increasingly rampant in the blockchain ecosystem, posing significant threats to the security of account assets. Existing Ethereum fraud detection methods typically model account transactions as graphs, but this approach primarily focuses on binary transactional relationships between accounts, failing to adequately capture the complex multi-party interaction patterns inherent in Ethereum. To address this, we propose a hypergraph modeling method for the Ponzi scheme detection method in Ethereum, called HyperDet. Specifically, we treat transaction hashes as hyperedges that connect all the relevant accounts involved in a transaction. Additionally, we design a two-step hypergraph sampling strategy to significantly reduce computational complexity. Furthermore, we introduce a dual-channel detection module, including the hypergraph detection channel and the hyper-homo graph detection channel, to be compatible with existing detection methods. Experimental results show that, compared to traditional homogeneous graph-based methods, the hyper-homo graph detection channel achieves significant performance improvements, demonstrating the superiority of hypergraph in Ponzi scheme detection. This research offers innovations for modeling complex relationships in blockchain data.
Network Anomaly Traffic Detection via Multi-view Feature Fusion
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Traditional anomalous traffic detection methods are based on single-view analysis, which has obvious limitations in dealing with complex attacks and encrypted communications. In this regard, we propose a Multi-view Feature Fusion (MuFF) method for network anomaly traffic detection. MuFF models the temporal and interactive relationships of packets in network traffic based on the temporal and interactive viewpoints respectively. It learns temporal and interactive features. These features are then fused from different perspectives for anomaly traffic detection. Extensive experiments on six real traffic datasets show that MuFF has excellent performance in network anomalous traffic detection, which makes up for the shortcomings of detection under a single perspective.
Dual-view Aware Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection for Ethereum
Jun 29, 2024



Abstract:The wide application of Ethereum technology has brought technological innovation to traditional industries. As one of Ethereum's core applications, smart contracts utilize diverse contract codes to meet various functional needs and have gained widespread use. However, the non-tamperability of smart contracts, coupled with vulnerabilities caused by natural flaws or human errors, has brought unprecedented challenges to blockchain security. Therefore, in order to ensure the healthy development of blockchain technology and the stability of the blockchain community, it is particularly important to study the vulnerability detection techniques for smart contracts. In this paper, we propose a Dual-view Aware Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Framework named DVDet. The framework initially converts the source code and bytecode of smart contracts into weighted graphs and control flow sequences, capturing potential risk features from these two perspectives and integrating them for analysis, ultimately achieving effective contract vulnerability detection. Comprehensive experiments on the Ethereum dataset show that our method outperforms others in detecting vulnerabilities.
Time-aware Metapath Feature Augmentation for Ponzi Detection in Ethereum
Oct 30, 2022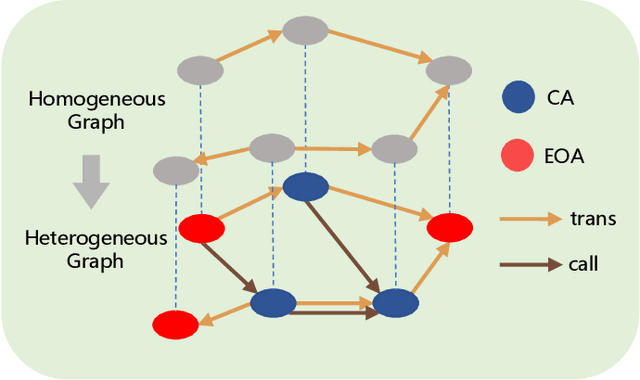



Abstract:With the development of Web 3.0 which emphasizes decentralization, blockchain technology ushers in its revolution and also brings numerous challenges, particularly in the field of cryptocurrency. Recently, a large number of criminal behaviors continuously emerge on blockchain, such as Ponzi schemes and phishing scams, which severely endanger decentralized finance. Existing graph-based abnormal behavior detection methods on blockchain usually focus on constructing homogeneous transaction graphs without distinguishing the heterogeneity of nodes and edges, resulting in partial loss of transaction pattern information. Although existing heterogeneous modeling methods can depict richer information through metapaths, the extracted metapaths generally neglect temporal dependencies between entities and do not reflect real behavior. In this paper, we introduce Time-aware Metapath Feature Augmentation (TMFAug) as a plug-and-play module to capture the real metapath-based transaction patterns during Ponzi scheme detection on Ethereum. The proposed module can be adaptively combined with existing graph-based Ponzi detection methods. Extensive experimental results show that our TMFAug can help existing Ponzi detection methods achieve significant performance improvements on the Ethereum dataset, indicating the effectiveness of heterogeneous temporal information for Ponzi scheme detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge