Chengrong Gong
3D-ANAS: 3D Asymmetric Neural Architecture Search for Fast Hyperspectral Image Classification
Jan 12, 2021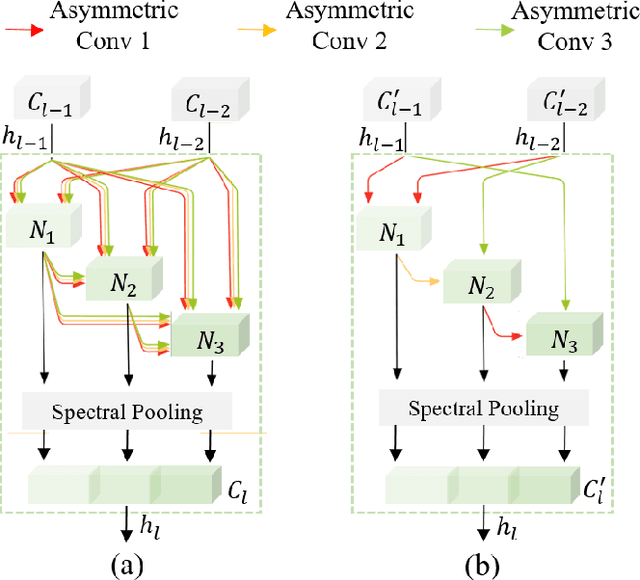
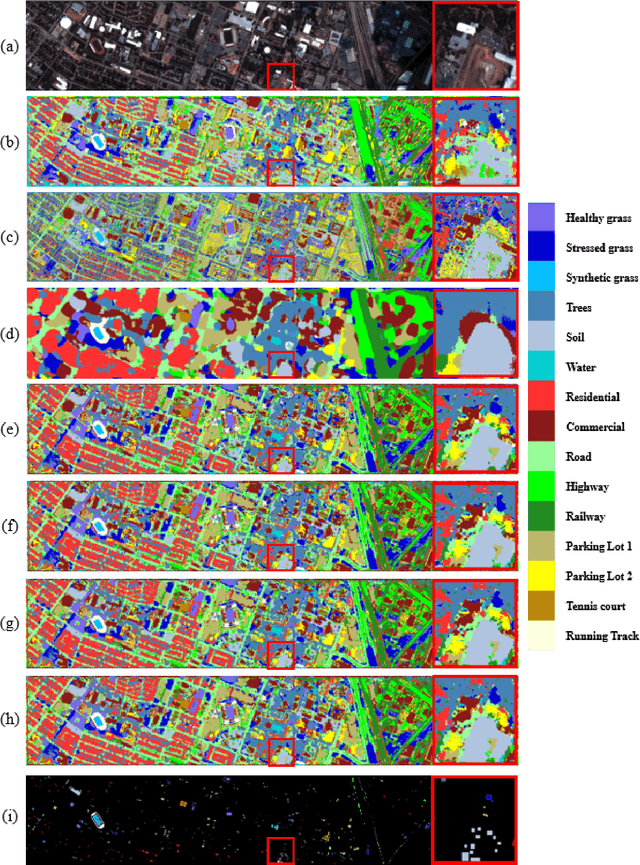

Abstract:Hyperspectral images involve abundant spectral and spatial information, playing an irreplaceable role in land-cover classification. Recently, based on deep learning technologies, an increasing number of HSI classification approaches have been proposed, which demonstrate promising performance. However, previous studies suffer from two major drawbacks: 1) the architecture of most deep learning models is manually designed, relies on specialized knowledge, and is relatively tedious. Moreover, in HSI classifications, datasets captured by different sensors have different physical properties. Correspondingly, different models need to be designed for different datasets, which further increases the workload of designing architectures; 2) the mainstream framework is a patch-to-pixel framework. The overlap regions of patches of adjacent pixels are calculated repeatedly, which increases computational cost and time cost. Besides, the classification accuracy is sensitive to the patch size, which is artificially set based on extensive investigation experiments. To overcome the issues mentioned above, we firstly propose a 3D asymmetric neural network search algorithm and leverage it to automatically search for efficient architectures for HSI classifications. By analysing the characteristics of HSIs, we specifically build a 3D asymmetric decomposition search space, where spectral and spatial information are processed with different decomposition convolutions. Furthermore, we propose a new fast classification framework, i,e., pixel-to-pixel classification framework, which has no repetitive operations and reduces the overall cost. Experiments on three public HSI datasets captured by different sensors demonstrate the networks designed by our 3D-ANAS achieve competitive performance compared to several state-of-the-art methods, while having a much faster inference speed.
Memory-Efficient Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search for Image Restoration
Dec 28, 2020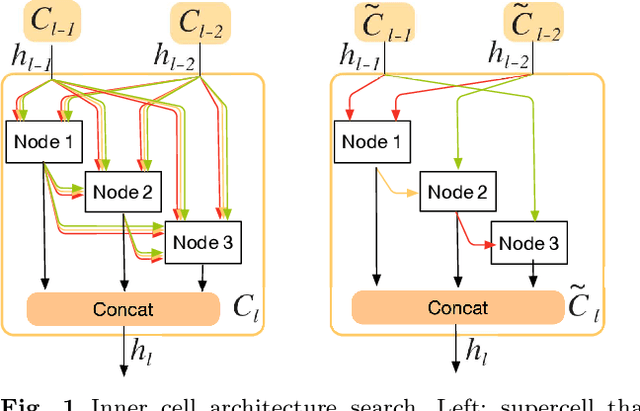
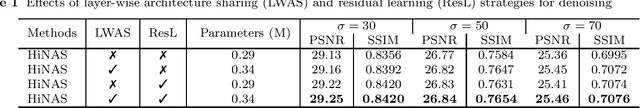
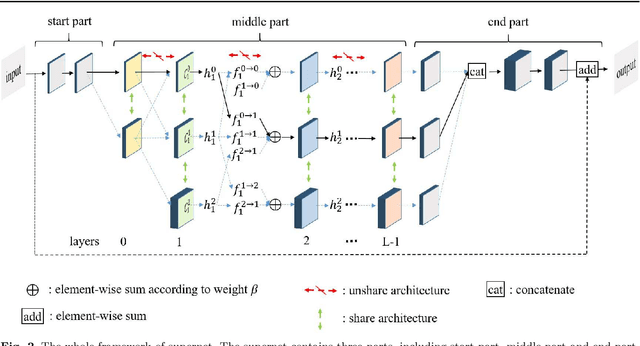
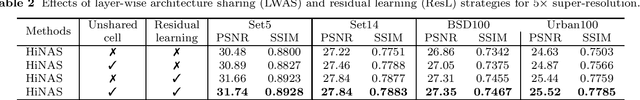
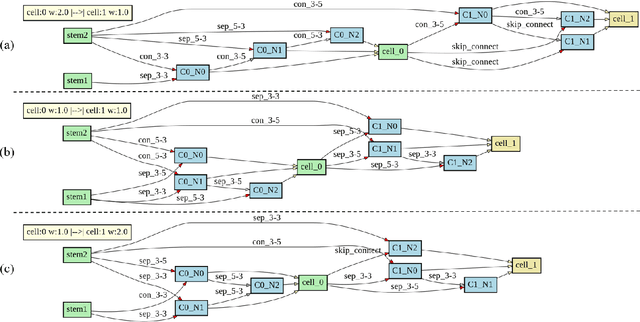
Abstract:Recently, much attention has been spent on neural architecture search (NAS) approaches, which often outperform manually designed architectures on highlevel vision tasks. Inspired by this, we attempt to leverage NAS technique to automatically design efficient network architectures for low-level image restoration tasks. In this paper, we propose a memory-efficient hierarchical NAS HiNAS (HiNAS) and apply to two such tasks: image denoising and image super-resolution. HiNAS adopts gradient based search strategies and builds an flexible hierarchical search space, including inner search space and outer search space, which in charge of designing cell architectures and deciding cell widths, respectively. For inner search space, we propose layerwise architecture sharing strategy (LWAS), resulting in more flexible architectures and better performance. For outer search space, we propose cell sharing strategy to save memory, and considerably accelerate the search speed. The proposed HiNAS is both memory and computation efficient. With a single GTX1080Ti GPU, it takes only about 1 hour for searching for denoising network on BSD 500 and 3.5 hours for searching for the super-resolution structure on DIV2K. Experimental results show that the architectures found by HiNAS have fewer parameters and enjoy a faster inference speed, while achieving highly competitive performance compared with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge