ChengDa Zheng
University of Toronto
Twitter discussions and emotions about COVID-19 pandemic: a machine learning approach
Jun 19, 2020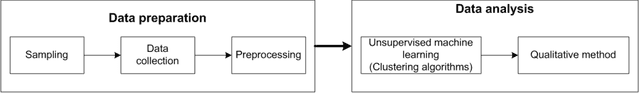
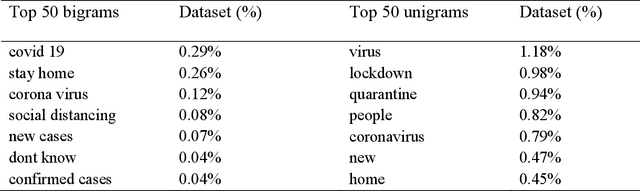


Abstract:The objective of the study is to examine coronavirus disease (COVID-19) related discussions, concerns, and sentiments that emerged from tweets posted by Twitter users. We analyze 4 million Twitter messages related to the COVID-19 pandemic using a list of 25 hashtags such as "coronavirus," "COVID-19," "quarantine" from March 1 to April 21 in 2020. We use a machine learning approach, Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), to identify popular unigram, bigrams, salient topics and themes, and sentiments in the collected Tweets. Popular unigrams include "virus," "lockdown," and "quarantine." Popular bigrams include "COVID-19," "stay home," "corona virus," "social distancing," and "new cases." We identify 13 discussion topics and categorize them into five different themes, such as "public health measures to slow the spread of COVID-19," "social stigma associated with COVID-19," "coronavirus news cases and deaths," "COVID-19 in the United States," and "coronavirus cases in the rest of the world". Across all identified topics, the dominant sentiments for the spread of coronavirus are anticipation that measures that can be taken, followed by a mixed feeling of trust, anger, and fear for different topics. The public reveals a significant feeling of fear when they discuss the coronavirus new cases and deaths than other topics. The study shows that Twitter data and machine learning approaches can be leveraged for infodemiology study by studying the evolving public discussions and sentiments during the COVID-19. Real-time monitoring and assessment of the Twitter discussion and concerns can be promising for public health emergency responses and planning. Already emerged pandemic fear, stigma, and mental health concerns may continue to influence public trust when there occurs a second wave of COVID-19 or a new surge of the imminent pandemic.
Machine learning on Big Data from Twitter to understand public reactions to COVID-19
May 22, 2020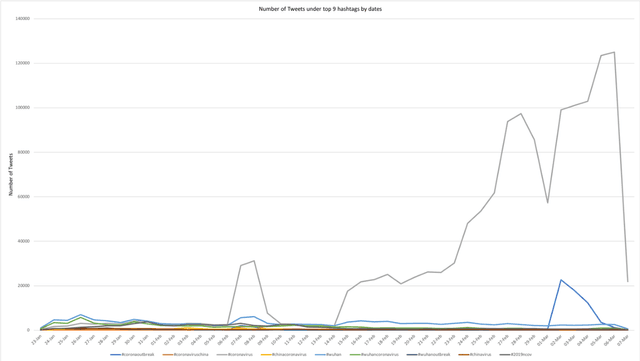

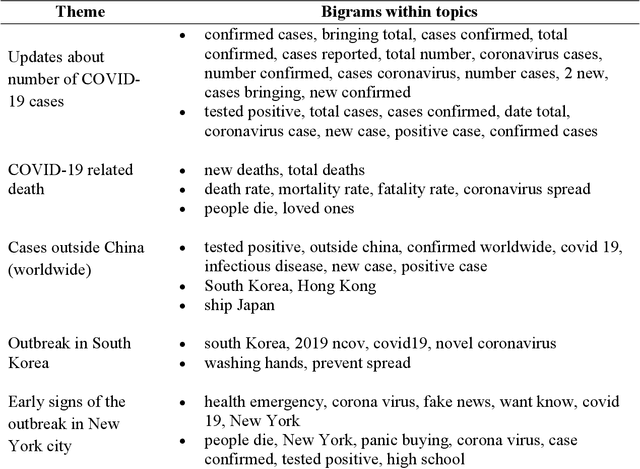

Abstract:The study aims to understand Twitter users' discussions and reactions about the COVID-19. We use machine learning techniques to analyze about 1.8 million Tweets messages related to coronavirus collected from January 20th to March 7th, 2020. A total of salient 11 topics are identified and then categorized into 10 themes, such as "cases outside China (worldwide)," "COVID-19 outbreak in South Korea," "early signs of the outbreak in New York," "Diamond Princess cruise," "economic impact," "Preventive/Protective measures," "authorities," and "supply chain". Results do not reveal treatment and/or symptoms related messages as a prevalent topic on Twitter. We also run sentiment analysis and the results show that trust for the authorities remained a prevalent emotion, but mixed feelings of trust for authorities, fear for the outbreak, and anticipation for the potential preventive measures will be taken are identified. Implications and limitations of the study are also discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge