Chen Yuan
Efficient Sequential Recommendation for Long Term User Interest Via Personalization
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Recent years have witnessed success of sequential modeling, generative recommender, and large language model for recommendation. Though the scaling law has been validated for sequential models, it showed inefficiency in computational capacity when considering real-world applications like recommendation, due to the non-linear(quadratic) increasing nature of the transformer model. To improve the efficiency of the sequential model, we introduced a novel approach to sequential recommendation that leverages personalization techniques to enhance efficiency and performance. Our method compresses long user interaction histories into learnable tokens, which are then combined with recent interactions to generate recommendations. This approach significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining high recommendation accuracy. Our method could be applied to existing transformer based recommendation models, e.g., HSTU and HLLM. Extensive experiments on multiple sequential models demonstrate its versatility and effectiveness. Source code is available at \href{https://github.com/facebookresearch/PerSRec}{https://github.com/facebookresearch/PerSRec}.
Enhancement of Power Equipment Management Using Knowledge Graph
Apr 28, 2019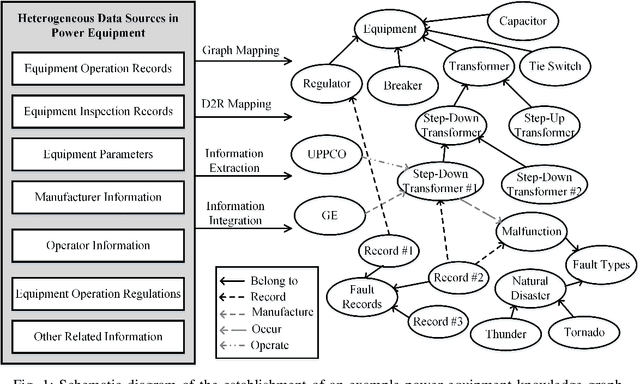


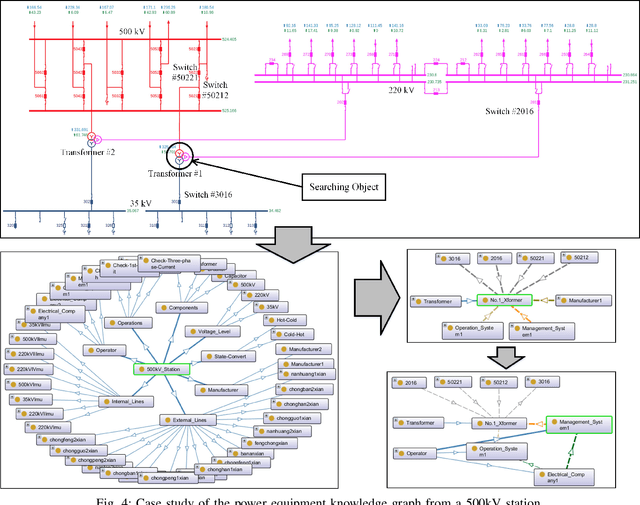
Abstract:Accurate retrieval of the power equipment information plays an important role in guiding the full-lifecycle management of power system assets. Because of data duplication, database decentralization, weak data relations, and sluggish data updates, the power asset management system eager to adopt a new strategy to avoid the information losses, bias, and improve the data storage efficiency and extraction process. Knowledge graph has been widely developed in large part owing to its schema-less nature. It enables the knowledge graph to grow seamlessly and allows new relations addition and entities insertion when needed. This study proposes an approach for constructing power equipment knowledge graph by merging existing multi-source heterogeneous power equipment related data. A graph-search method to illustrate exhaustive results to the desired information based on the constructed knowledge graph is proposed. A case of a 500 kV station example is then demonstrated to show relevant search results and to explain that the knowledge graph can improve the efficiency of power equipment management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge