Chen Yi Lu
SKALD: Learning-Based Shot Assembly for Coherent Multi-Shot Video Creation
Mar 11, 2025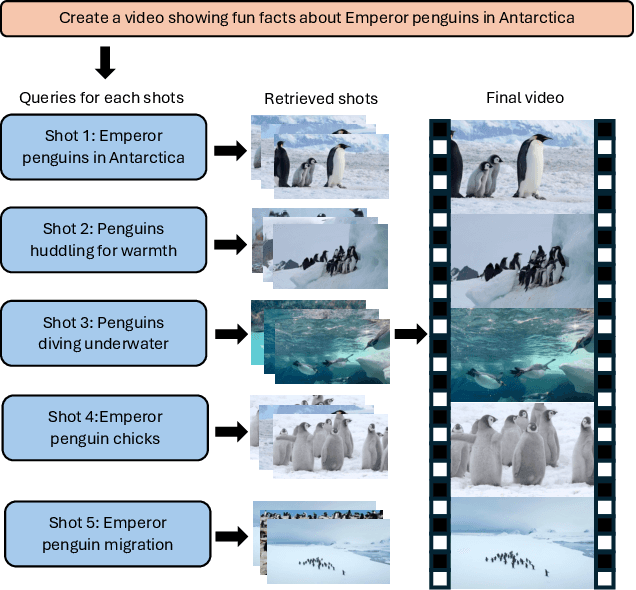
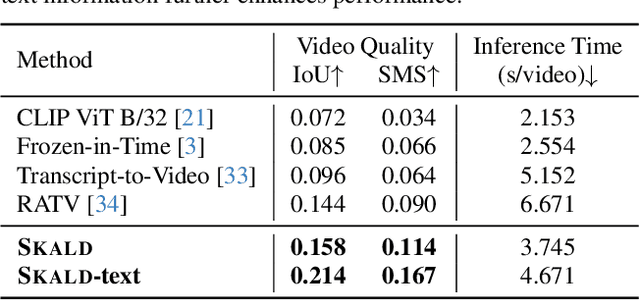
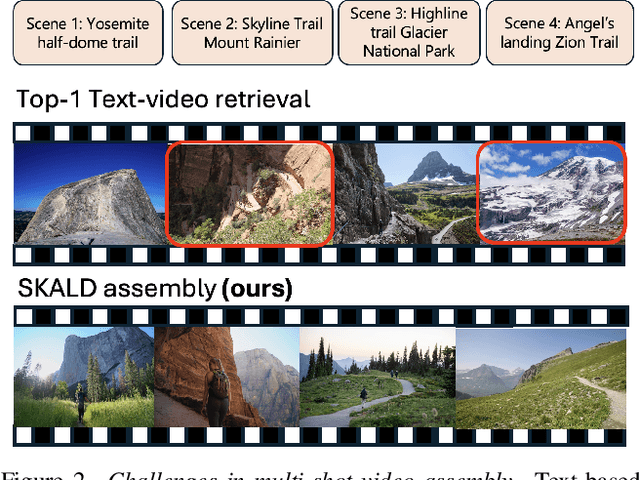
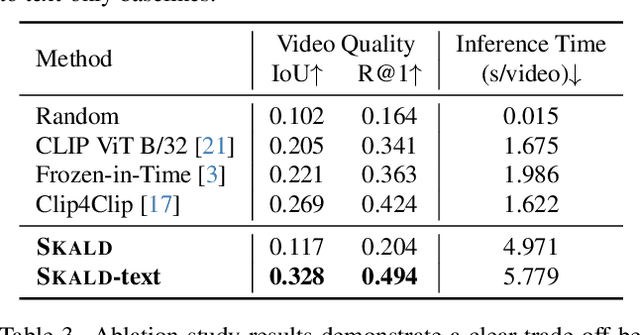
Abstract:We present SKALD, a multi-shot video assembly method that constructs coherent video sequences from candidate shots with minimal reliance on text. Central to our approach is the Learned Clip Assembly (LCA) score, a learning-based metric that measures temporal and semantic relationships between shots to quantify narrative coherence. We tackle the exponential complexity of combining multiple shots with an efficient beam-search algorithm guided by the LCA score. To train our model effectively with limited human annotations, we propose two tasks for the LCA encoder: Shot Coherence Learning, which uses contrastive learning to distinguish coherent and incoherent sequences, and Feature Regression, which converts these learned representations into a real-valued coherence score. We develop two variants: a base SKALD model that relies solely on visual coherence and SKALD-text, which integrates auxiliary text information when available. Experiments on the VSPD and our curated MSV3C datasets show that SKALD achieves an improvement of up to 48.6% in IoU and a 43% speedup over the state-of-the-art methods. A user study further validates our approach, with 45% of participants favoring SKALD-assembled videos, compared to 22% preferring text-based assembly methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge