Chao-Feng Li
3D RoI-aware U-Net for Accurate and Efficient Colorectal Tumor Segmentation
Jul 19, 2018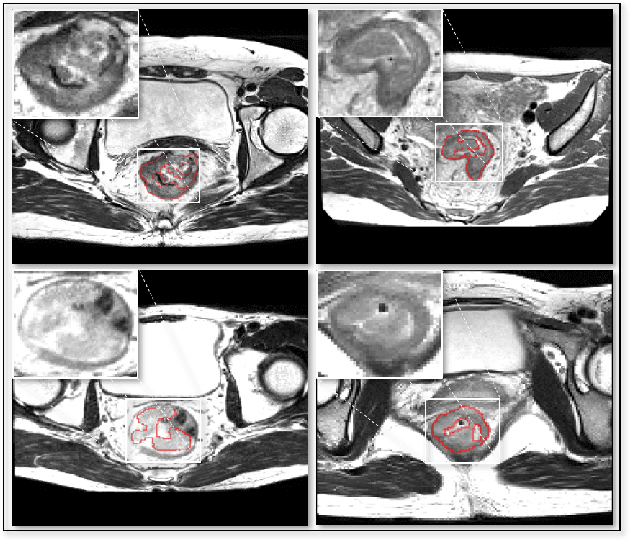
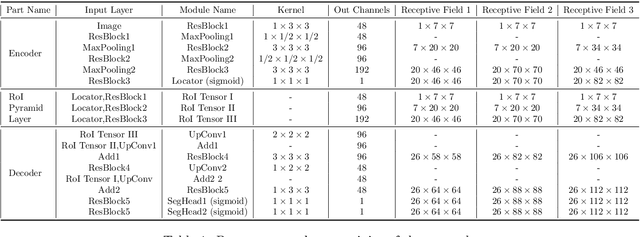
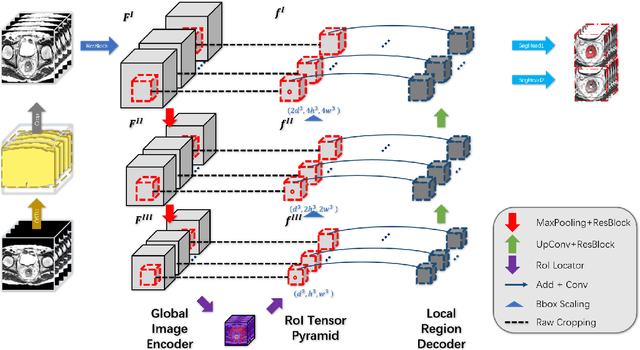

Abstract:Segmentation of colorectal cancerous regions from Magnetic Resonance (MR) images is a crucial procedure for radiotherapy which conventionally requires accurate delineation of tumour boundaries at an expense of labor, time and reproducibility. To address this important yet challenging task within the framework of performance-leading deep learning methods, regions of interest (RoIs) localization from large whole volume 3D images serves as a preceding operation that brings about multiple benefits in terms of speed, target completeness and reduction of false positives. Distinct from sliding window or discrete localization-segmentation based models, we propose a novel multi-task framework referred to as 3D RoI-aware U-Net (3D RU-Net), for RoI localization and intra-RoI segmentation where the two tasks share one backbone encoder network. With the region proposals from the encoder, we crop multi-level feature maps from the backbone network to form a GPU memory-efficient decoder for detail-preserving intra-RoI segmentation. To effectively train the model, we designed a Dice formulated loss function for the global-to-local multi-task learning procedure. Based on the promising efficiency gains demonstrated by the proposed method, we went on to ensemble multiple models to achieve even higher performance costing minor extra computational expensiveness. Extensive experiments were subsequently conducted on 64 cancerous cases with a four-fold cross-validation, and the results showed significant superiority in terms of accuracy and efficiency over conventional state-of-the art frameworks. In conclusion, the proposed method has a huge potential for extension to other 3D object segmentation tasks from medical images due to its inherent generalizability. The code for the proposed method is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge