Chang Jin
When Silence Is Golden: Can LLMs Learn to Abstain in Temporal QA and Beyond?
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) rarely admit uncertainty, often producing fluent but misleading answers, rather than abstaining (i.e., refusing to answer). This weakness is even evident in temporal question answering, where models frequently ignore time-sensitive evidence and conflate facts across different time-periods. In this paper, we present the first empirical study of training LLMs with an abstention ability while reasoning about temporal QA. Existing approaches such as calibration might be unreliable in capturing uncertainty in complex reasoning. We instead frame abstention as a teachable skill and introduce a pipeline that couples Chain-of-Thought (CoT) supervision with Reinforcement Learning (RL) guided by abstention-aware rewards. Our goal is to systematically analyze how different information types and training techniques affect temporal reasoning with abstention behavior in LLMs. Through extensive experiments studying various methods, we find that RL yields strong empirical gains on reasoning: a model initialized by Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct surpasses GPT-4o by $3.46\%$ and $5.80\%$ in Exact Match on TimeQA-Easy and Hard, respectively. Moreover, it improves the True Positive rate on unanswerable questions by $20\%$ over a pure supervised fine-tuned (SFT) variant. Beyond performance, our analysis shows that SFT induces overconfidence and harms reliability, while RL improves prediction accuracy but exhibits similar risks. Finally, by comparing implicit reasoning cues (e.g., original context, temporal sub-context, knowledge graphs) with explicit CoT supervision, we find that implicit information provides limited benefit for reasoning with abstention. Our study provides new insights into how abstention and reasoning can be jointly optimized, providing a foundation for building more reliable LLMs.
M$^{3}$-20M: A Large-Scale Multi-Modal Molecule Dataset for AI-driven Drug Design and Discovery
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces M$^{3}$-20M, a large-scale Multi-Modal Molecular dataset that contains over 20 million molecules. Designed to support AI-driven drug design and discovery, M$^{3}$-20M is 71 times more in the number of molecules than the largest existing dataset, providing an unprecedented scale that can highly benefit training or fine-tuning large (language) models with superior performance for drug design and discovery. This dataset integrates one-dimensional SMILES, two-dimensional molecular graphs, three-dimensional molecular structures, physicochemical properties, and textual descriptions collected through web crawling and generated by using GPT-3.5, offering a comprehensive view of each molecule. To demonstrate the power of M$^{3}$-20M in drug design and discovery, we conduct extensive experiments on two key tasks: molecule generation and molecular property prediction, using large language models including GLM4, GPT-3.5, and GPT-4. Our experimental results show that M$^{3}$-20M can significantly boost model performance in both tasks. Specifically, it enables the models to generate more diverse and valid molecular structures and achieve higher property prediction accuracy than the existing single-modal datasets, which validates the value and potential of M$^{3}$-20M in supporting AI-driven drug design and discovery. The dataset is available at \url{https://github.com/bz99bz/M-3}.
AdMix: A Mixed Sample Data Augmentation Method for Neural Machine Translation
May 10, 2022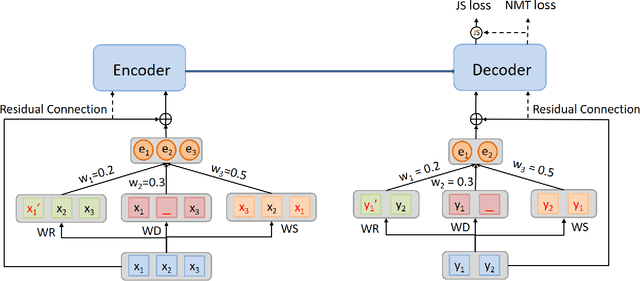
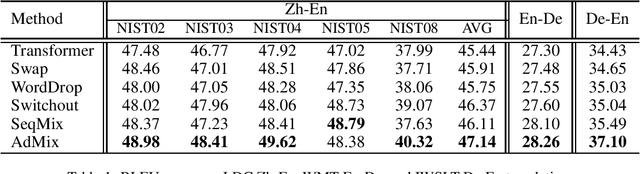
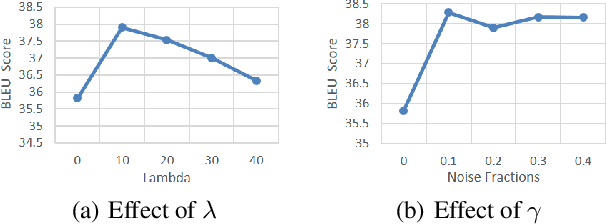
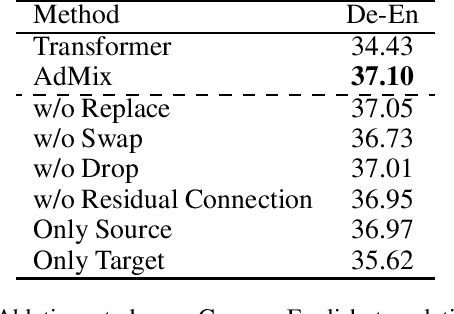
Abstract:In Neural Machine Translation (NMT), data augmentation methods such as back-translation have proven their effectiveness in improving translation performance. In this paper, we propose a novel data augmentation approach for NMT, which is independent of any additional training data. Our approach, AdMix, consists of two parts: 1) introduce faint discrete noise (word replacement, word dropping, word swapping) into the original sentence pairs to form augmented samples; 2) generate new synthetic training data by softly mixing the augmented samples with their original samples in training corpus. Experiments on three translation datasets of different scales show that AdMix achieves signifi cant improvements (1.0 to 2.7 BLEU points) over strong Transformer baseline. When combined with other data augmentation techniques (e.g., back-translation), our approach can obtain further improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge