Cassandra Kent
Robotic Manipulation Datasets for Offline Compositional Reinforcement Learning
Jul 13, 2023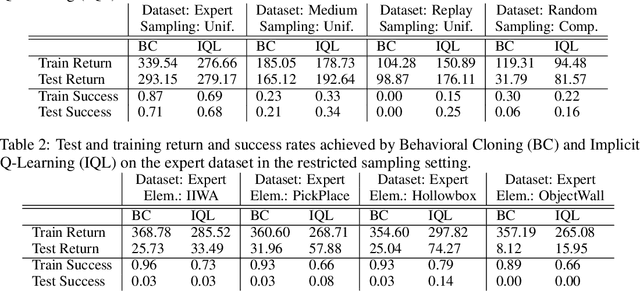
Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) is a promising direction that allows RL agents to pre-train on large datasets, avoiding the recurrence of expensive data collection. To advance the field, it is crucial to generate large-scale datasets. Compositional RL is particularly appealing for generating such large datasets, since 1) it permits creating many tasks from few components, 2) the task structure may enable trained agents to solve new tasks by combining relevant learned components, and 3) the compositional dimensions provide a notion of task relatedness. This paper provides four offline RL datasets for simulated robotic manipulation created using the 256 tasks from CompoSuite [Mendez et al., 2022a]. Each dataset is collected from an agent with a different degree of performance, and consists of 256 million transitions. We provide training and evaluation settings for assessing an agent's ability to learn compositional task policies. Our benchmarking experiments on each setting show that current offline RL methods can learn the training tasks to some extent and that compositional methods significantly outperform non-compositional methods. However, current methods are still unable to extract the tasks' compositional structure to generalize to unseen tasks, showing a need for further research in offline compositional RL.
A Domain-Agnostic Approach for Characterization of Lifelong Learning Systems
Jan 18, 2023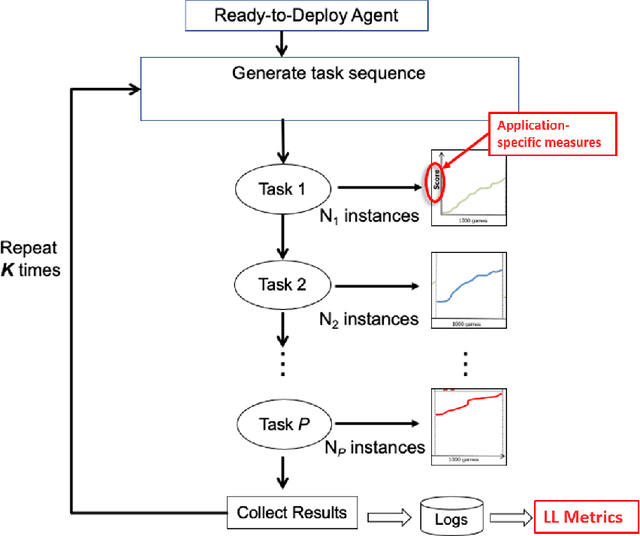
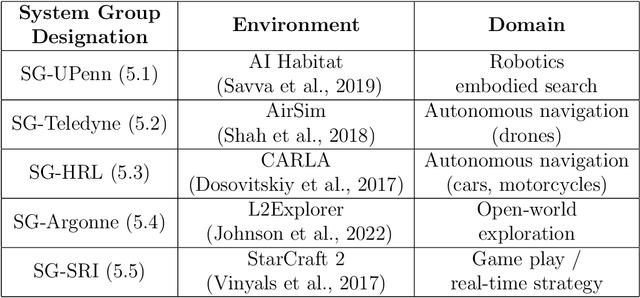
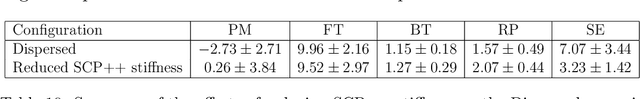
Abstract:Despite the advancement of machine learning techniques in recent years, state-of-the-art systems lack robustness to "real world" events, where the input distributions and tasks encountered by the deployed systems will not be limited to the original training context, and systems will instead need to adapt to novel distributions and tasks while deployed. This critical gap may be addressed through the development of "Lifelong Learning" systems that are capable of 1) Continuous Learning, 2) Transfer and Adaptation, and 3) Scalability. Unfortunately, efforts to improve these capabilities are typically treated as distinct areas of research that are assessed independently, without regard to the impact of each separate capability on other aspects of the system. We instead propose a holistic approach, using a suite of metrics and an evaluation framework to assess Lifelong Learning in a principled way that is agnostic to specific domains or system techniques. Through five case studies, we show that this suite of metrics can inform the development of varied and complex Lifelong Learning systems. We highlight how the proposed suite of metrics quantifies performance trade-offs present during Lifelong Learning system development - both the widely discussed Stability-Plasticity dilemma and the newly proposed relationship between Sample Efficient and Robust Learning. Further, we make recommendations for the formulation and use of metrics to guide the continuing development of Lifelong Learning systems and assess their progress in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge