Casey Casalnuovo
Do People Prefer "Natural" code?
Oct 08, 2019
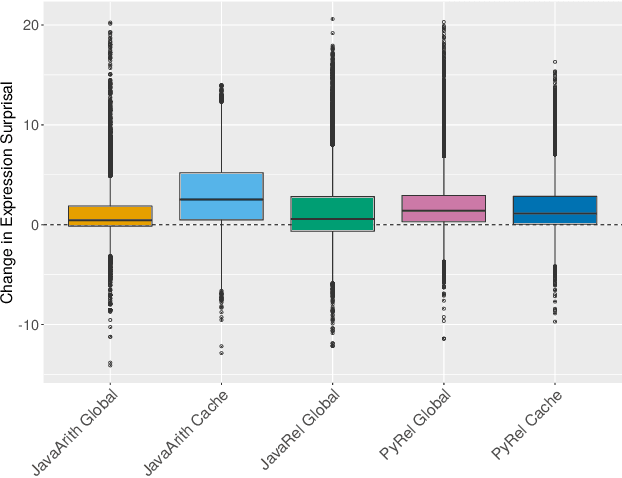
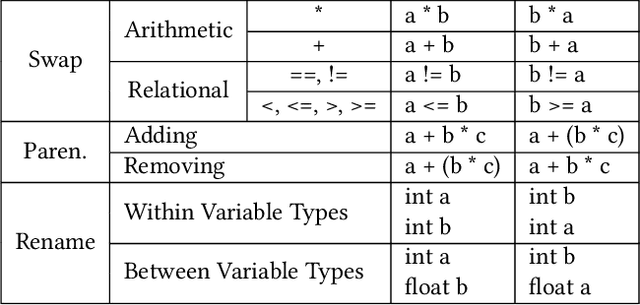
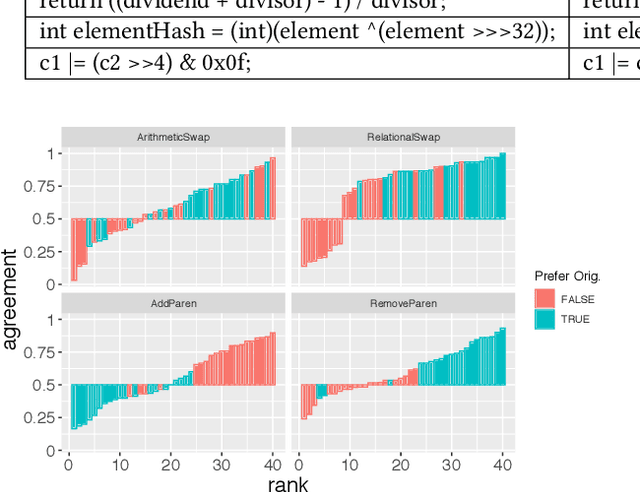
Abstract:Natural code is known to be very repetitive (much more so than natural language corpora); furthermore, this repetitiveness persists, even after accounting for the simpler syntax of code. However, programming languages are very expressive, allowing a great many different ways (all clear and unambiguous) to express even very simple computations. So why is natural code repetitive? We hypothesize that the reasons for this lie in fact that code is bimodal: it is executed by machines, but also read by humans. This bimodality, we argue, leads developers to write code in certain preferred ways that would be familiar to code readers. To test this theory, we 1) model familiarity using a language model estimated over a large training corpus and 2) run an experiment applying several meaning preserving transformations to Java and Python expressions in a distinct test corpus to see if forms more familiar to readers (as predicted by the language models) are in fact the ones actually written. We find that these transformations generally produce program structures that are less common in practice, supporting the theory that the high repetitiveness in code is a matter of deliberate preference. Finally, 3) we use a human subject study to show alignment between language model score and human preference for the first time in code, providing support for using this measure to improve code.
Studying the Difference Between Natural and Programming Language Corpora
Jun 06, 2018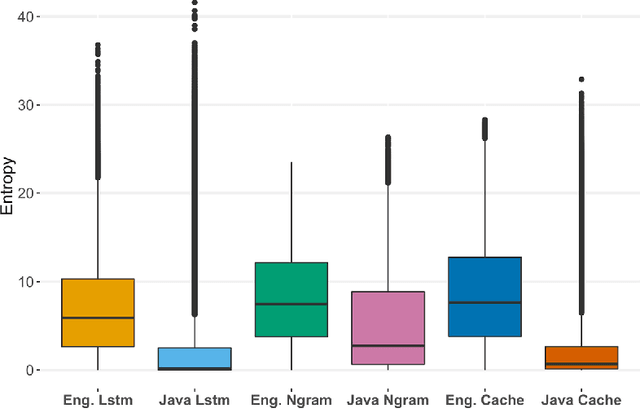
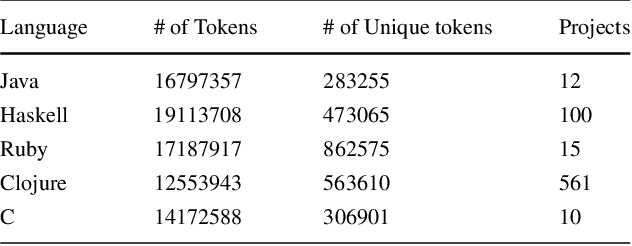
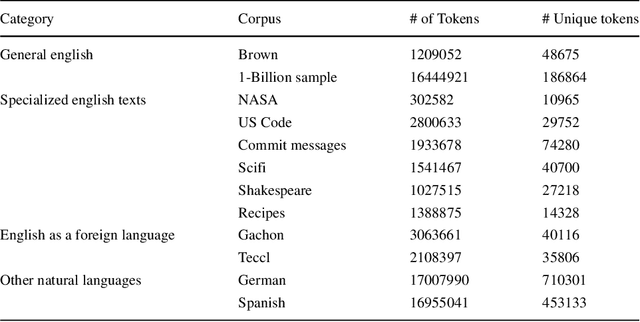
Abstract:Code corpora, as observed in large software systems, are now known to be far more repetitive and predictable than natural language corpora. But why? Does the difference simply arise from the syntactic limitations of programming languages? Or does it arise from the differences in authoring decisions made by the writers of these natural and programming language texts? We conjecture that the differences are not entirely due to syntax, but also from the fact that reading and writing code is un-natural for humans, and requires substantial mental effort; so, people prefer to write code in ways that are familiar to both reader and writer. To support this argument, we present results from two sets of studies: 1) a first set aimed at attenuating the effects of syntax, and 2) a second, aimed at measuring repetitiveness of text written in other settings (e.g. second language, technical/specialized jargon), which are also effortful to write. We find find that this repetition in source code is not entirely the result of grammar constraints, and thus some repetition must result from human choice. While the evidence we find of similar repetitive behavior in technical and learner corpora does not conclusively show that such language is used by humans to mitigate difficulty, it is consistent with that theory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge