Carmen Martin-Turrero
MEG: Medical Knowledge-Augmented Large Language Models for Question Answering
Nov 07, 2024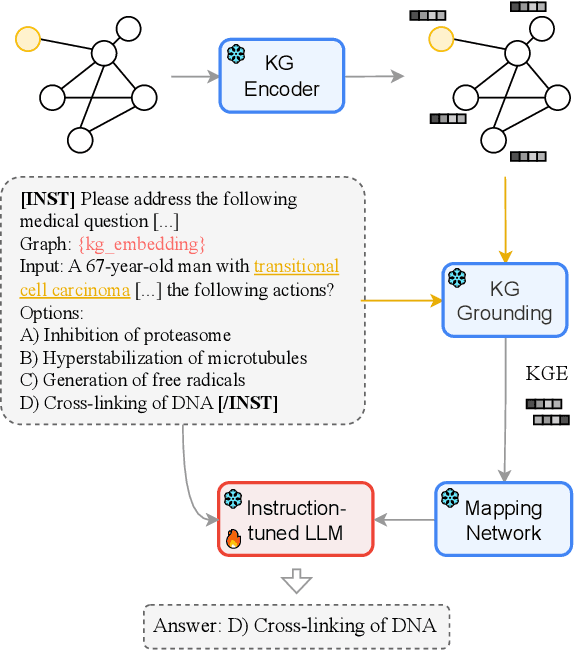

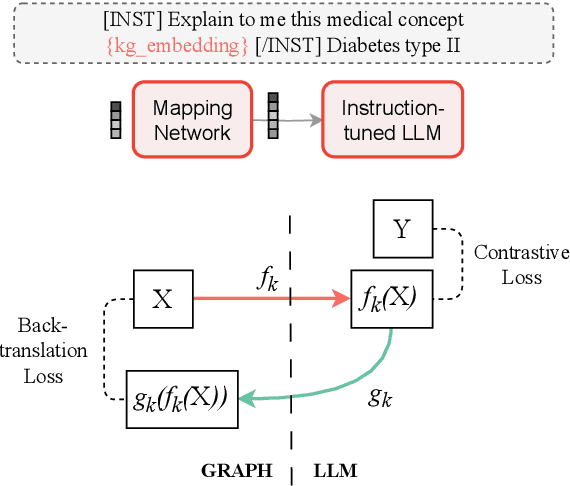

Abstract:Question answering is a natural language understanding task that involves reasoning over both explicit context and unstated, relevant domain knowledge. Large language models (LLMs), which underpin most contemporary question answering systems, struggle to induce how concepts relate in specialized domains such as medicine. Existing medical LLMs are also costly to train. In this work, we present MEG, a parameter-efficient approach for medical knowledge-augmented LLMs. MEG uses a lightweight mapping network to integrate graph embeddings into the LLM, enabling it to leverage external knowledge in a cost-effective way. We evaluate our method on four popular medical multiple-choice datasets and show that LLMs greatly benefit from the factual grounding provided by knowledge graph embeddings. MEG attains an average of +10.2% accuracy over the Mistral-Instruct baseline, and +6.7% over specialized models like BioMistral. We also show results based on Llama-3. Finally, we show that MEG's performance remains robust to the choice of graph encoder.
ALERT-Transformer: Bridging Asynchronous and Synchronous Machine Learning for Real-Time Event-based Spatio-Temporal Data
Feb 08, 2024



Abstract:We seek to enable classic processing of continuous ultra-sparse spatiotemporal data generated by event-based sensors with dense machine learning models. We propose a novel hybrid pipeline composed of asynchronous sensing and synchronous processing that combines several ideas: (1) an embedding based on PointNet models -- the ALERT module -- that can continuously integrate new and dismiss old events thanks to a leakage mechanism, (2) a flexible readout of the embedded data that allows to feed any downstream model with always up-to-date features at any sampling rate, (3) exploiting the input sparsity in a patch-based approach inspired by Vision Transformer to optimize the efficiency of the method. These embeddings are then processed by a transformer model trained for object and gesture recognition. Using this approach, we achieve performances at the state-of-the-art with a lower latency than competitors. We also demonstrate that our asynchronous model can operate at any desired sampling rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge