Carlota Salinas
Experimental Insights Towards Explainable and Interpretable Pedestrian Crossing Prediction
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:In the context of autonomous driving, pedestrian crossing prediction is a key component for improving road safety. Presently, the focus of these predictions extends beyond achieving trustworthy results; it is shifting towards the explainability and interpretability of these predictions. This research introduces a novel neuro-symbolic approach that combines deep learning and fuzzy logic for an explainable and interpretable pedestrian crossing prediction. We have developed an explainable predictor (ExPedCross), which utilizes a set of explainable features and employs a fuzzy inference system to predict whether the pedestrian will cross or not. Our approach was evaluated on both the PIE and JAAD datasets. The results offer experimental insights into achieving explainability and interpretability in the pedestrian crossing prediction task. Furthermore, the testing results yield a set of guidelines and recommendations regarding the process of dataset selection, feature selection, and explainability.
WiFiNet: WiFi-based indoor localisation using CNNs
Apr 14, 2021
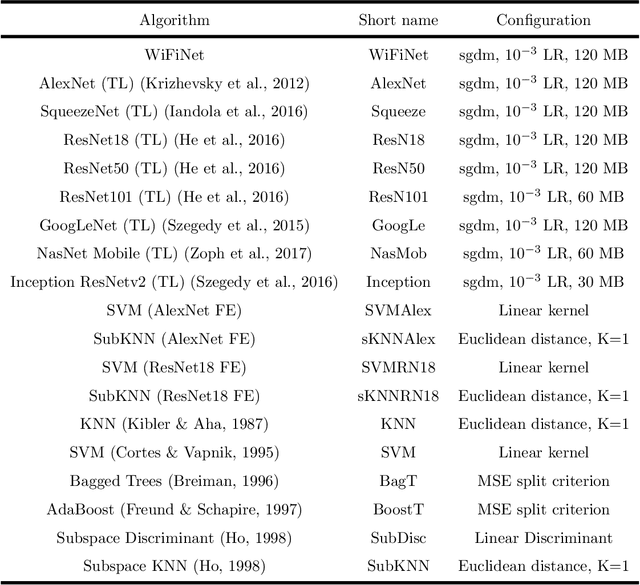
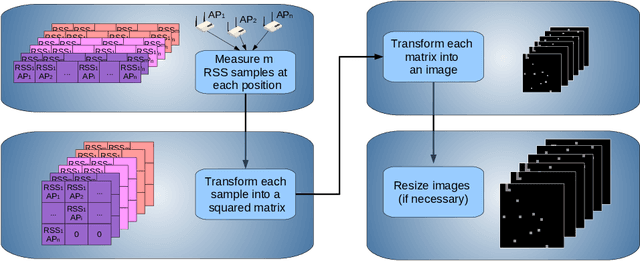
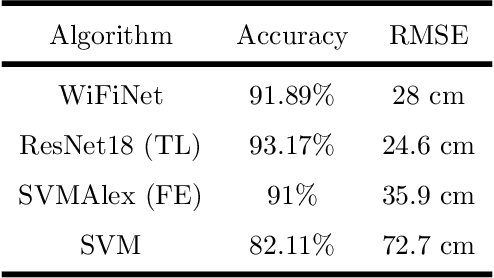
Abstract:Different technologies have been proposed to provide indoor localisation: magnetic field, bluetooth , WiFi, etc. Among them, WiFi is the one with the highest availability and highest accuracy. This fact allows for an ubiquitous accurate localisation available for almost any environment and any device. However, WiFi-based localisation is still an open problem. In this article, we propose a new WiFi-based indoor localisation system that takes advantage of the great ability of Convolutional Neural Networks in classification problems. Three different approaches were used to achieve this goal: a custom architecture called WiFiNet designed and trained specifically to solve this problem and the most popular pre-trained networks using both transfer learning and feature extraction. Results indicate that WiFiNet is as a great approach for indoor localisation in a medium-sized environment (30 positions and 113 access points) as it reduces the mean localisation error (33%) and the processing time when compared with state-of-the-art WiFi indoor localisation algorithms such as SVM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge