Carlos Güemes-Palau
Barcelona Neural Networking Center, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Spain
Ordered Topological Deep Learning: a Network Modeling Case Study
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:Computer networks are the foundation of modern digital infrastructure, facilitating global communication and data exchange. As demand for reliable high-bandwidth connectivity grows, advanced network modeling techniques become increasingly essential to optimize performance and predict network behavior. Traditional modeling methods, such as packet-level simulators and queueing theory, have notable limitations --either being computationally expensive or relying on restrictive assumptions that reduce accuracy. In this context, the deep learning-based RouteNet family of models has recently redefined network modeling by showing an unprecedented cost-performance trade-off. In this work, we revisit RouteNet's sophisticated design and uncover its hidden connection to Topological Deep Learning (TDL), an emerging field that models higher-order interactions beyond standard graph-based methods. We demonstrate that, although originally formulated as a heterogeneous Graph Neural Network, RouteNet serves as the first instantiation of a new form of TDL. More specifically, this paper presents OrdGCCN, a novel TDL framework that introduces the notion of ordered neighbors in arbitrary discrete topological spaces, and shows that RouteNet's architecture can be naturally described as an ordered topological neural network. To the best of our knowledge, this marks the first successful real-world application of state-of-the-art TDL principles --which we confirm through extensive testbed experiments--, laying the foundation for the next generation of ordered TDL-driven applications.
RouteNet-Gauss: Hardware-Enhanced Network Modeling with Machine Learning
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:Network simulation is pivotal in network modeling, assisting with tasks ranging from capacity planning to performance estimation. Traditional approaches such as Discrete Event Simulation (DES) face limitations in terms of computational cost and accuracy. This paper introduces RouteNet-Gauss, a novel integration of a testbed network with a Machine Learning (ML) model to address these challenges. By using the testbed as a hardware accelerator, RouteNet-Gauss generates training datasets rapidly and simulates network scenarios with high fidelity to real-world conditions. Experimental results show that RouteNet-Gauss significantly reduces prediction errors by up to 95% and achieves a 488x speedup in inference time compared to state-of-the-art DES-based methods. RouteNet-Gauss's modular architecture is dynamically constructed based on the specific characteristics of the network scenario, such as topology and routing. This enables it to understand and generalize to different network configurations beyond those seen during training, including networks up to 10x larger. Additionally, it supports Temporal Aggregated Performance Estimation (TAPE), providing configurable temporal granularity and maintaining high accuracy in flow performance metrics. This approach shows promise in improving both simulation efficiency and accuracy, offering a valuable tool for network operators.
Building a Graph-based Deep Learning network model from captured traffic traces
Oct 18, 2023
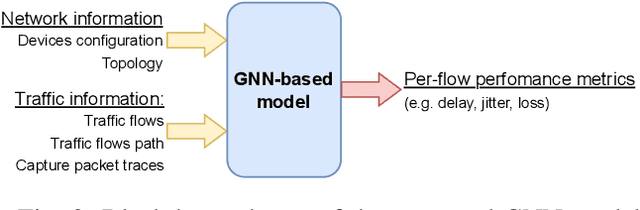
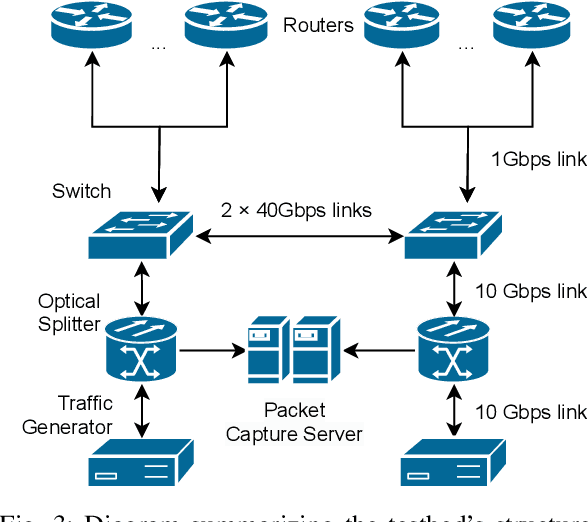

Abstract:Currently the state of the art network models are based or depend on Discrete Event Simulation (DES). While DES is highly accurate, it is also computationally costly and cumbersome to parallelize, making it unpractical to simulate high performance networks. Additionally, simulated scenarios fail to capture all of the complexities present in real network scenarios. While there exists network models based on Machine Learning (ML) techniques to minimize these issues, these models are also trained with simulated data and hence vulnerable to the same pitfalls. Consequently, the Graph Neural Networking Challenge 2023 introduces a dataset of captured traffic traces that can be used to build a ML-based network model without these limitations. In this paper we propose a Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based solution specifically designed to better capture the complexities of real network scenarios. This is done through a novel encoding method to capture information from the sequence of captured packets, and an improved message passing algorithm to better represent the dependencies present in physical networks. We show that the proposed solution it is able to learn and generalize to unseen captured network scenarios.
Accelerating Deep Reinforcement Learning for Digital Twin Network Optimization with Evolutionary Strategies
Feb 01, 2022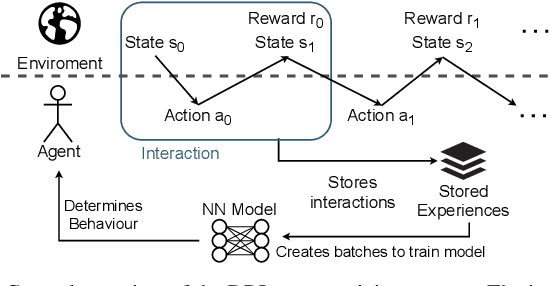
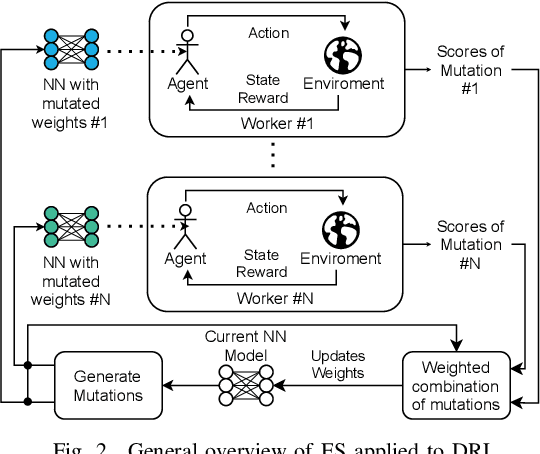
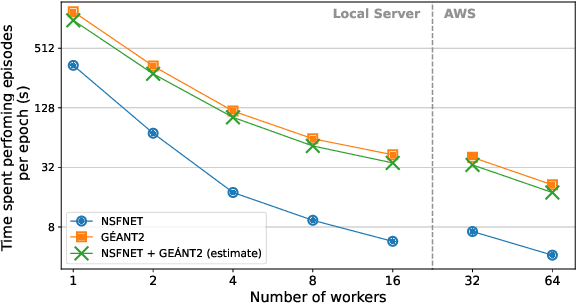
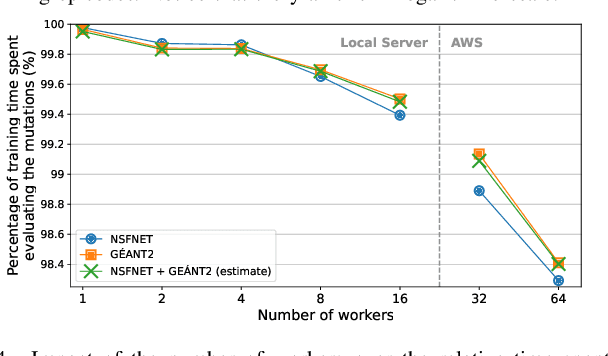
Abstract:The recent growth of emergent network applications (e.g., satellite networks, vehicular networks) is increasing the complexity of managing modern communication networks. As a result, the community proposed the Digital Twin Networks (DTN) as a key enabler of efficient network management. Network operators can leverage the DTN to perform different optimization tasks (e.g., Traffic Engineering, Network Planning). Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) showed a high performance when applied to solve network optimization problems. In the context of DTN, DRL can be leveraged to solve optimization problems without directly impacting the real-world network behavior. However, DRL scales poorly with the problem size and complexity. In this paper, we explore the use of Evolutionary Strategies (ES) to train DRL agents for solving a routing optimization problem. The experimental results show that ES achieved a training time speed-up of 128 and 6 for the NSFNET and GEANT2 topologies respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge