Bruno Costa
Efficient data-driven encoding of scene motion using Eccentricity
Mar 03, 2021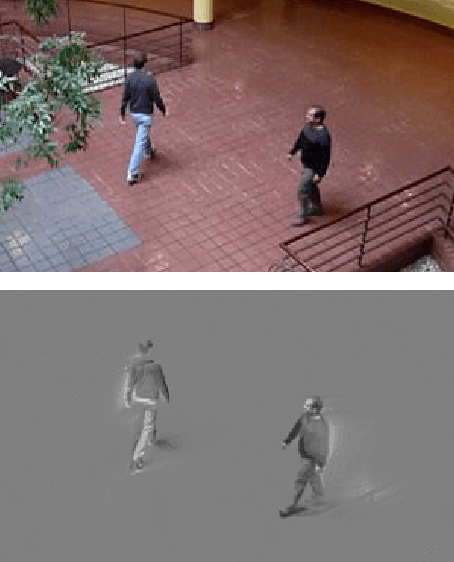
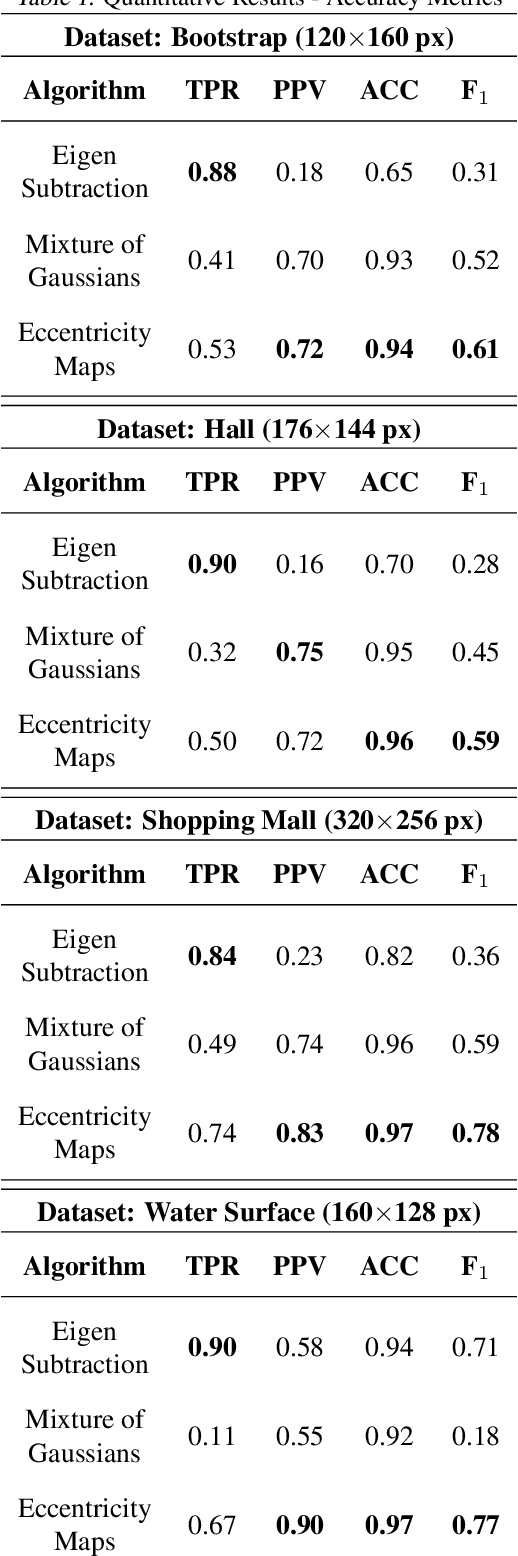
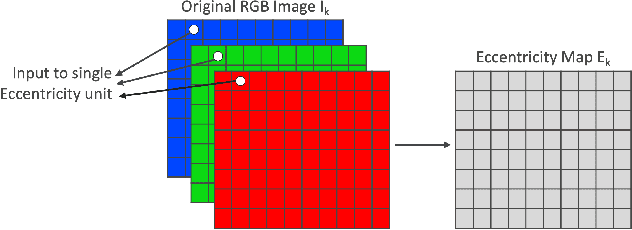
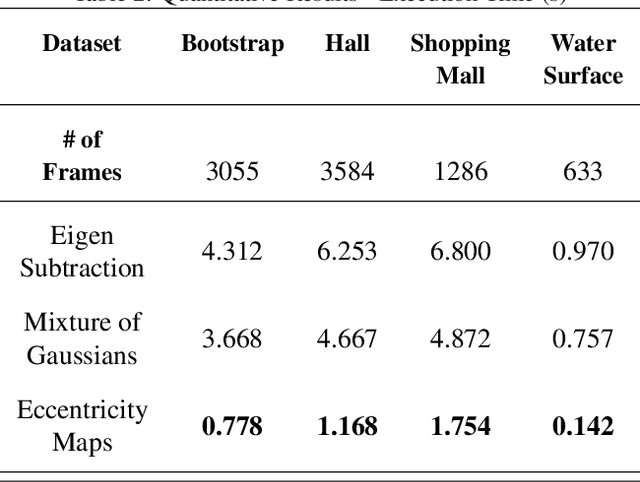
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach of representing dynamic visual scenes with static maps generated from video/image streams. Such representation allows easy visual assessment of motion in dynamic environments. These maps are 2D matrices calculated recursively, in a pixel-wise manner, that is based on the recently introduced concept of Eccentricity data analysis. Eccentricity works as a metric of a discrepancy between a particular pixel of an image and its normality model, calculated in terms of mean and variance of past readings of the same spatial region of the image. While Eccentricity maps carry temporal information about the scene, actual images do not need to be stored nor processed in batches. Rather, all the calculations are done recursively, based on a small amount of statistical information stored in memory, thus resulting in a very computationally efficient (processor- and memory-wise) method. The list of potential applications includes video-based activity recognition, intent recognition, object tracking, video description, and so on.
Pay Voice: Point of Sale Recognition for Visually Impaired People
Dec 14, 2018



Abstract:Millions of visually impaired people depend on relatives and friends to perform their everyday tasks. One relevant step towards self-sufficiency is to provide them with means to verify the value and operation presented in payment machines. In this work, we developed and released a smartphone application, named Pay Voice, that uses image processing, optical character recognition (OCR) and voice synthesis to recognize the value and operation presented in POS and PIN pad machines, and thus informing the user with auditive and visual feedback. The proposed approach presented significant results for value and operation recognition, especially for POS, due to the higher display quality. Importantly, we achieved the key performance indicators, namely, more than 80% of accuracy in a real-world scenario, and less than $5$ seconds of processing time for recognition. Pay Voice is publicly available on Google Play and App Store for free.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge