Brian C. Allen
Diagnostic Impact of Cine Clips for Thyroid Nodule Assessment on Ultrasound
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Background: Thyroid ultrasound is commonly performed using a combination of static images and cine clips (video recordings). However, the exact utility and impact of cine images remains unknown. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of cine imaging on accuracy and consistency of thyroid nodule assessment, using the American College of Radiology Thyroid Reporting and Data System (ACR TI-RADS). Methods: 50 benign and 50 malignant thyroid nodules with cytopathology results were included. A reader study with 4 specialty-trained radiologists was then conducted over 3 rounds, assessing only static images in the first two rounds and both static and cine images in the third round. TI-RADS scores and the consequent management recommendations were then evaluated by comparing them to the malignancy status of the nodules. Results: Mean sensitivity for malignancy detection was 0.65 for static images and 0.67 with both static and cine images (p>0.5). Specificity was 0.20 for static images and 0.22 with both static and cine images (p>0.5). Management recommendations were similar with and without cine images. Intrareader agreement on feature assignments remained consistent across all rounds, though TI-RADS point totals were slightly higher with cine images. Conclusion: The inclusion of cine imaging for thyroid nodule assessment on ultrasound did not significantly change diagnostic performance. Current practice guidelines, which do not mandate cine imaging, are sufficient for accurate diagnosis.
Deep Learning for Classification of Thyroid Nodules on Ultrasound: Validation on an Independent Dataset
Jul 27, 2022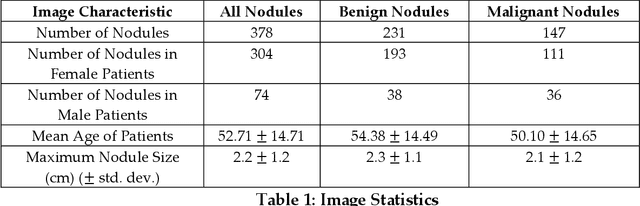
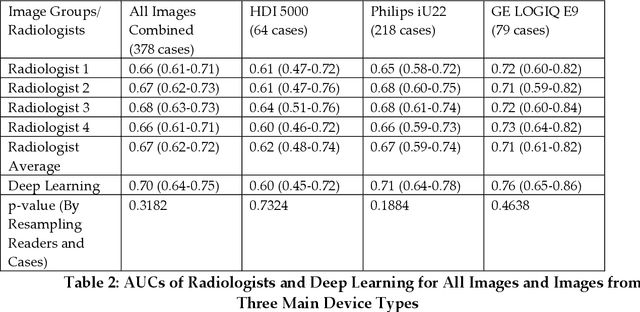
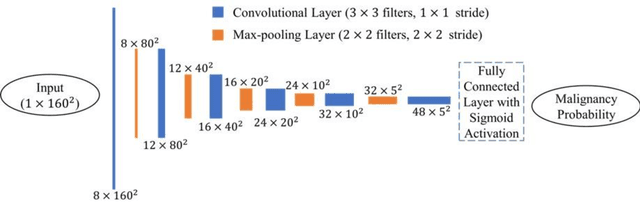
Abstract:Objectives: The purpose is to apply a previously validated deep learning algorithm to a new thyroid nodule ultrasound image dataset and compare its performances with radiologists. Methods: Prior study presented an algorithm which is able to detect thyroid nodules and then make malignancy classifications with two ultrasound images. A multi-task deep convolutional neural network was trained from 1278 nodules and originally tested with 99 separate nodules. The results were comparable with that of radiologists. The algorithm was further tested with 378 nodules imaged with ultrasound machines from different manufacturers and product types than the training cases. Four experienced radiologists were requested to evaluate the nodules for comparison with deep learning. Results: The Area Under Curve (AUC) of the deep learning algorithm and four radiologists were calculated with parametric, binormal estimation. For the deep learning algorithm, the AUC was 0.70 (95% CI: 0.64 - 0.75). The AUC of radiologists were 0.66 (95% CI: 0.61 - 0.71), 0.67 (95% CI:0.62 - 0.73), 0.68 (95% CI: 0.63 - 0.73), and 0.66 (95%CI: 0.61 - 0.71). Conclusion: In the new testing dataset, the deep learning algorithm achieved similar performances with all four radiologists.
Multistep Automated Data Labelling Procedure (MADLaP) for Thyroid Nodules on Ultrasound: An Artificial Intelligence Approach for Automating Image Annotation
Jun 28, 2022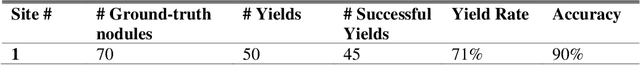
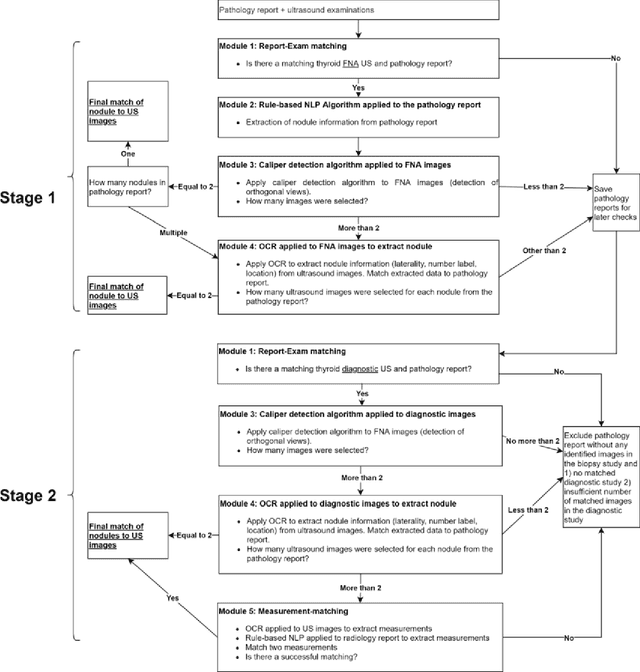
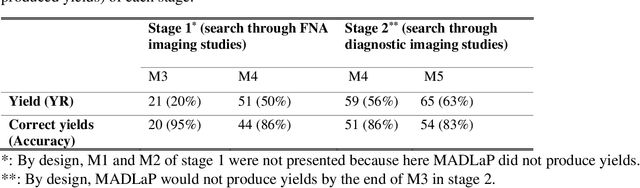

Abstract:Machine learning (ML) for diagnosis of thyroid nodules on ultrasound is an active area of research. However, ML tools require large, well-labelled datasets, the curation of which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. The purpose of our study was to develop and test a deep-learning-based tool to facilitate and automate the data annotation process for thyroid nodules; we named our tool Multistep Automated Data Labelling Procedure (MADLaP). MADLaP was designed to take multiple inputs included pathology reports, ultrasound images, and radiology reports. Using multiple step-wise modules including rule-based natural language processing, deep-learning-based imaging segmentation, and optical character recognition, MADLaP automatically identified images of a specific thyroid nodule and correctly assigned a pathology label. The model was developed using a training set of 378 patients across our health system and tested on a separate set of 93 patients. Ground truths for both sets were selected by an experienced radiologist. Performance metrics including yield (how many labeled images the model produced) and accuracy (percentage correct) were measured using the test set. MADLaP achieved a yield of 63% and an accuracy of 83%. The yield progressively increased as the input data moved through each module, while accuracy peaked part way through. Error analysis showed that inputs from certain examination sites had lower accuracy (40%) than the other sites (90%, 100%). MADLaP successfully created curated datasets of labeled ultrasound images of thyroid nodules. While accurate, the relatively suboptimal yield of MADLaP exposed some challenges when trying to automatically label radiology images from heterogeneous sources. The complex task of image curation and annotation could be automated, allowing for enrichment of larger datasets for use in machine learning development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge