Brian Brewington
Learning 3D Semantic Segmentation with only 2D Image Supervision
Oct 21, 2021
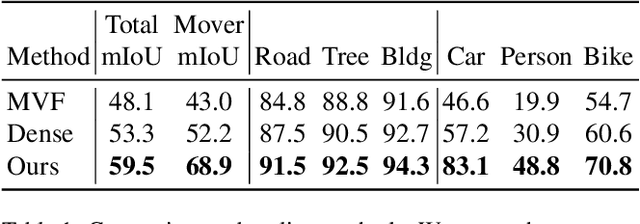
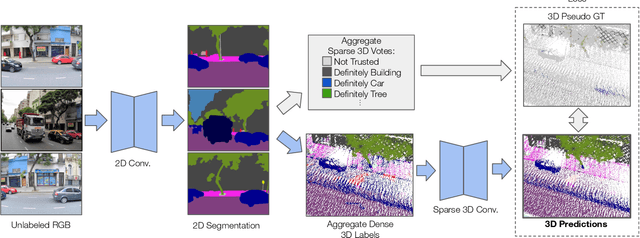
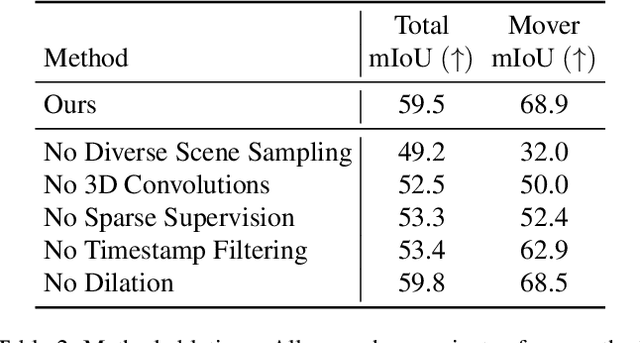
Abstract:With the recent growth of urban mapping and autonomous driving efforts, there has been an explosion of raw 3D data collected from terrestrial platforms with lidar scanners and color cameras. However, due to high labeling costs, ground-truth 3D semantic segmentation annotations are limited in both quantity and geographic diversity, while also being difficult to transfer across sensors. In contrast, large image collections with ground-truth semantic segmentations are readily available for diverse sets of scenes. In this paper, we investigate how to use only those labeled 2D image collections to supervise training 3D semantic segmentation models. Our approach is to train a 3D model from pseudo-labels derived from 2D semantic image segmentations using multiview fusion. We address several novel issues with this approach, including how to select trusted pseudo-labels, how to sample 3D scenes with rare object categories, and how to decouple input features from 2D images from pseudo-labels during training. The proposed network architecture, 2D3DNet, achieves significantly better performance (+6.2-11.4 mIoU) than baselines during experiments on a new urban dataset with lidar and images captured in 20 cities across 5 continents.
Virtual Multi-view Fusion for 3D Semantic Segmentation
Jul 26, 2020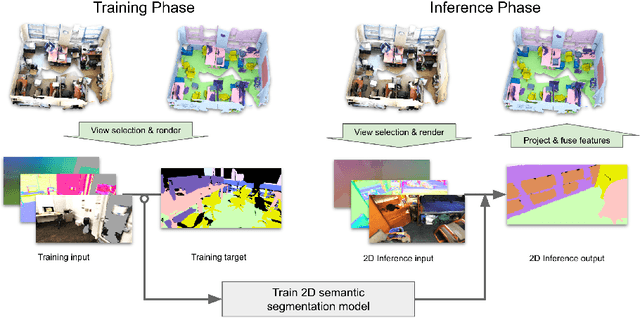
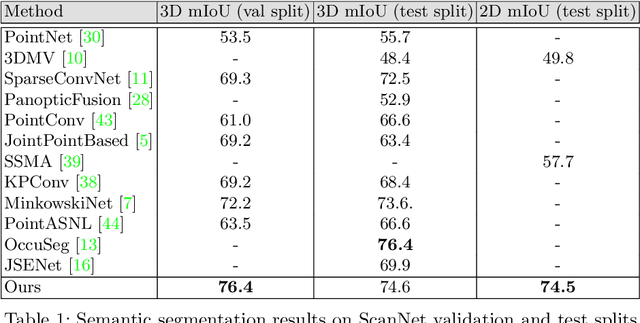
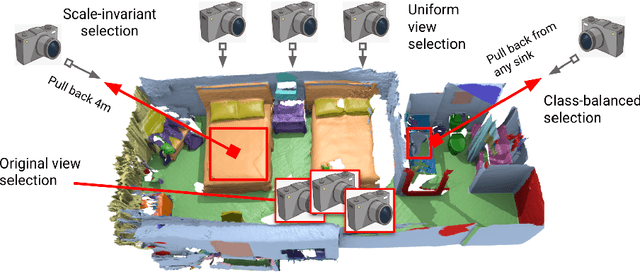
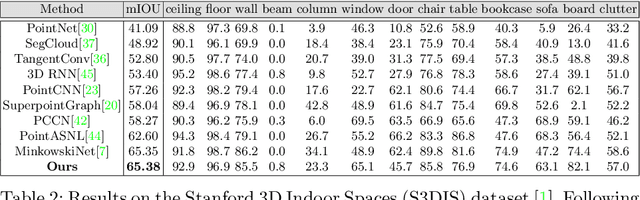
Abstract:Semantic segmentation of 3D meshes is an important problem for 3D scene understanding. In this paper we revisit the classic multiview representation of 3D meshes and study several techniques that make them effective for 3D semantic segmentation of meshes. Given a 3D mesh reconstructed from RGBD sensors, our method effectively chooses different virtual views of the 3D mesh and renders multiple 2D channels for training an effective 2D semantic segmentation model. Features from multiple per view predictions are finally fused on 3D mesh vertices to predict mesh semantic segmentation labels. Using the large scale indoor 3D semantic segmentation benchmark of ScanNet, we show that our virtual views enable more effective training of 2D semantic segmentation networks than previous multiview approaches. When the 2D per pixel predictions are aggregated on 3D surfaces, our virtual multiview fusion method is able to achieve significantly better 3D semantic segmentation results compared to all prior multiview approaches and competitive with recent 3D convolution approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge