Brecht Verbeken
Michael Pokorny
Probing the Trajectories of Reasoning Traces in Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly solve difficult problems by producing "reasoning traces" before emitting a final response. However, it remains unclear how accuracy and decision commitment evolve along a reasoning trajectory, and whether intermediate trace segments provide answer-relevant information beyond generic length or stylistic effects. Here, we propose a protocol to systematically probe the trajectories of reasoning traces in LLMs by 1) generating a model's reasoning trace, 2) truncating it at fixed token-percentiles, and 3) injecting each partial trace back into the model (or a different model) to measure the induced distribution over answer choices via next-token probabilities. We apply this protocol to the open-source Qwen3-4B/-8B/-14B and gpt-oss-20b/-120b models across the multiple-choice GPQA Diamond and MMLU-Pro benchmarks. We find that accuracy and decision commitment consistently increase as the percentage of provided reasoning tokens grows. These gains are primarily driven by relevant content in the model generation rather than context length or generic "reasoning style" effects. Stronger models often backtrack successfully from incorrect partial traces, but immediate answers often remain anchored in the weaker model's incorrect response. More broadly, we show that trajectory probing provides diagnostics for efficient and safer deployment of reasoning models as the measurements can inform practical trace-handling and monitoring policies that improve reliability without assuming intermediate tokens are inherently faithful explanations.
Benchmarks Saturate When The Model Gets Smarter Than The Judge
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools to track progress in the development of Large Language Models (LLMs), yet inaccuracies in datasets and evaluation methods consistently undermine their effectiveness. Here, we present Omni-MATH-2, a manually revised version of the Omni-MATH dataset comprising a clean, exact-answer subset ($n{=}4181$) and a tagged, non-standard subset ($n{=}247$). Each problem was audited to ensure LaTeX compilability, solvability and verifiability, which involved adding missing figures or information, labeling problems requiring a proof, estimation or image, and removing clutter. This process significantly reduces dataset-induced noise, thereby providing a more precise assessment of model performance. The annotated dataset also allows us to evaluate judge-induced noise by comparing GPT-5 mini with the original Omni-Judge, revealing substantial discrepancies between judges on both the clean and tagged problem subsets. Expert annotations reveal that Omni-Judge is wrong in $96.4\%$ of the judge disagreements, indicating its inability to differentiate between models' abilities, even well before saturation of the benchmark occurs. As problems become more challenging, we find that increasingly competent judges become essential in order to prevent judge errors from masking genuine differences between models. Finally, neither judge identifies the present failure modes for the subset of tagged problems, demonstrating that dataset quality and judge reliability are both critical to develop accurate benchmarks of model performance.
Estimating problem difficulty without ground truth using Large Language Model comparisons
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in the finetuning of large language models (LLMs) have significantly improved their performance on established benchmarks, emphasizing the need for increasingly difficult, synthetic data. A key step in this data generation pipeline is a method for estimating problem difficulty. Current approaches, such as human calibration or performance-based scoring, fail to generalize to out-of-distribution problems, i.e. problems currently unsolvable by humans and LLMs, because they are not scalable, time-consuming, and ground truth dependent. Therefore, we propose a new method for estimating problem difficulty, LLM compare, that addresses these limitations. An LLM performs pairwise difficulty comparisons, and then Bradley-Terry scores are computed based on the outcomes. To validate our method, we first propose a conceptual framework that positions existing approaches on three orthogonal planes--construction, scale and dependence--identifying which quadrants a measure needs to occupy to score out-of-distribution problems. LLM compare naturally occupies all desirable quadrants as the first measure that is continuous and dynamic, model-agnostic and independent of ground truth information. As a second validation, we show that LLM compare demonstrates strong alignment with human annotations: Pearson $r \geq 0.80$ for $n=1876$. Thirdly, we show that LLM compare is robust to hallucinations, with less than $6\%$ degradation in Pearson correlation for $10\%$ noise injection. Our work represents a significant step towards replacing time-consuming human annotations and synthetic data generation, and will be an important driver for curriculum design, model evaluation, and AI-assisted research ideation.
How Deep Do Large Language Models Internalize Scientific Literature and Citation Practices?
Apr 03, 2025
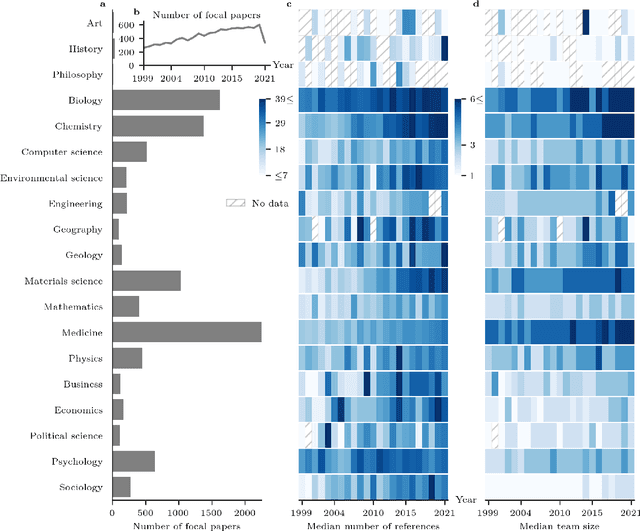
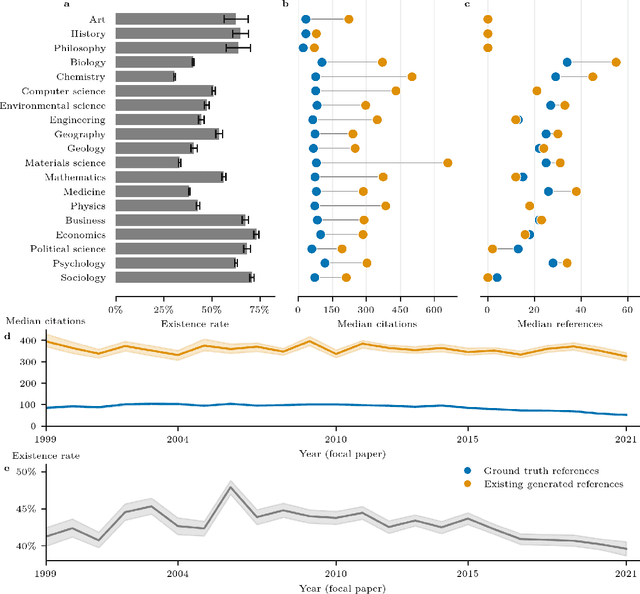
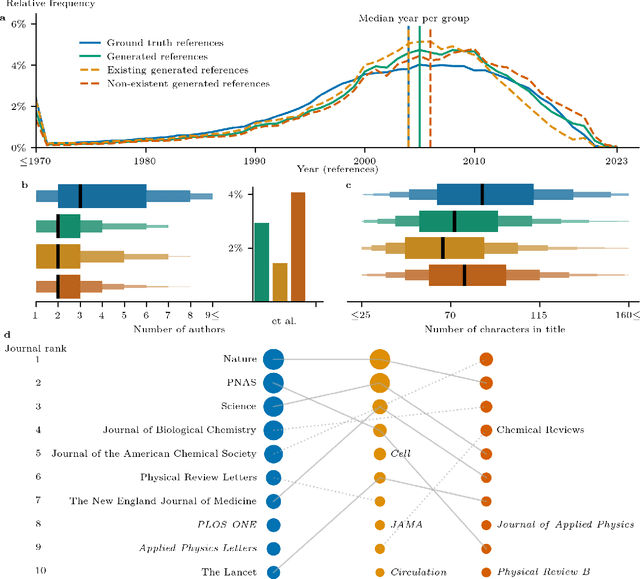
Abstract:The spread of scientific knowledge depends on how researchers discover and cite previous work. The adoption of large language models (LLMs) in the scientific research process introduces a new layer to these citation practices. However, it remains unclear to what extent LLMs align with human citation practices, how they perform across domains, and may influence citation dynamics. Here, we show that LLMs systematically reinforce the Matthew effect in citations by consistently favoring highly cited papers when generating references. This pattern persists across scientific domains despite significant field-specific variations in existence rates, which refer to the proportion of generated references that match existing records in external bibliometric databases. Analyzing 274,951 references generated by GPT-4o for 10,000 papers, we find that LLM recommendations diverge from traditional citation patterns by preferring more recent references with shorter titles and fewer authors. Emphasizing their content-level relevance, the generated references are semantically aligned with the content of each paper at levels comparable to the ground truth references and display similar network effects while reducing author self-citations. These findings illustrate how LLMs may reshape citation practices and influence the trajectory of scientific discovery by reflecting and amplifying established trends. As LLMs become more integrated into the scientific research process, it is important to understand their role in shaping how scientific communities discover and build upon prior work.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge