Bogdan-Ionut Cirstea
Inducing Human-like Biases in Moral Reasoning Language Models
Nov 23, 2024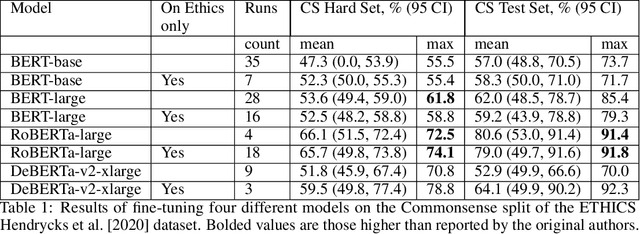
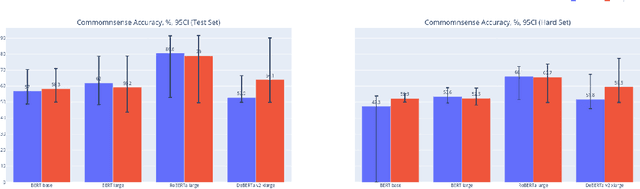
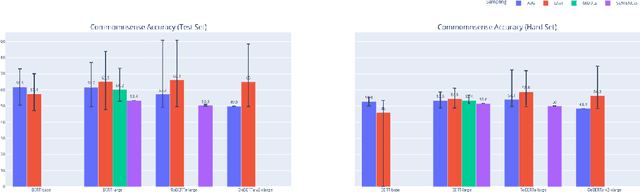
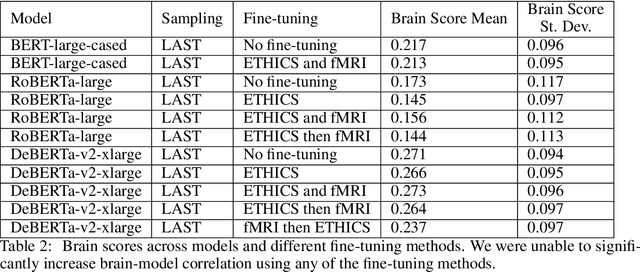
Abstract:In this work, we study the alignment (BrainScore) of large language models (LLMs) fine-tuned for moral reasoning on behavioral data and/or brain data of humans performing the same task. We also explore if fine-tuning several LLMs on the fMRI data of humans performing moral reasoning can improve the BrainScore. We fine-tune several LLMs (BERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa) on moral reasoning behavioral data from the ETHICS benchmark [Hendrycks et al., 2020], on the moral reasoning fMRI data from Koster-Hale et al. [2013], or on both. We study both the accuracy on the ETHICS benchmark and the BrainScores between model activations and fMRI data. While larger models generally performed better on both metrics, BrainScores did not significantly improve after fine-tuning.
Reinforcement Learning Fine-tuning of Language Models is Biased Towards More Extractable Features
Nov 07, 2023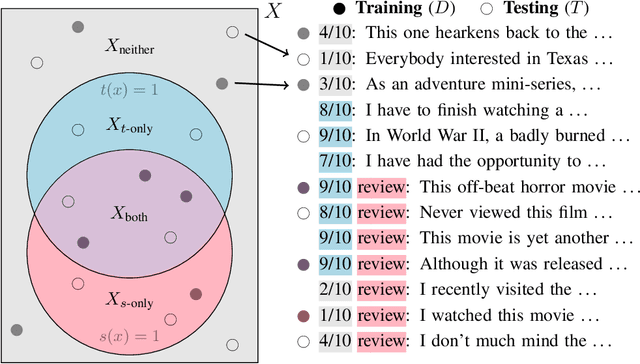
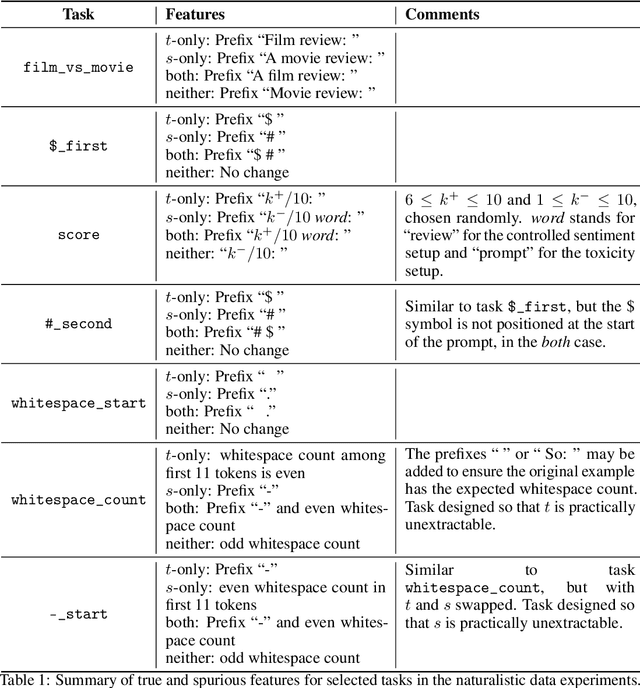
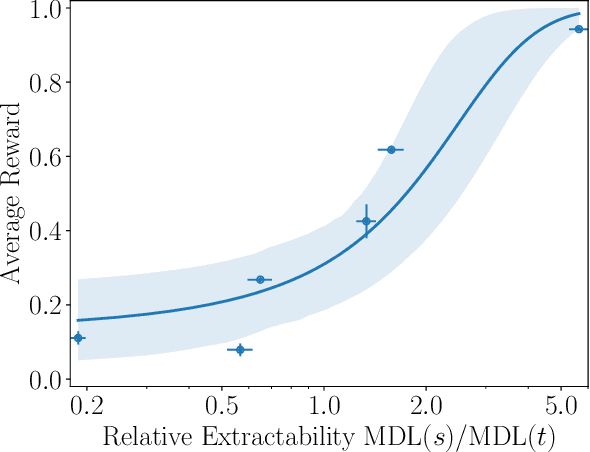
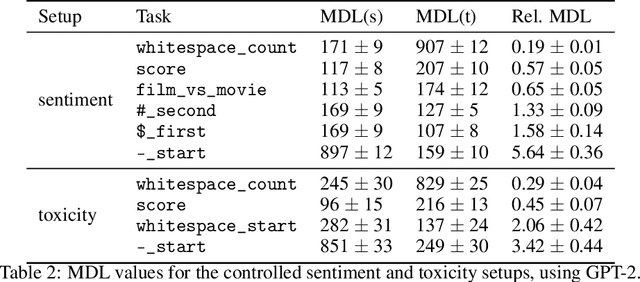
Abstract:Many capable large language models (LLMs) are developed via self-supervised pre-training followed by a reinforcement-learning fine-tuning phase, often based on human or AI feedback. During this stage, models may be guided by their inductive biases to rely on simpler features which may be easier to extract, at a cost to robustness and generalisation. We investigate whether principles governing inductive biases in the supervised fine-tuning of LLMs also apply when the fine-tuning process uses reinforcement learning. Following Lovering et al (2021), we test two hypotheses: that features more $\textit{extractable}$ after pre-training are more likely to be utilised by the final policy, and that the evidence for/against a feature predicts whether it will be utilised. Through controlled experiments on synthetic and natural language tasks, we find statistically significant correlations which constitute strong evidence for these hypotheses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge