Binbin Feng
LogoNet: a fine-grained network for instance-level logo sketch retrieval
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:Sketch-based image retrieval, which aims to use sketches as queries to retrieve images containing the same query instance, receives increasing attention in recent years. Although dramatic progress has been made in sketch retrieval, few efforts are devoted to logo sketch retrieval which is still hindered by the following challenges: Firstly, logo sketch retrieval is more difficult than typical sketch retrieval problem, since a logo sketch usually contains much less visual contents with only irregular strokes and lines. Secondly, instance-specific sketches demonstrate dramatic appearance variances, making them less identifiable when querying the same logo instance. Thirdly, there exist several sketch retrieval benchmarking datasets nowadays, whereas an instance-level logo sketch dataset is still publicly unavailable. To address the above-mentioned limitations, we make twofold contributions in this study for instance-level logo sketch retrieval. To begin with, we construct an instance-level logo sketch dataset containing 2k logo instances and exceeding 9k sketches. To our knowledge, this is the first publicly available instance-level logo sketch dataset. Next, we develop a fine-grained triple-branch CNN architecture based on hybrid attention mechanism termed LogoNet for accurate logo sketch retrieval. More specifically, we embed the hybrid attention mechanism into the triple-branch architecture for capturing the key query-specific information from the limited visual cues in the logo sketches. Experimental evaluations both on our assembled dataset and public benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed network.
Optimized SC-F-LOAM: Optimized Fast LiDAR Odometry and Mapping Using Scan Context
Apr 11, 2022
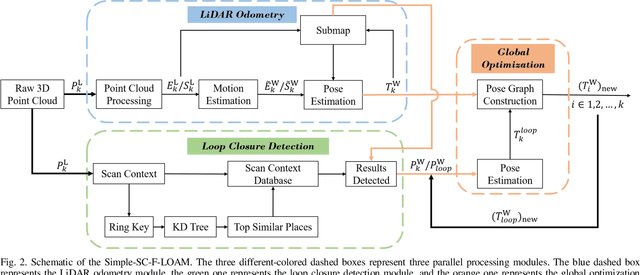
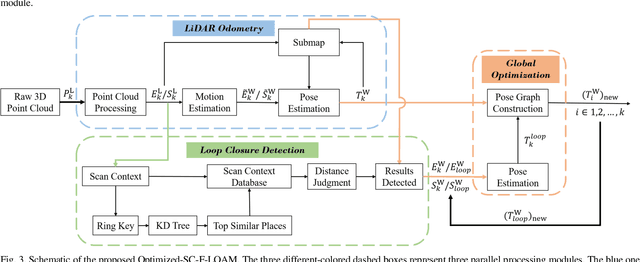

Abstract:LiDAR odometry can achieve accurate vehicle pose estimation for short driving range or in small-scale environments, but for long driving range or in large-scale environments, the accuracy deteriorates as a result of cumulative estimation errors. This drawback necessitates the inclusion of loop closure detection in a SLAM framework to suppress the adverse effects of cumulative errors. To improve the accuracy of pose estimation, we propose a new LiDAR-based SLAM method which uses F-LOAM as LiDAR odometry, Scan Context for loop closure detection, and GTSAM for global optimization. In our approach, an adaptive distance threshold (instead of a fixed threshold) is employed for loop closure detection, which achieves more accurate loop closure detection results. Besides, a feature-based matching method is used in our approach to compute vehicle pose transformations between loop closure point cloud pairs, instead of using the raw point cloud obtained by the LiDAR sensor, which significantly reduces the computation time. The KITTI dataset and a UGV platform are used for verifications of our method, and the experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms typical LiDAR odometry/SLAM methods in the literature. Our code is made publicly available for the benefit of the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge