Bijan Shoushtarian
Breast Histopathology Image Retrieval by Attention-based Adversarially Regularized Variational Graph Autoencoder with Contrastive Learning-Based Feature Extraction
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Breast cancer is a significant global health concern, particularly for women. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in mitigating its impact, with histopathology examinations playing a vital role in swift diagnosis. However, these examinations often require a substantial workforce and experienced medical experts for proper recognition and cancer grading. Automated image retrieval systems have the potential to assist pathologists in identifying cancerous tissues, thereby accelerating the diagnostic process. Nevertheless, due to considerable variability among the tissue and cell patterns in histological images, proposing an accurate image retrieval model is very challenging. This work introduces a novel attention-based adversarially regularized variational graph autoencoder model for breast histological image retrieval. Additionally, we incorporated cluster-guided contrastive learning as the graph feature extractor to boost the retrieval performance. We evaluated the proposed model's performance on two publicly available datasets of breast cancer histological images and achieved superior or very competitive retrieval performance, with average mAP scores of 96.5% for the BreakHis dataset and 94.7% for the BACH dataset, and mVP scores of 91.9% and 91.3%, respectively. Our proposed retrieval model has the potential to be used in clinical settings to enhance diagnostic performance and ultimately benefit patients.
Automatic Detection of Microaneurysms in OCT Images Using Bag of Features
May 10, 2022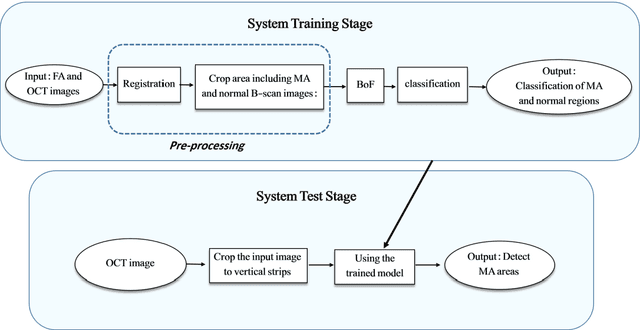
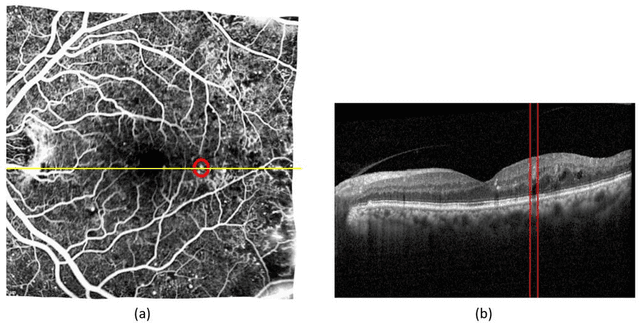
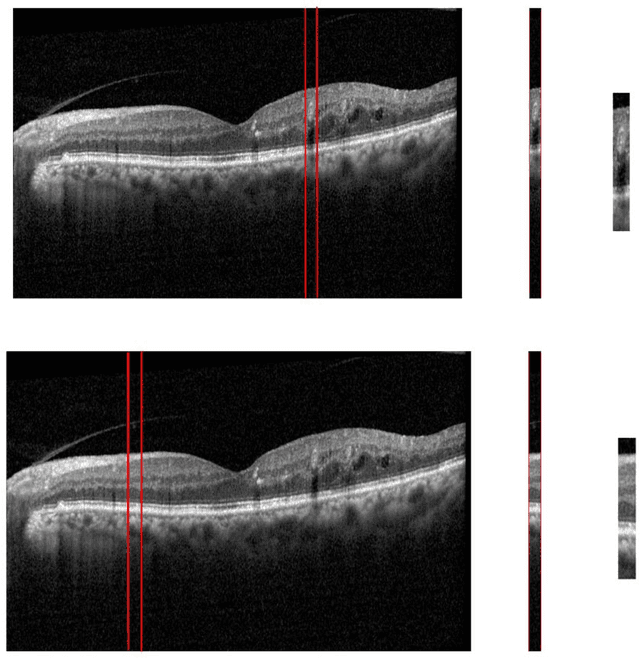
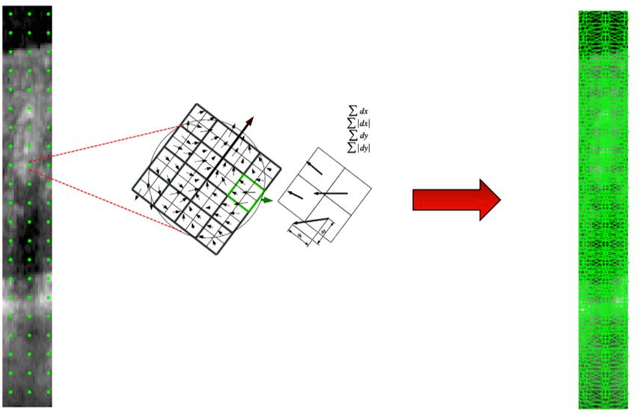
Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) caused by diabetes occurs as a result of changes in the retinal vessels and causes visual impairment. Microaneurysms (MAs) are the early clinical signs of DR, whose timely diagnosis can help detecting DR in the early stages of its development. It has been observed that MAs are more common in the inner retinal layers compared to the outer retinal layers in eyes suffering from DR. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a noninvasive imaging technique that provides a cross-sectional view of the retina and it has been used in recent years to diagnose many eye diseases. As a result, in this paper has attempted to identify areas with MA from normal areas of the retina using OCT images. This work is done using the dataset collected from FA and OCT images of 20 patients with DR. In this regard, firstly Fluorescein Angiography (FA) and OCT images were registered. Then the MA and normal areas were separated and the features of each of these areas were extracted using the Bag of Features (BOF) approach with Speeded-Up Robust Feature (SURF) descriptor. Finally, the classification process was performed using a multilayer perceptron network. For each of the criteria of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision, the obtained results were 96.33%, 97.33%, 95.4%, and 95.28%, respectively. Utilizing OCT images to detect MAsautomatically is a new idea and the results obtained as preliminary research in this field are promising .
Multiple-Vehicle Tracking in the Highway Using Appearance Model and Visual Object Tracking
Jun 12, 2020


Abstract:In recent decades, due to the groundbreaking improvements in machine vision, many daily tasks are performed by computers. One of these tasks is multiple-vehicle tracking, which is widely used in different areas such as video surveillance and traffic monitoring. This paper focuses on introducing an efficient novel approach with acceptable accuracy. This is achieved through an efficient appearance and motion model based on the features extracted from each object. For this purpose, two different approaches have been used to extract features, i.e. features extracted from a deep neural network, and traditional features. Then the results from these two approaches are compared with state-of-the-art trackers. The results are obtained by executing the methods on the UA-DETRACK benchmark. The first method led to 58.9% accuracy while the second method caused up to 15.9%. The proposed methods can still be improved by extracting more distinguishable features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge