Bharat Srikishan
Model-Agnostic Knowledge Guided Correction for Improved Neural Surrogate Rollout
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Modeling the evolution of physical systems is critical to many applications in science and engineering. As the evolution of these systems is governed by partial differential equations (PDEs), there are a number of computational simulations which resolve these systems with high accuracy. However, as these simulations incur high computational costs, they are infeasible to be employed for large-scale analysis. A popular alternative to simulators are neural network surrogates which are trained in a data-driven manner and are much more computationally efficient. However, these surrogate models suffer from high rollout error when used autoregressively, especially when confronted with training data paucity. Existing work proposes to improve surrogate rollout error by either including physical loss terms directly in the optimization of the model or incorporating computational simulators as `differentiable layers' in the neural network. Both of these approaches have their challenges, with physical loss functions suffering from slow convergence for stiff PDEs and simulator layers requiring gradients which are not always available, especially in legacy simulators. We propose the Hybrid PDE Predictor with Reinforcement Learning (HyPER) model: a model-agnostic, RL based, cost-aware model which combines a neural surrogate, RL decision model, and a physics simulator (with or without gradients) to reduce surrogate rollout error significantly. In addition to reducing in-distribution rollout error by **47%-78%**, HyPER learns an intelligent policy that is adaptable to changing physical conditions and resistant to noise corruption. Code available at https://github.com/scailab/HyPER.
Reinforcement Learning as a Parsimonious Alternative to Prediction Cascades: A Case Study on Image Segmentation
Feb 19, 2024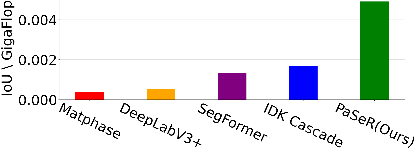

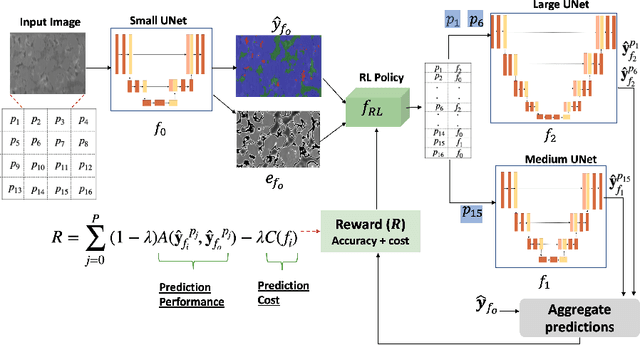

Abstract:Deep learning architectures have achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on computer vision tasks such as object detection and image segmentation. This may be attributed to the use of over-parameterized, monolithic deep learning architectures executed on large datasets. Although such architectures lead to increased accuracy, this is usually accompanied by a large increase in computation and memory requirements during inference. While this is a non-issue in traditional machine learning pipelines, the recent confluence of machine learning and fields like the Internet of Things has rendered such large architectures infeasible for execution in low-resource settings. In such settings, previous efforts have proposed decision cascades where inputs are passed through models of increasing complexity until desired performance is achieved. However, we argue that cascaded prediction leads to increased computational cost due to wasteful intermediate computations. To address this, we propose PaSeR (Parsimonious Segmentation with Reinforcement Learning) a non-cascading, cost-aware learning pipeline as an alternative to cascaded architectures. Through experimental evaluation on real-world and standard datasets, we demonstrate that PaSeR achieves better accuracy while minimizing computational cost relative to cascaded models. Further, we introduce a new metric IoU/GigaFlop to evaluate the balance between cost and performance. On the real-world task of battery material phase segmentation, PaSeR yields a minimum performance improvement of 174% on the IoU/GigaFlop metric with respect to baselines. We also demonstrate PaSeR's adaptability to complementary models trained on a noisy MNIST dataset, where it achieved a minimum performance improvement on IoU/GigaFlop of 13.4% over SOTA models. Code and data are available at https://github.com/scailab/paser .
Causal Discovery with Stage Variables for Health Time Series
May 05, 2023Abstract:Using observational data to learn causal relationships is essential when randomized experiments are not possible, such as in healthcare. Discovering causal relationships in time-series health data is even more challenging when relationships change over the course of a disease, such as medications that are most effective early on or for individuals with severe disease. Stage variables such as weeks of pregnancy, disease stages, or biomarkers like HbA1c, can influence what causal relationships are true for a patient. However, causal inference within each stage is often not possible due to limited amounts of data, and combining all data risks incorrect or missed inferences. To address this, we propose Causal Discovery with Stage Variables (CDSV), which uses stage variables to reweight data from multiple time-series while accounting for different causal relationships in each stage. In simulated data, CDSV discovers more causes with fewer false discoveries compared to baselines, in eICU it has a lower FDR than baselines, and in MIMIC-III it discovers more clinically relevant causes of high blood pressure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge