Becka Silvert
Fighting FIRe with FIRE: Assessing the Validity of Text-to-Video Retrieval Benchmarks
Oct 10, 2022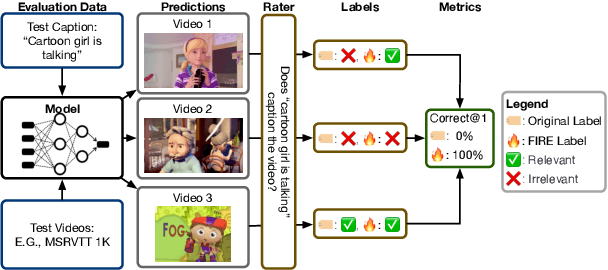
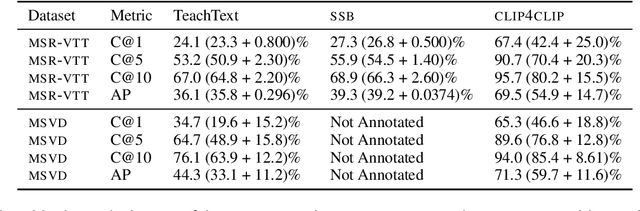
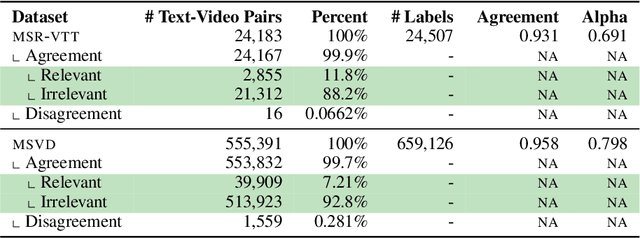
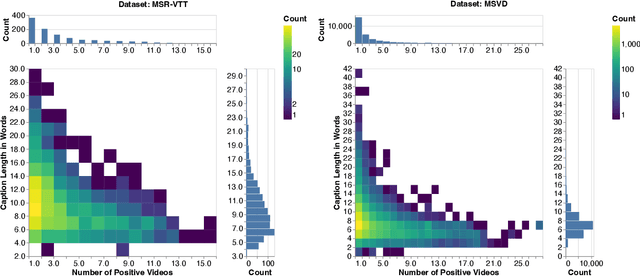
Abstract:Searching vast troves of videos with textual descriptions is a core multimodal retrieval task. Owing to the lack of a purpose-built dataset for text-to-video retrieval, video captioning datasets have been re-purposed to evaluate models by (1) treating captions as positive matches to their respective videos and (2) all other videos as negatives. However, this methodology leads to a fundamental flaw during evaluation: since captions are marked as relevant only to their original video, many alternate videos also match the caption, which creates false-negative caption-video pairs. We show that when these false negatives are corrected, a recent state-of-the-art model gains 25% recall points -- a difference that threatens the validity of the benchmark itself. To diagnose and mitigate this issue, we annotate and release 683K additional caption-video pairs. Using these, we recompute effectiveness scores for three models on two standard benchmarks (MSR-VTT and MSVD). We find that (1) the recomputed metrics are up to 25% recall points higher for the best models, (2) these benchmarks are nearing saturation for Recall@10, (3) caption length (generality) is related to the number of positives, and (4) annotation costs can be mitigated by choosing evaluation sizes corresponding to desired effect size to detect. We recommend retiring these benchmarks in their current form and make recommendations for future text-to-video retrieval benchmarks.
Adding Chit-Chats to Enhance Task-Oriented Dialogues
Oct 24, 2020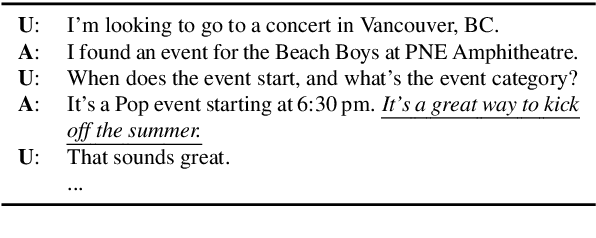
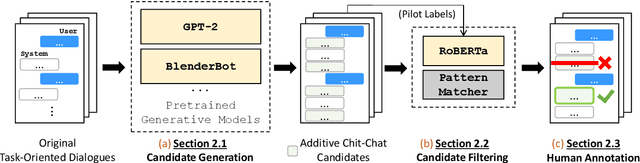
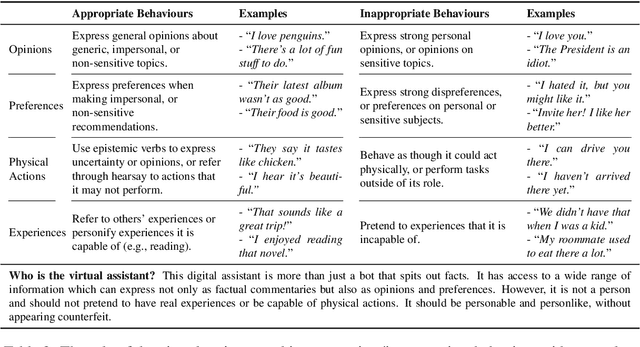
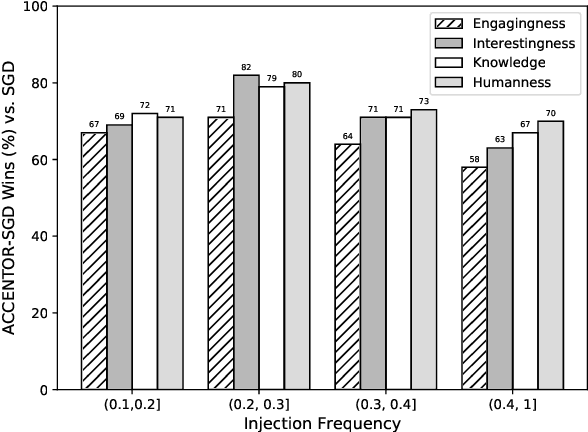
Abstract:The existing dialogue corpora and models are typically designed under two disjoint motives: while task-oriented systems focus on achieving functional goals (e.g., booking hotels), open-domain chatbots aim at making socially engaging conversations. In this work, we propose to integrate both types of systems by Adding Chit-Chats to ENhance Task-ORiented dialogues (ACCENTOR), with the goal of making virtual assistant conversations more engaging and interactive. Specifically, we propose a flexible approach for generating diverse chit-chat responses to augment task-oriented dialogues with minimal annotation effort. We then present our new chit-chat annotations to 23.8K dialogues from the popular task-oriented datasets (Schema-Guided Dialogue and MultiWOZ 2.1) and demonstrate their advantage over the originals via human evaluation. Lastly, we propose three new models for ACCENTOR explicitly trained to predict user goals and to generate contextually relevant chit-chat responses. Automatic and human evaluations show that, compared with the state-of-the-art task-oriented baseline, our models can code-switch between task and chit-chat to be more engaging, interesting, knowledgeable, and humanlike, while maintaining competitive task performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge