Bangya Liu
MV-S2V: Multi-View Subject-Consistent Video Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Existing Subject-to-Video Generation (S2V) methods have achieved high-fidelity and subject-consistent video generation, yet remain constrained to single-view subject references. This limitation renders the S2V task reducible to an S2I + I2V pipeline, failing to exploit the full potential of video subject control. In this work, we propose and address the challenging Multi-View S2V (MV-S2V) task, which synthesizes videos from multiple reference views to enforce 3D-level subject consistency. Regarding the scarcity of training data, we first develop a synthetic data curation pipeline to generate highly customized synthetic data, complemented by a small-scale real-world captured dataset to boost the training of MV-S2V. Another key issue lies in the potential confusion between cross-subject and cross-view references in conditional generation. To overcome this, we further introduce Temporally Shifted RoPE (TS-RoPE) to distinguish between different subjects and distinct views of the same subject in reference conditioning. Our framework achieves superior 3D subject consistency w.r.t. multi-view reference images and high-quality visual outputs, establishing a new meaningful direction for subject-driven video generation. Our project page is available at: https://szy-young.github.io/mv-s2v
ByteLoom: Weaving Geometry-Consistent Human-Object Interactions through Progressive Curriculum Learning
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Human-object interaction (HOI) video generation has garnered increasing attention due to its promising applications in digital humans, e-commerce, advertising, and robotics imitation learning. However, existing methods face two critical limitations: (1) a lack of effective mechanisms to inject multi-view information of the object into the model, leading to poor cross-view consistency, and (2) heavy reliance on fine-grained hand mesh annotations for modeling interaction occlusions. To address these challenges, we introduce ByteLoom, a Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based framework that generates realistic HOI videos with geometrically consistent object illustration, using simplified human conditioning and 3D object inputs. We first propose an RCM-cache mechanism that leverages Relative Coordinate Maps (RCM) as a universal representation to maintain object's geometry consistency and precisely control 6-DoF object transformations in the meantime. To compensate HOI dataset scarcity and leverage existing datasets, we further design a training curriculum that enhances model capabilities in a progressive style and relaxes the demand of hand mesh. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method faithfully preserves human identity and the object's multi-view geometry, while maintaining smooth motion and object manipulation.
CETCAM: Camera-Controllable Video Generation via Consistent and Extensible Tokenization
Dec 22, 2025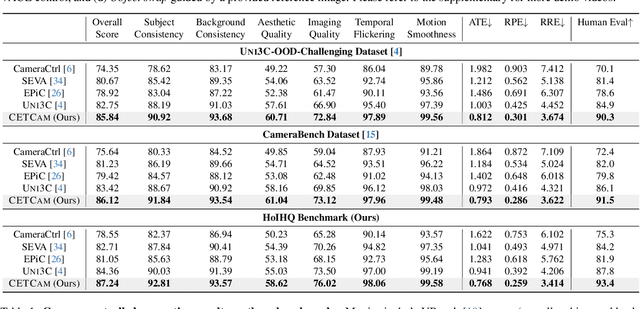
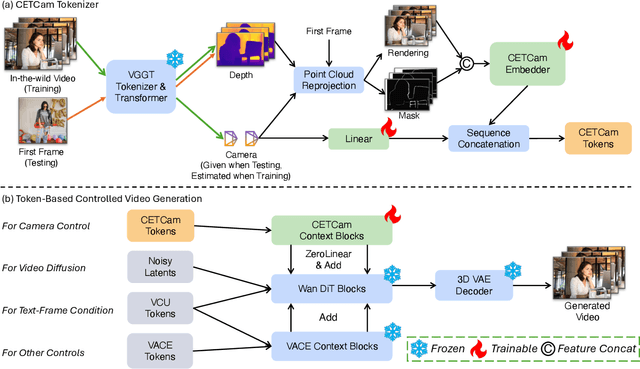
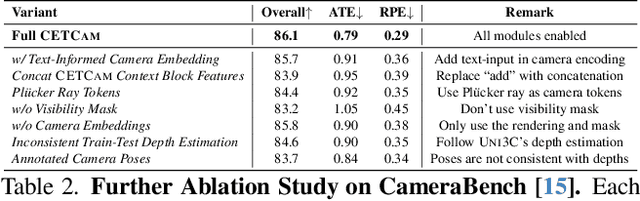

Abstract:Achieving precise camera control in video generation remains challenging, as existing methods often rely on camera pose annotations that are difficult to scale to large and dynamic datasets and are frequently inconsistent with depth estimation, leading to train-test discrepancies. We introduce CETCAM, a camera-controllable video generation framework that eliminates the need for camera annotations through a consistent and extensible tokenization scheme. CETCAM leverages recent advances in geometry foundation models, such as VGGT, to estimate depth and camera parameters and converts them into unified, geometry-aware tokens. These tokens are seamlessly integrated into a pretrained video diffusion backbone via lightweight context blocks. Trained in two progressive stages, CETCAM first learns robust camera controllability from diverse raw video data and then refines fine-grained visual quality using curated high-fidelity datasets. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art geometric consistency, temporal stability, and visual realism. Moreover, CETCAM exhibits strong adaptability to additional control modalities, including inpainting and layout control, highlighting its flexibility beyond camera control. The project page is available at https://sjtuytc.github.io/CETCam_project_page.github.io/.
Privacy-Aware Sharing of Raw Spatial Sensor Data for Cooperative Perception
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Cooperative perception between vehicles is poised to offer robust and reliable scene understanding. Recently, we are witnessing experimental systems research building testbeds that share raw spatial sensor data for cooperative perception. While there has been a marked improvement in accuracies and is the natural way forward, we take a moment to consider the problems with such an approach for eventual adoption by automakers. In this paper, we first argue that new forms of privacy concerns arise and discourage stakeholders to share raw sensor data. Next, we present SHARP, a research framework to minimize privacy leakage and drive stakeholders towards the ambitious goal of raw data based cooperative perception. Finally, we discuss open questions for networked systems, mobile computing, perception researchers, industry and government in realizing our proposed framework.
Can Test-Time Scaling Improve World Foundation Model?
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:World foundation models, which simulate the physical world by predicting future states from current observations and inputs, have become central to many applications in physical intelligence, including autonomous driving and robotics. However, these models require substantial computational resources for pretraining and are further constrained by available data during post-training. As such, scaling computation at test time emerges as both a critical and practical alternative to traditional model enlargement or re-training. In this work, we introduce SWIFT, a test-time scaling framework tailored for WFMs. SWIFT integrates our extensible WFM evaluation toolkit with process-level inference strategies, including fast tokenization, probability-based Top-K pruning, and efficient beam search. Empirical results on the COSMOS model demonstrate that test-time scaling exists even in a compute-optimal way. Our findings reveal that test-time scaling laws hold for WFMs and that SWIFT provides a scalable and effective pathway for improving WFM inference without retraining or increasing model size. The code is available at https://github.com/Mia-Cong/SWIFT.git.
SwinGS: Sliding Window Gaussian Splatting for Volumetric Video Streaming with Arbitrary Length
Sep 12, 2024

Abstract:Recent advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have garnered significant attention in computer vision and computer graphics due to its high rendering speed and remarkable quality. While extant research has endeavored to extend the application of 3DGS from static to dynamic scenes, such efforts have been consistently impeded by excessive model sizes, constraints on video duration, and content deviation. These limitations significantly compromise the streamability of dynamic 3D Gaussian models, thereby restricting their utility in downstream applications, including volumetric video, autonomous vehicle, and immersive technologies such as virtual, augmented, and mixed reality. This paper introduces SwinGS, a novel framework for training, delivering, and rendering volumetric video in a real-time streaming fashion. To address the aforementioned challenges and enhance streamability, SwinGS integrates spacetime Gaussian with Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) to adapt the model to fit various 3D scenes across frames, in the meantime employing a sliding window captures Gaussian snapshots for each frame in an accumulative way. We implement a prototype of SwinGS and demonstrate its streamability across various datasets and scenes. Additionally, we develop an interactive WebGL viewer enabling real-time volumetric video playback on most devices with modern browsers, including smartphones and tablets. Experimental results show that SwinGS reduces transmission costs by 83.6% compared to previous work with ignorable compromise in PSNR. Moreover, SwinGS easily scales to long video sequences without compromising quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge