Bangchao Deng
CasFT: Future Trend Modeling for Information Popularity Prediction with Dynamic Cues-Driven Diffusion Models
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:The rapid spread of diverse information on online social platforms has prompted both academia and industry to realize the importance of predicting content popularity, which could benefit a wide range of applications, such as recommendation systems and strategic decision-making. Recent works mainly focused on extracting spatiotemporal patterns inherent in the information diffusion process within a given observation period so as to predict its popularity over a future period of time. However, these works often overlook the future popularity trend, as future popularity could either increase exponentially or stagnate, introducing uncertainties to the prediction performance. Additionally, how to transfer the preceding-term dynamics learned from the observed diffusion process into future-term trends remains an unexplored challenge. Against this background, we propose CasFT, which leverages observed information Cascades and dynamic cues extracted via neural ODEs as conditions to guide the generation of Future popularity-increasing Trends through a diffusion model. These generated trends are then combined with the spatiotemporal patterns in the observed information cascade to make the final popularity prediction. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that CasFT significantly improves the prediction accuracy, compared to state-of-the-art approaches, yielding 2.2%-19.3% improvement across different datasets.
On Your Mark, Get Set, Predict! Modeling Continuous-Time Dynamics of Cascades for Information Popularity Prediction
Sep 25, 2024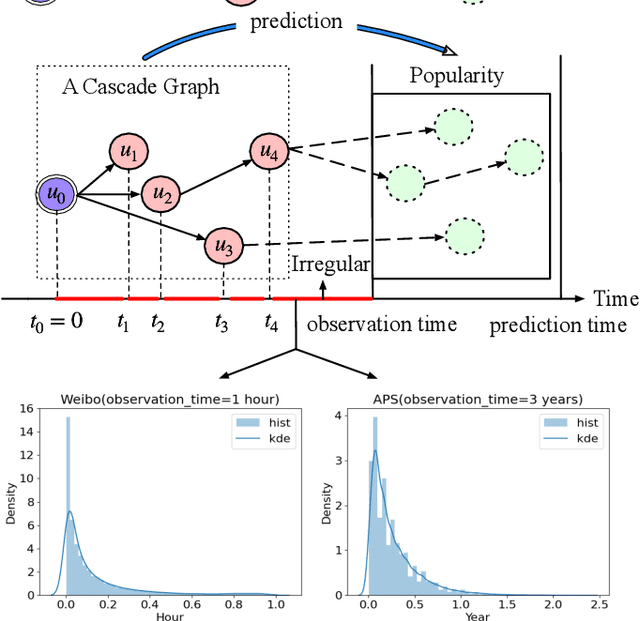
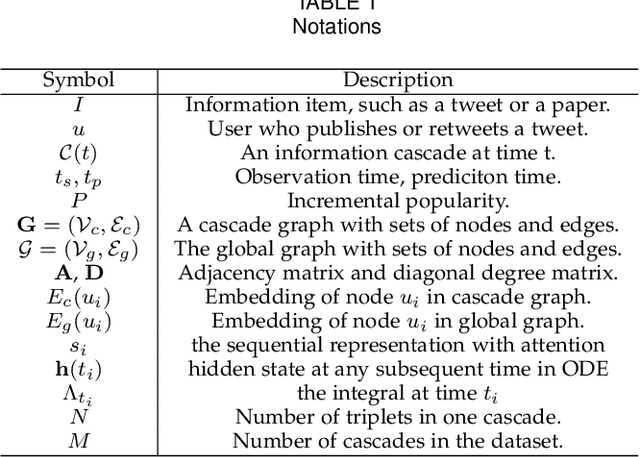
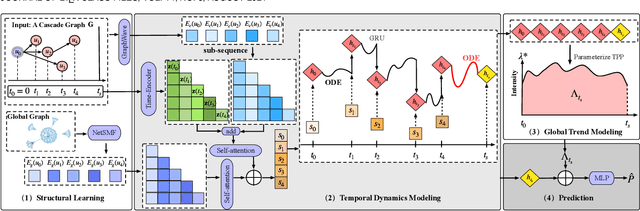

Abstract:Information popularity prediction is important yet challenging in various domains, including viral marketing and news recommendations. The key to accurately predicting information popularity lies in subtly modeling the underlying temporal information diffusion process behind observed events of an information cascade, such as the retweets of a tweet. To this end, most existing methods either adopt recurrent networks to capture the temporal dynamics from the first to the last observed event or develop a statistical model based on self-exciting point processes to make predictions. However, information diffusion is intrinsically a complex continuous-time process with irregularly observed discrete events, which is oversimplified using recurrent networks as they fail to capture the irregular time intervals between events, or using self-exciting point processes as they lack flexibility to capture the complex diffusion process. Against this background, we propose ConCat, modeling the Continuous-time dynamics of Cascades for information popularity prediction. On the one hand, it leverages neural Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) to model irregular events of a cascade in continuous time based on the cascade graph and sequential event information. On the other hand, it considers cascade events as neural temporal point processes (TPPs) parameterized by a conditional intensity function which can also benefit the popularity prediction task. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate ConCat on three real-world datasets. Results show that ConCat achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines, yielding a 2.3%-33.2% improvement over the best-performing baselines across the three datasets.
REPLAY: Modeling Time-Varying Temporal Regularities of Human Mobility for Location Prediction over Sparse Trajectories
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Location prediction forecasts a user's location based on historical user mobility traces. To tackle the intrinsic sparsity issue of real-world user mobility traces, spatiotemporal contexts have been shown as significantly useful. Existing solutions mostly incorporate spatiotemporal distances between locations in mobility traces, either by feeding them as additional inputs to Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) or by using them to search for informative past hidden states for prediction. However, such distance-based methods fail to capture the time-varying temporal regularities of human mobility, where human mobility is often more regular in the morning than in other periods, for example; this suggests the usefulness of the actual timestamps besides the temporal distances. Against this background, we propose REPLAY, a general RNN architecture learning to capture the time-varying temporal regularities for location prediction. Specifically, REPLAY not only resorts to the spatiotemporal distances in sparse trajectories to search for the informative past hidden states, but also accommodates the time-varying temporal regularities by incorporating smoothed timestamp embeddings using Gaussian weighted averaging with timestamp-specific learnable bandwidths, which can flexibly adapt to the temporal regularities of different strengths across different timestamps. Our extensive evaluation compares REPLAY against a sizable collection of state-of-the-art techniques on two real-world datasets. Results show that REPLAY consistently and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.7\%-10.9\% in the location prediction task, and the bandwidths reveal interesting patterns of the time-varying temporal regularities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge