Aysegul Dundar
RoPECraft: Training-Free Motion Transfer with Trajectory-Guided RoPE Optimization on Diffusion Transformers
May 19, 2025Abstract:We propose RoPECraft, a training-free video motion transfer method for diffusion transformers that operates solely by modifying their rotary positional embeddings (RoPE). We first extract dense optical flow from a reference video, and utilize the resulting motion offsets to warp the complex-exponential tensors of RoPE, effectively encoding motion into the generation process. These embeddings are then further optimized during denoising time steps via trajectory alignment between the predicted and target velocities using a flow-matching objective. To keep the output faithful to the text prompt and prevent duplicate generations, we incorporate a regularization term based on the phase components of the reference video's Fourier transform, projecting the phase angles onto a smooth manifold to suppress high-frequency artifacts. Experiments on benchmarks reveal that RoPECraft outperforms all recently published methods, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
3D Stylization via Large Reconstruction Model
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:With the growing success of text or image guided 3D generators, users demand more control over the generation process, appearance stylization being one of them. Given a reference image, this requires adapting the appearance of a generated 3D asset to reflect the visual style of the reference while maintaining visual consistency from multiple viewpoints. To tackle this problem, we draw inspiration from the success of 2D stylization methods that leverage the attention mechanisms in large image generation models to capture and transfer visual style. In particular, we probe if large reconstruction models, commonly used in the context of 3D generation, has a similar capability. We discover that the certain attention blocks in these models capture the appearance specific features. By injecting features from a visual style image to such blocks, we develop a simple yet effective 3D appearance stylization method. Our method does not require training or test time optimization. Through both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, we demonstrate that our approach achieves superior results in terms of 3D appearance stylization, significantly improving efficiency while maintaining high-quality visual outcomes.
MD-ProjTex: Texturing 3D Shapes with Multi-Diffusion Projection
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:We introduce MD-ProjTex, a method for fast and consistent text-guided texture generation for 3D shapes using pretrained text-to-image diffusion models. At the core of our approach is a multi-view consistency mechanism in UV space, which ensures coherent textures across different viewpoints. Specifically, MD-ProjTex fuses noise predictions from multiple views at each diffusion step and jointly updates the per-view denoising directions to maintain 3D consistency. In contrast to existing state-of-the-art methods that rely on optimization or sequential view synthesis, MD-ProjTex is computationally more efficient and achieves better quantitative and qualitative results.
Identity Preserving 3D Head Stylization with Multiview Score Distillation
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:3D head stylization transforms realistic facial features into artistic representations, enhancing user engagement across gaming and virtual reality applications. While 3D-aware generators have made significant advancements, many 3D stylization methods primarily provide near-frontal views and struggle to preserve the unique identities of original subjects, often resulting in outputs that lack diversity and individuality. This paper addresses these challenges by leveraging the PanoHead model, synthesizing images from a comprehensive 360-degree perspective. We propose a novel framework that employs negative log-likelihood distillation (LD) to enhance identity preservation and improve stylization quality. By integrating multi-view grid score and mirror gradients within the 3D GAN architecture and introducing a score rank weighing technique, our approach achieves substantial qualitative and quantitative improvements. Our findings not only advance the state of 3D head stylization but also provide valuable insights into effective distillation processes between diffusion models and GANs, focusing on the critical issue of identity preservation. Please visit the https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization for more visuals.
Dual Encoder GAN Inversion for High-Fidelity 3D Head Reconstruction from Single Images
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:3D GAN inversion aims to project a single image into the latent space of a 3D Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), thereby achieving 3D geometry reconstruction. While there exist encoders that achieve good results in 3D GAN inversion, they are predominantly built on EG3D, which specializes in synthesizing near-frontal views and is limiting in synthesizing comprehensive 3D scenes from diverse viewpoints. In contrast to existing approaches, we propose a novel framework built on PanoHead, which excels in synthesizing images from a 360-degree perspective. To achieve realistic 3D modeling of the input image, we introduce a dual encoder system tailored for high-fidelity reconstruction and realistic generation from different viewpoints. Accompanying this, we propose a stitching framework on the triplane domain to get the best predictions from both. To achieve seamless stitching, both encoders must output consistent results despite being specialized for different tasks. For this reason, we carefully train these encoders using specialized losses, including an adversarial loss based on our novel occlusion-aware triplane discriminator. Experiments reveal that our approach surpasses the existing encoder training methods qualitatively and quantitatively. Please visit the project page: https://berkegokmen1.github.io/dual-enc-3d-gan-inv.
CLIPAway: Harmonizing Focused Embeddings for Removing Objects via Diffusion Models
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Advanced image editing techniques, particularly inpainting, are essential for seamlessly removing unwanted elements while preserving visual integrity. Traditional GAN-based methods have achieved notable success, but recent advancements in diffusion models have produced superior results due to their training on large-scale datasets, enabling the generation of remarkably realistic inpainted images. Despite their strengths, diffusion models often struggle with object removal tasks without explicit guidance, leading to unintended hallucinations of the removed object. To address this issue, we introduce CLIPAway, a novel approach leveraging CLIP embeddings to focus on background regions while excluding foreground elements. CLIPAway enhances inpainting accuracy and quality by identifying embeddings that prioritize the background, thus achieving seamless object removal. Unlike other methods that rely on specialized training datasets or costly manual annotations, CLIPAway provides a flexible, plug-and-play solution compatible with various diffusion-based inpainting techniques.
Reference-Based 3D-Aware Image Editing with Triplane
Apr 04, 2024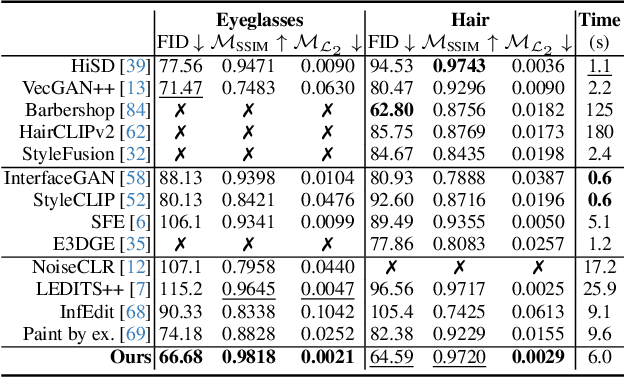

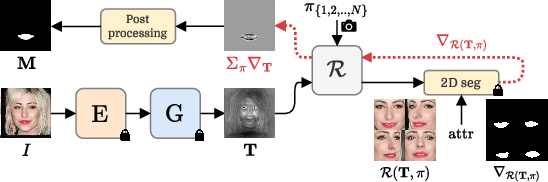
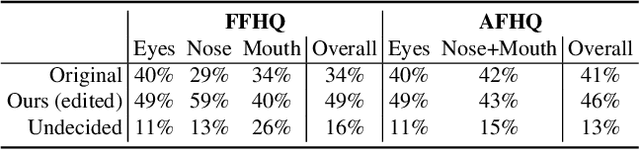
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have emerged as powerful tools not only for high-quality image generation but also for real image editing through manipulation of their interpretable latent spaces. Recent advancements in GANs include the development of 3D-aware models such as EG3D, characterized by efficient triplane-based architectures enabling the reconstruction of 3D geometry from single images. However, scant attention has been devoted to providing an integrated framework for high-quality reference-based 3D-aware image editing within this domain. This study addresses this gap by exploring and demonstrating the effectiveness of EG3D's triplane space for achieving advanced reference-based edits, presenting a unique perspective on 3D-aware image editing through our novel pipeline. Our approach integrates the encoding of triplane features, spatial disentanglement and automatic localization of features in the triplane domain, and fusion learning for desired image editing. Moreover, our framework demonstrates versatility across domains, extending its effectiveness to animal face edits and partial stylization of cartoon portraits. The method shows significant improvements over relevant 3D-aware latent editing and 2D reference-based editing methods, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Project page: https://three-bee.github.io/triplane_edit
Warping the Residuals for Image Editing with StyleGAN
Dec 18, 2023
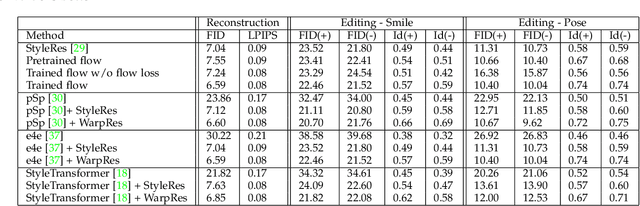
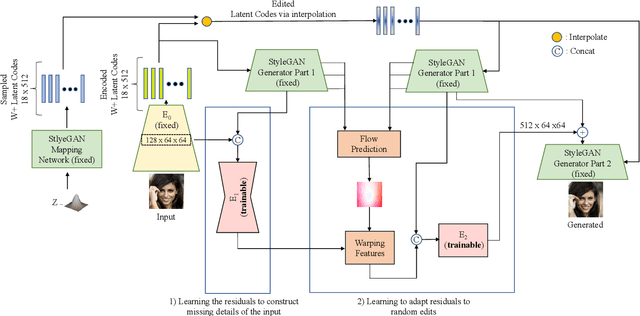
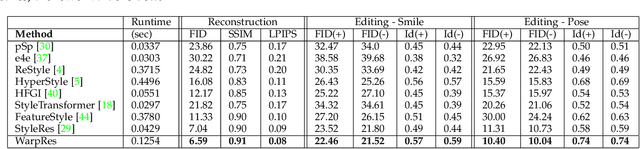
Abstract:StyleGAN models show editing capabilities via their semantically interpretable latent organizations which require successful GAN inversion methods to edit real images. Many works have been proposed for inverting images into StyleGAN's latent space. However, their results either suffer from low fidelity to the input image or poor editing qualities, especially for edits that require large transformations. That is because low-rate latent spaces lose many image details due to the information bottleneck even though it provides an editable space. On the other hand, higher-rate latent spaces can pass all the image details to StyleGAN for perfect reconstruction of images but suffer from low editing qualities. In this work, we present a novel image inversion architecture that extracts high-rate latent features and includes a flow estimation module to warp these features to adapt them to edits. The flows are estimated from StyleGAN features of edited and unedited latent codes. By estimating the high-rate features and warping them for edits, we achieve both high-fidelity to the input image and high-quality edits. We run extensive experiments and compare our method with state-of-the-art inversion methods. Qualitative metrics and visual comparisons show significant improvements.
Diverse Semantic Image Editing with Style Codes
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:Semantic image editing requires inpainting pixels following a semantic map. It is a challenging task since this inpainting requires both harmony with the context and strict compliance with the semantic maps. The majority of the previous methods proposed for this task try to encode the whole information from erased images. However, when an object is added to a scene such as a car, its style cannot be encoded from the context alone. On the other hand, the models that can output diverse generations struggle to output images that have seamless boundaries between the generated and unerased parts. Additionally, previous methods do not have a mechanism to encode the styles of visible and partially visible objects differently for better performance. In this work, we propose a framework that can encode visible and partially visible objects with a novel mechanism to achieve consistency in the style encoding and final generations. We extensively compare with previous conditional image generation and semantic image editing algorithms. Our extensive experiments show that our method significantly improves over the state-of-the-art. Our method not only achieves better quantitative results but also provides diverse results. Please refer to the project web page for the released code and demo: https://github.com/hakansivuk/DivSem.
Diverse Inpainting and Editing with GAN Inversion
Jul 27, 2023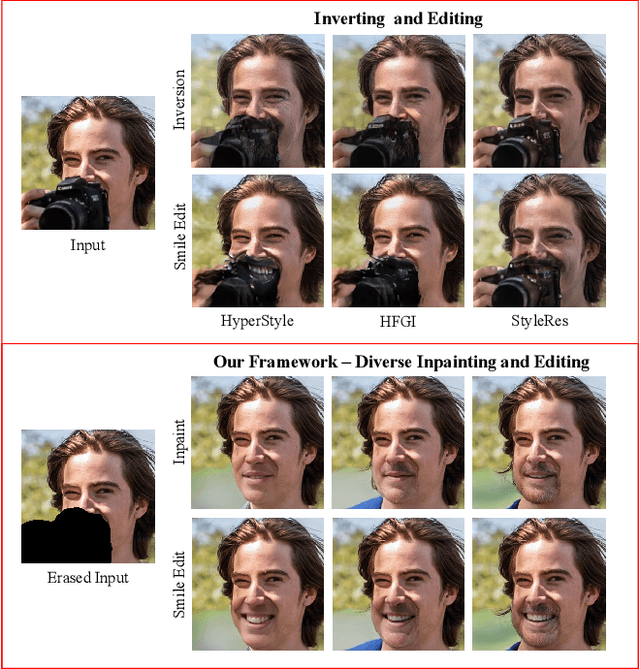
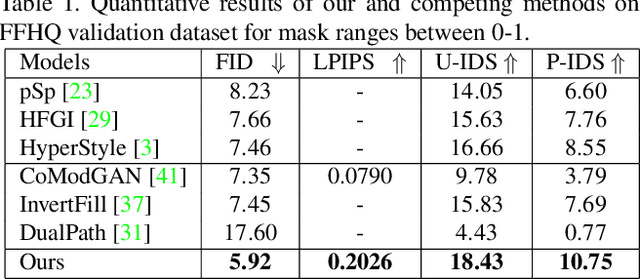
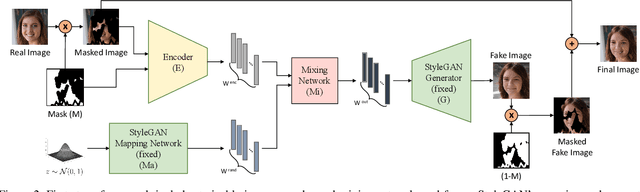
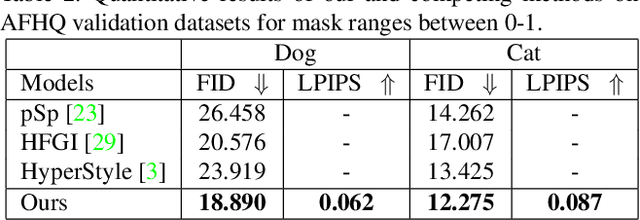
Abstract:Recent inversion methods have shown that real images can be inverted into StyleGAN's latent space and numerous edits can be achieved on those images thanks to the semantically rich feature representations of well-trained GAN models. However, extensive research has also shown that image inversion is challenging due to the trade-off between high-fidelity reconstruction and editability. In this paper, we tackle an even more difficult task, inverting erased images into GAN's latent space for realistic inpaintings and editings. Furthermore, by augmenting inverted latent codes with different latent samples, we achieve diverse inpaintings. Specifically, we propose to learn an encoder and mixing network to combine encoded features from erased images with StyleGAN's mapped features from random samples. To encourage the mixing network to utilize both inputs, we train the networks with generated data via a novel set-up. We also utilize higher-rate features to prevent color inconsistencies between the inpainted and unerased parts. We run extensive experiments and compare our method with state-of-the-art inversion and inpainting methods. Qualitative metrics and visual comparisons show significant improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge