Aykut Ozgun Onol
Plan-Guided Reinforcement Learning for Whole-Body Manipulation
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Synthesizing complex whole-body manipulation behaviors has fundamental challenges due to the rapidly growing combinatorics inherent to contact interaction planning. While model-based methods have shown promising results in solving long-horizon manipulation tasks, they often work under strict assumptions, such as known model parameters, oracular observation of the environment state, and simplified dynamics, resulting in plans that cannot easily transfer to hardware. Learning-based approaches, such as imitation learning (IL) and reinforcement learning (RL), have been shown to be robust when operating over in-distribution states; however, they need heavy human supervision. Specifically, model-free RL requires a tedious reward-shaping process. IL methods, on the other hand, rely on human demonstrations that involve advanced teleoperation methods. In this work, we propose a plan-guided reinforcement learning (PGRL) framework to combine the advantages of model-based planning and reinforcement learning. Our method requires minimal human supervision because it relies on plans generated by model-based planners to guide the exploration in RL. In exchange, RL derives a more robust policy thanks to domain randomization. We test this approach on a whole-body manipulation task on Punyo, an upper-body humanoid robot with compliant, air-filled arm coverings, to pivot and lift a large box. Our preliminary results indicate that the proposed methodology is promising to address challenges that remain difficult for either model- or learning-based strategies alone.
Contact-Implicit Planning and Control for Non-Prehensile Manipulation Using State-Triggered Constraints
Oct 18, 2022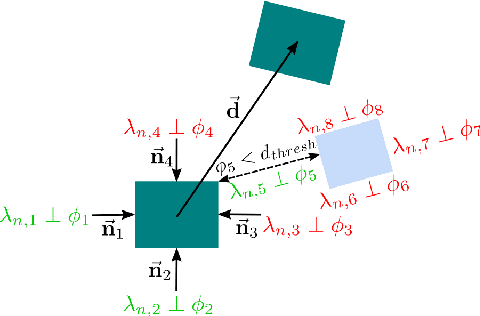

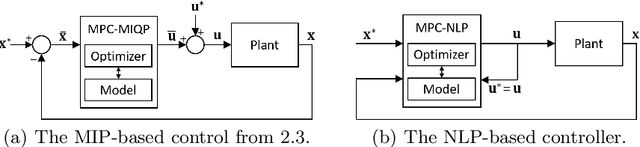
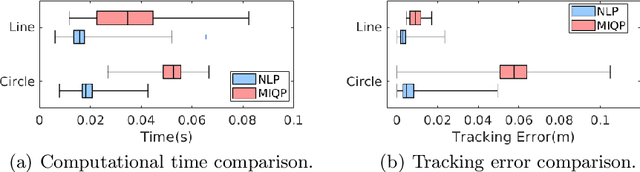
Abstract:We present a contact-implicit planning approach that can generate contact-interaction trajectories for non-prehensile manipulation problems without tuning or a tailored initial guess and with high success rates. This is achieved by leveraging the concept of state-triggered constraints (STCs) to capture the hybrid dynamics induced by discrete contact modes without explicitly reasoning about the combinatorics. STCs enable triggering arbitrary constraints by a strict inequality condition in a continuous way. We first use STCs to develop an automatic contact constraint activation method to minimize the effective constraint space based on the utility of contact candidates for a given task. Then, we introduce a re-formulation of the Coulomb friction model based on STCs that is more efficient for the discovery of tangential forces than the well-studied complementarity constraints-based approach. Last, we include the proposed friction model in the planning and control of quasi-static planar pushing. The performance of the STC-based contact activation and friction methods is evaluated by extensive simulation experiments in a dynamic pushing scenario. The results demonstrate that our methods outperform the baselines based on complementarity constraints with a significant decrease in the planning time and a higher success rate. We then compare the proposed quasi-static pushing controller against a mixed-integer programming-based approach in simulation and find that our method is computationally more efficient and provides a better tracking accuracy, with the added benefit of not requiring an initial control trajectory. Finally, we present hardware experiments demonstrating the usability of our framework in executing complex trajectories in real-time even with a low-accuracy tracking system.
Affordance-Based Mobile Robot Navigation Among Movable Obstacles
Feb 09, 2021



Abstract:Avoiding obstacles in the perceived world has been the classical approach to autonomous mobile robot navigation. However, this usually leads to unnatural and inefficient motions that significantly differ from the way humans move in tight and dynamic spaces, as we do not refrain interacting with the environment around us when necessary. Inspired by this observation, we propose a framework for autonomous robot navigation among movable obstacles (NAMO) that is based on the theory of affordances and contact-implicit motion planning. We consider a realistic scenario in which a mobile service robot negotiates unknown obstacles in the environment while navigating to a goal state. An affordance extraction procedure is performed for novel obstacles to detect their movability, and a contact-implicit trajectory optimization method is used to enable the robot to interact with movable obstacles to improve the task performance or to complete an otherwise infeasible task. We demonstrate the performance of the proposed framework by hardware experiments with Toyota's Human Support Robot.
Tuning-Free Contact-Implicit Trajectory Optimization
Jun 11, 2020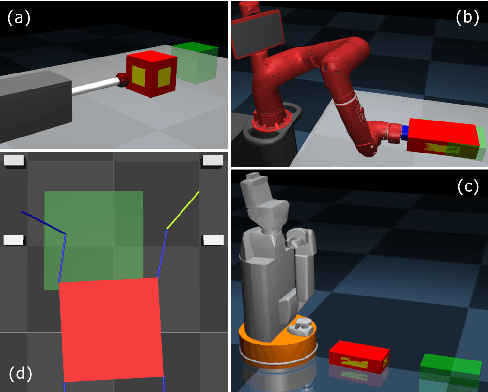



Abstract:We present a contact-implicit trajectory optimization framework that can plan contact-interaction trajectories for different robot architectures and tasks using a trivial initial guess and without requiring any parameter tuning. This is achieved by using a relaxed contact model along with an automatic penalty adjustment loop for suppressing the relaxation. Moreover, the structure of the problem enables us to exploit the contact information implied by the use of relaxation in the previous iteration, such that the solution is explicitly improved with little computational overhead. We test the proposed approach in simulation experiments for non-prehensile manipulation using a 7-DOF arm and a mobile robot and for planar locomotion using a humanoid-like robot in zero gravity. The results demonstrate that our method provides an out-of-the-box solution with good performance for a wide range of applications.
Contact-Implicit Trajectory Optimization Based on a Variable Smooth Contact Model and Successive Convexification
Mar 04, 2019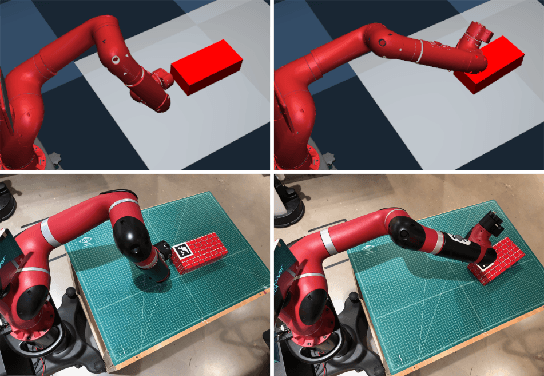


Abstract:In this paper, we propose a contact-implicit trajectory optimization (CITO) method based on a variable smooth contact model (VSCM) and successive convexification (SCvx). The VSCM facilitates the convergence of gradient-based optimization without compromising physical fidelity. On the other hand, the proposed SCvx-based approach combines the advantages of direct and shooting methods for CITO. For evaluations, we consider non-prehensile manipulation tasks. The proposed method is compared to a version based on iterative linear quadratic regulator (iLQR) on a planar example. The results demonstrate that both methods can find physically-consistent motions that complete the tasks without a meaningful initial guess owing to the VSCM. The proposed SCvx-based method outperforms the iLQR-based method in terms of convergence, computation time, and the quality of motions found. Finally, the proposed SCvx-based method is tested on a standard robot platform and shown to perform efficiently for a real-world application.
A Comparative Analysis of Contact Models in Trajectory Optimization for Manipulation
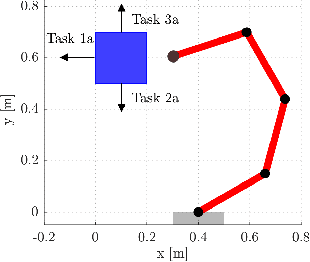
Jul 30, 2018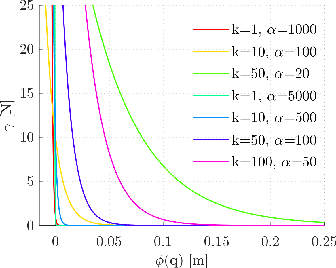
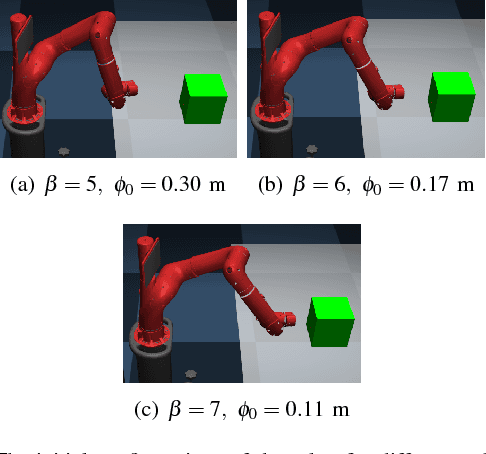
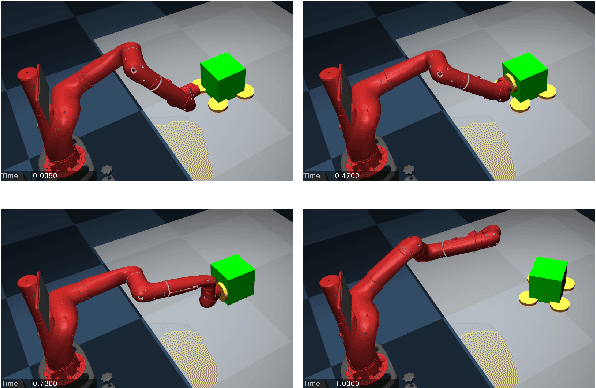
Abstract:In this paper, we analyze the effects of contact models on contact-implicit trajectory optimization for manipulation. We consider three different approaches: (1) a contact model that is based on complementarity constraints, (2) a smooth contact model, and our proposed method (3) a variable smooth contact model. We compare these models in simulation in terms of physical accuracy, quality of motions, and computation time. In each case, the optimization process is initialized by setting all torque variables to zero, namely, without a meaningful initial guess. For simulations, we consider a pushing task with varying complexity for a 7 degrees-of-freedom robot arm. Our results demonstrate that the optimization based on the proposed variable smooth contact model provides a good trade-off between the physical fidelity and quality of motions at the cost of increased computation time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge