Ayisha Al Busaidi
A self-supervised text-vision framework for automated brain abnormality detection
May 05, 2024



Abstract:Artificial neural networks trained on large, expert-labelled datasets are considered state-of-the-art for a range of medical image recognition tasks. However, categorically labelled datasets are time-consuming to generate and constrain classification to a pre-defined, fixed set of classes. For neuroradiological applications in particular, this represents a barrier to clinical adoption. To address these challenges, we present a self-supervised text-vision framework that learns to detect clinically relevant abnormalities in brain MRI scans by directly leveraging the rich information contained in accompanying free-text neuroradiology reports. Our training approach consisted of two-steps. First, a dedicated neuroradiological language model - NeuroBERT - was trained to generate fixed-dimensional vector representations of neuroradiology reports (N = 50,523) via domain-specific self-supervised learning tasks. Next, convolutional neural networks (one per MRI sequence) learnt to map individual brain scans to their corresponding text vector representations by optimising a mean square error loss. Once trained, our text-vision framework can be used to detect abnormalities in unreported brain MRI examinations by scoring scans against suitable query sentences (e.g., 'there is an acute stroke', 'there is hydrocephalus' etc.), enabling a range of classification-based applications including automated triage. Potentially, our framework could also serve as a clinical decision support tool, not only by suggesting findings to radiologists and detecting errors in provisional reports, but also by retrieving and displaying examples of pathologies from historical examinations that could be relevant to the current case based on textual descriptors.
Automated triaging of head MRI examinations using convolutional neural networks
Jun 15, 2021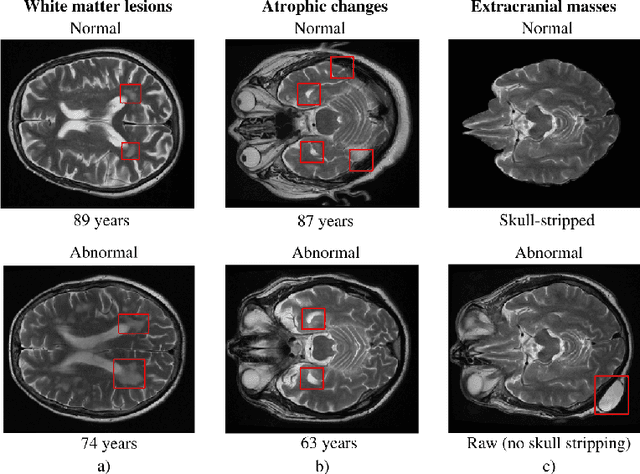
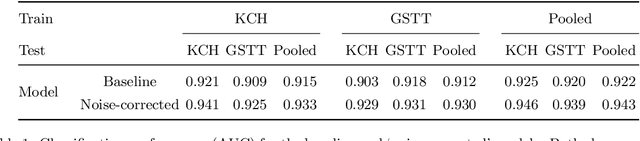
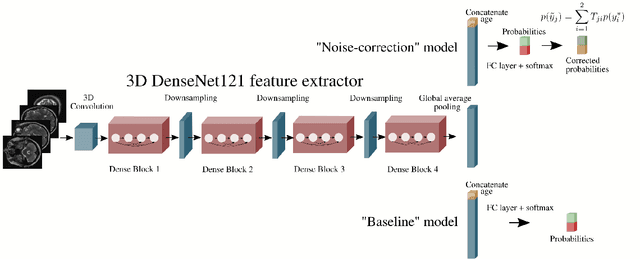
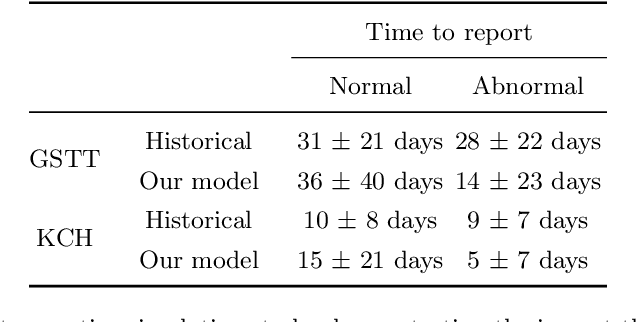
Abstract:The growing demand for head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations, along with a global shortage of radiologists, has led to an increase in the time taken to report head MRI scans around the world. For many neurological conditions, this delay can result in increased morbidity and mortality. An automated triaging tool could reduce reporting times for abnormal examinations by identifying abnormalities at the time of imaging and prioritizing the reporting of these scans. In this work, we present a convolutional neural network for detecting clinically-relevant abnormalities in $\text{T}_2$-weighted head MRI scans. Using a validated neuroradiology report classifier, we generated a labelled dataset of 43,754 scans from two large UK hospitals for model training, and demonstrate accurate classification (area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) = 0.943) on a test set of 800 scans labelled by a team of neuroradiologists. Importantly, when trained on scans from only a single hospital the model generalized to scans from the other hospital ($\Delta$AUC $\leq$ 0.02). A simulation study demonstrated that our model would reduce the mean reporting time for abnormal examinations from 28 days to 14 days and from 9 days to 5 days at the two hospitals, demonstrating feasibility for use in a clinical triage environment.
Machine Learning and Glioblastoma: Treatment Response Monitoring Biomarkers in 2021
Apr 15, 2021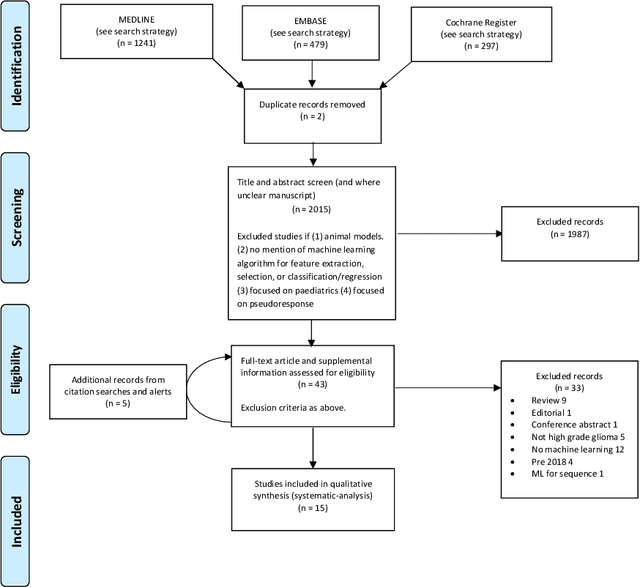
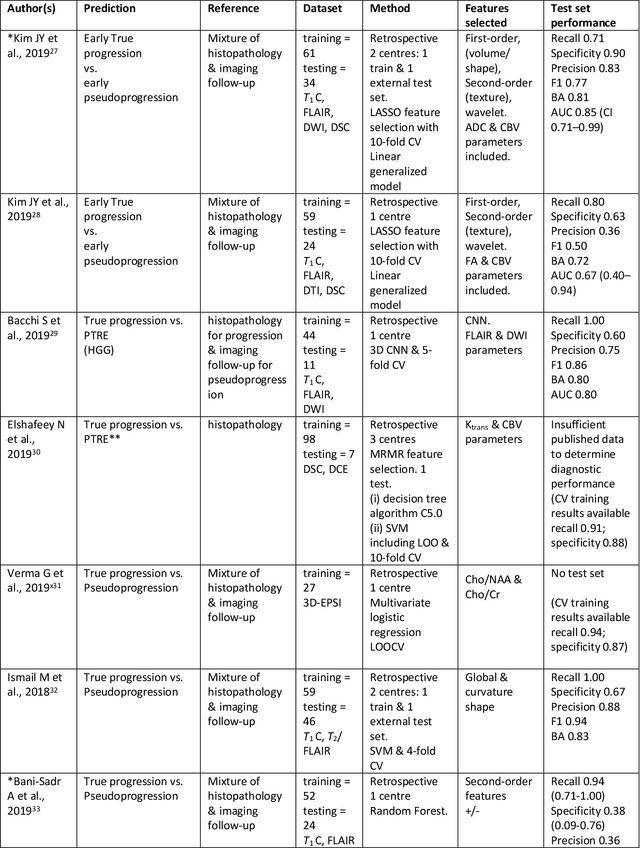
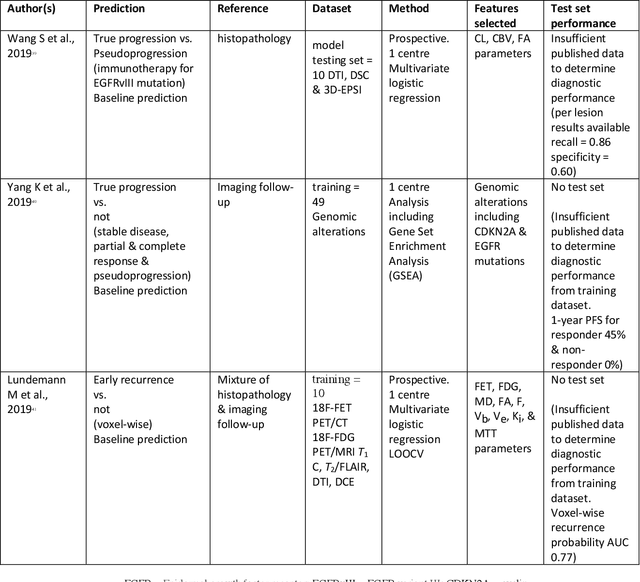
Abstract:The aim of the systematic review was to assess recently published studies on diagnostic test accuracy of glioblastoma treatment response monitoring biomarkers in adults, developed through machine learning (ML). Articles were searched for using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Register. Included study participants were adult patients with high grade glioma who had undergone standard treatment (maximal resection, radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide) and subsequently underwent follow-up imaging to determine treatment response status. Risk of bias and applicability was assessed with QUADAS 2 methodology. Contingency tables were created for hold-out test sets and recall, specificity, precision, F1-score, balanced accuracy calculated. Fifteen studies were included with 1038 patients in training sets and 233 in test sets. To determine whether there was progression or a mimic, the reference standard combination of follow-up imaging and histopathology at re-operation was applied in 67% of studies. The small numbers of patient included in studies, the high risk of bias and concerns of applicability in the study designs (particularly in relation to the reference standard and patient selection due to confounding), and the low level of evidence, suggest that limited conclusions can be drawn from the data. There is likely good diagnostic performance of machine learning models that use MRI features to distinguish between progression and mimics. The diagnostic performance of ML using implicit features did not appear to be superior to ML using explicit features. There are a range of ML-based solutions poised to become treatment response monitoring biomarkers for glioblastoma. To achieve this, the development and validation of ML models require large, well-annotated datasets where the potential for confounding in the study design has been carefully considered.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge