Avisek Gupta
MK-SGC-SC: Multiple Kernel Guided Sparse Graph Construction in Spectral Clustering for Unsupervised Speaker Diarization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Speaker diarization aims to segment audio recordings into regions corresponding to individual speakers. Although unsupervised speaker diarization is inherently challenging, the prospect of identifying speaker regions without pretraining or weak supervision motivates research on clustering techniques. In this work, we share the notable observation that measuring multiple kernel similarities of speaker embeddings to thereafter craft a sparse graph for spectral clustering in a principled manner is sufficient to achieve state-of-the-art performances in a fully unsupervised setting. Specifically, we consider four polynomial kernels and a degree one arccosine kernel to measure similarities in speaker embeddings, using which sparse graphs are constructed in a principled manner to emphasize local similarities. Experiments show the proposed approach excels in unsupervised speaker diarization over a variety of challenging environments in the DIHARD-III, AMI, and VoxConverse corpora. To encourage further research, our implementations are available at https://github.com/nikhilraghav29/MK-SGC-SC.
Enhancing MRI-Based Classification of Alzheimer's Disease with Explainable 3D Hybrid Compact Convolutional Transformers
Mar 24, 2024



Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD), characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory loss, presents a formidable global health challenge, underscoring the critical importance of early and precise diagnosis for timely interventions and enhanced patient outcomes. While MRI scans provide valuable insights into brain structures, traditional analysis methods often struggle to discern intricate 3D patterns crucial for AD identification. Addressing this challenge, we introduce an alternative end-to-end deep learning model, the 3D Hybrid Compact Convolutional Transformers 3D (HCCT). By synergistically combining convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs), the 3D HCCT adeptly captures both local features and long-range relationships within 3D MRI scans. Extensive evaluations on prominent AD benchmark dataset, ADNI, demonstrate the 3D HCCT's superior performance, surpassing state of the art CNN and transformer-based methods in classification accuracy. Its robust generalization capability and interpretability marks a significant stride in AD classification from 3D MRI scans, promising more accurate and reliable diagnoses for improved patient care and superior clinical outcomes.
Fuzzy Clustering to Identify Clusters at Different Levels of Fuzziness: An Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization Approach
Aug 09, 2018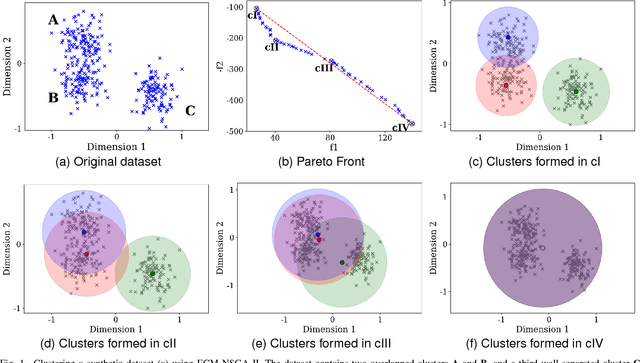
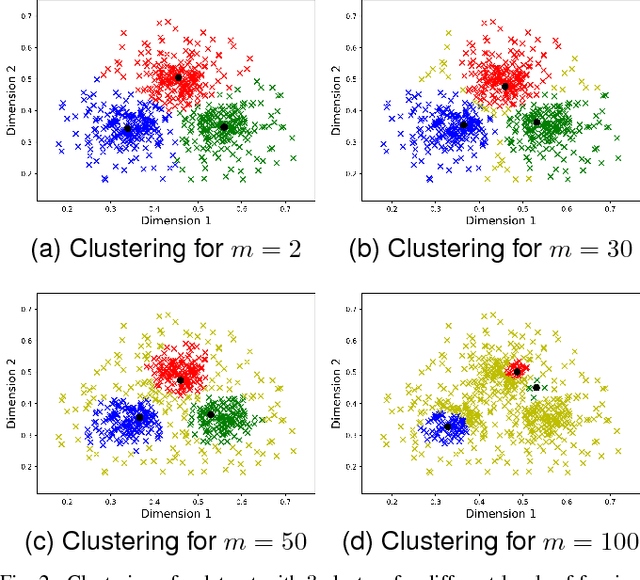
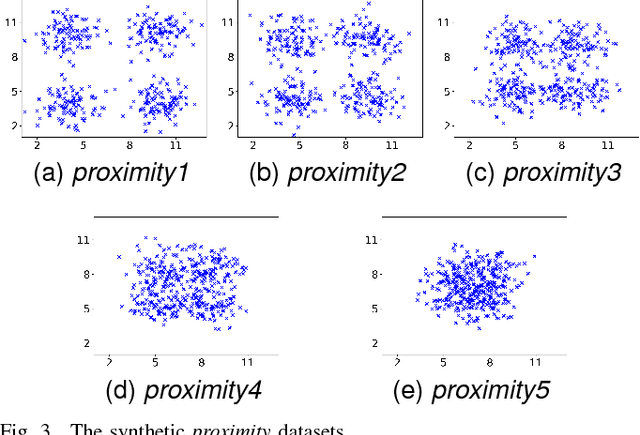
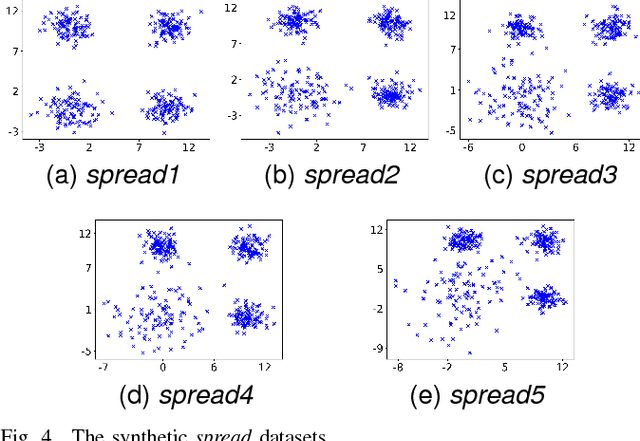
Abstract:Fuzzy clustering methods identify naturally occurring clusters in a dataset, where the extent to which different clusters are overlapped can differ. Most methods have a parameter to fix the level of fuzziness. However, the appropriate level of fuzziness depends on the application at hand. This paper presents Entropy $c$-Means (ECM), a method of fuzzy clustering that simultaneously optimizes two contradictory objective functions, resulting in the creation of fuzzy clusters with different levels of fuzziness. This allows ECM to identify clusters with different degrees of overlap. ECM optimizes the two objective functions using two multi-objective optimization methods, Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II), and Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm based on Decomposition (MOEA/D). We also propose a method to select a suitable trade-off clustering from the Pareto front. Experiments on challenging synthetic datasets as well as real-world datasets show that ECM leads to better cluster detection compared to the conventional fuzzy clustering methods as well as previously used multi-objective methods for fuzzy clustering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge