Atiye Sadat Hashemi
Latent Space Score-based Diffusion Model for Probabilistic Multivariate Time Series Imputation
Sep 13, 2024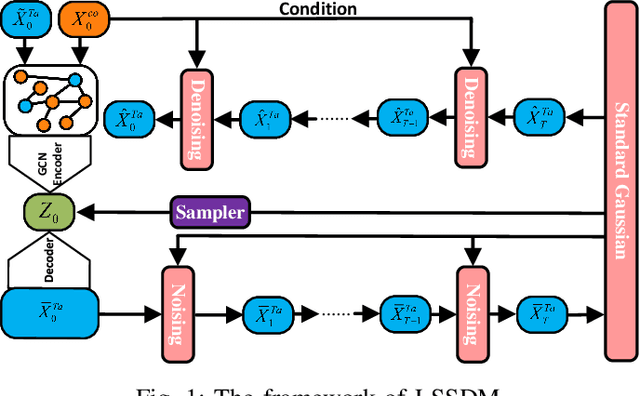
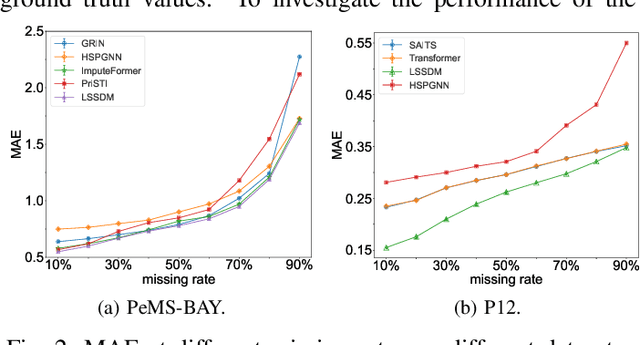
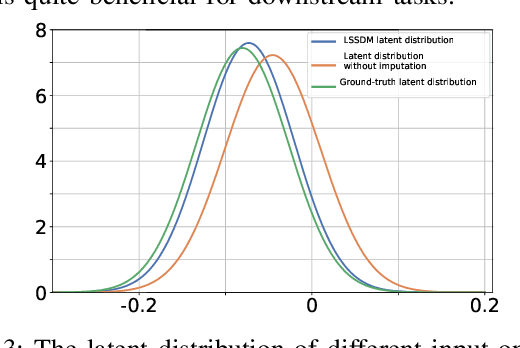
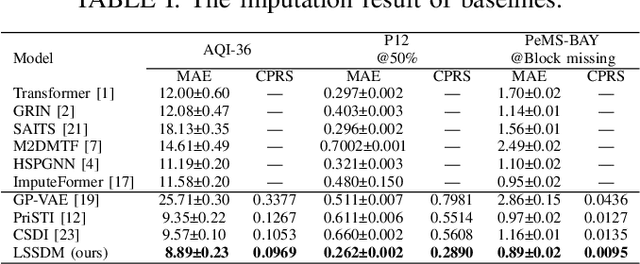
Abstract:Accurate imputation is essential for the reliability and success of downstream tasks. Recently, diffusion models have attracted great attention in this field. However, these models neglect the latent distribution in a lower-dimensional space derived from the observed data, which limits the generative capacity of the diffusion model. Additionally, dealing with the original missing data without labels becomes particularly problematic. To address these issues, we propose the Latent Space Score-Based Diffusion Model (LSSDM) for probabilistic multivariate time series imputation. Observed values are projected onto low-dimensional latent space and coarse values of the missing data are reconstructed without knowing their ground truth values by this unsupervised learning approach. Finally, the reconstructed values are fed into a conditional diffusion model to obtain the precise imputed values of the time series. In this way, LSSDM not only possesses the power to identify the latent distribution but also seamlessly integrates the diffusion model to obtain the high-fidelity imputed values and assess the uncertainty of the dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that LSSDM achieves superior imputation performance while also providing a better explanation and uncertainty analysis of the imputation mechanism. The website of the code is \textit{https://github.com/gorgen2020/LSSDM\_imputation}.
Transferable Universal Adversarial Perturbations Using Generative Models
Oct 29, 2020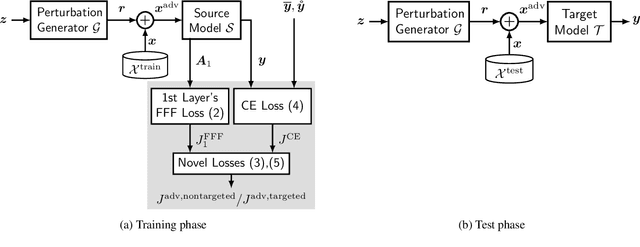
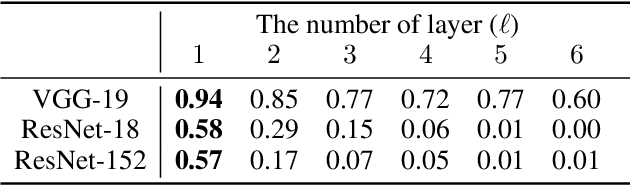
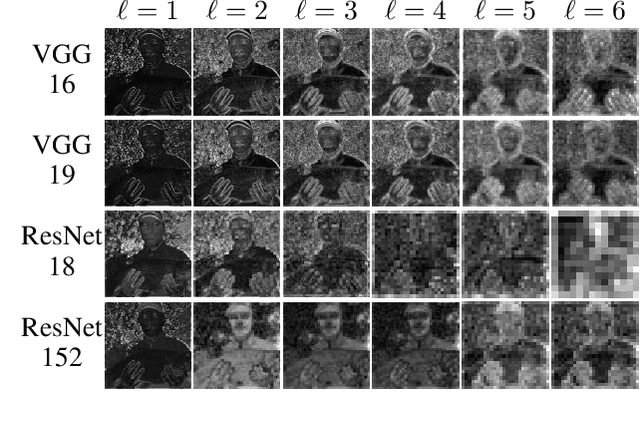
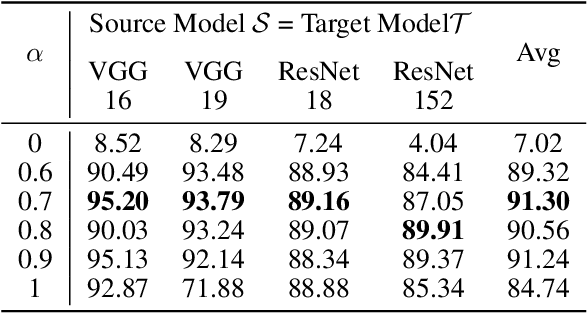
Abstract:Deep neural networks tend to be vulnerable to adversarial perturbations, which by adding to a natural image can fool a respective model with high confidence. Recently, the existence of image-agnostic perturbations, also known as universal adversarial perturbations (UAPs), were discovered. However, existing UAPs still lack a sufficiently high fooling rate, when being applied to an unknown target model. In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning technique for generating more transferable UAPs. We utilize a perturbation generator and some given pretrained networks so-called source models to generate UAPs using the ImageNet dataset. Due to the similar feature representation of various model architectures in the first layer, we propose a loss formulation that focuses on the adversarial energy only in the respective first layer of the source models. This supports the transferability of our generated UAPs to any other target model. We further empirically analyze our generated UAPs and demonstrate that these perturbations generalize very well towards different target models. Surpassing the current state of the art in both, fooling rate and model-transferability, we can show the superiority of our proposed approach. Using our generated non-targeted UAPs, we obtain an average fooling rate of 93.36% on the source models (state of the art: 82.16%). Generating our UAPs on the deep ResNet-152, we obtain about a 12% absolute fooling rate advantage vs. cutting-edge methods on VGG-16 and VGG-19 target models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge