Athar Sefid
SciBERTSUM: Extractive Summarization for Scientific Documents
Jan 21, 2022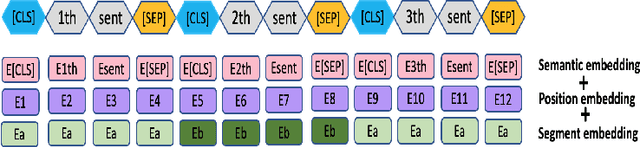
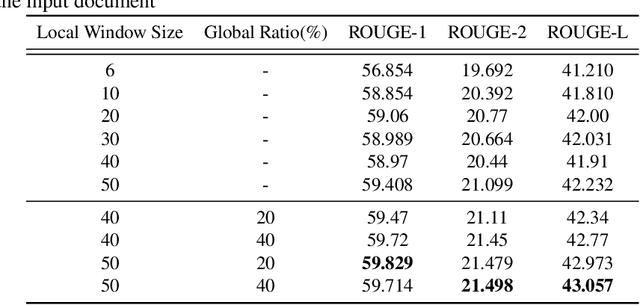
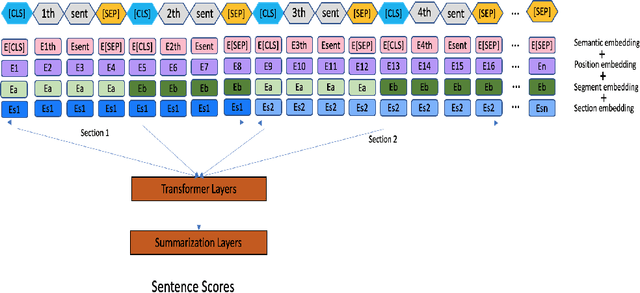
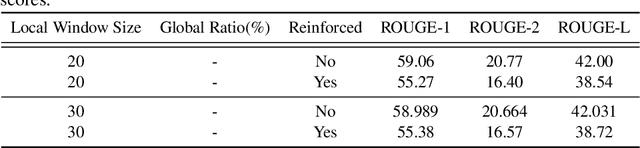
Abstract:The summarization literature focuses on the summarization of news articles. The news articles in the CNN-DailyMail are relatively short documents with about 30 sentences per document on average. We introduce SciBERTSUM, our summarization framework designed for the summarization of long documents like scientific papers with more than 500 sentences. SciBERTSUM extends BERTSUM to long documents by 1) adding a section embedding layer to include section information in the sentence vector and 2) applying a sparse attention mechanism where each sentences will attend locally to nearby sentences and only a small number of sentences attend globally to all other sentences. We used slides generated by the authors of scientific papers as reference summaries since they contain the technical details from the paper. The results show the superiority of our model in terms of ROUGE scores.
Extractive Research Slide Generation Using Windowed Labeling Ranking
Jun 06, 2021



Abstract:Presentation slides describing the content of scientific and technical papers are an efficient and effective way to present that work. However, manually generating presentation slides is labor intensive. We propose a method to automatically generate slides for scientific papers based on a corpus of 5000 paper-slide pairs compiled from conference proceedings websites. The sentence labeling module of our method is based on SummaRuNNer, a neural sequence model for extractive summarization. Instead of ranking sentences based on semantic similarities in the whole document, our algorithm measures importance and novelty of sentences by combining semantic and lexical features within a sentence window. Our method outperforms several baseline methods including SummaRuNNer by a significant margin in terms of ROUGE score.
Extractive Summarizer for Scholarly Articles
Aug 25, 2020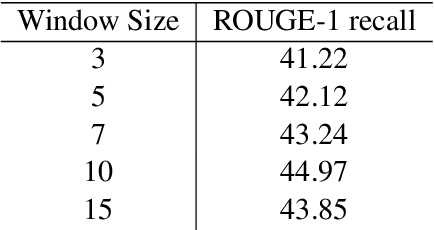
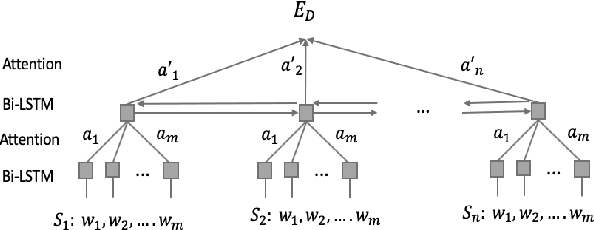
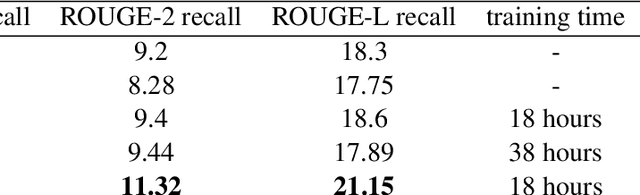
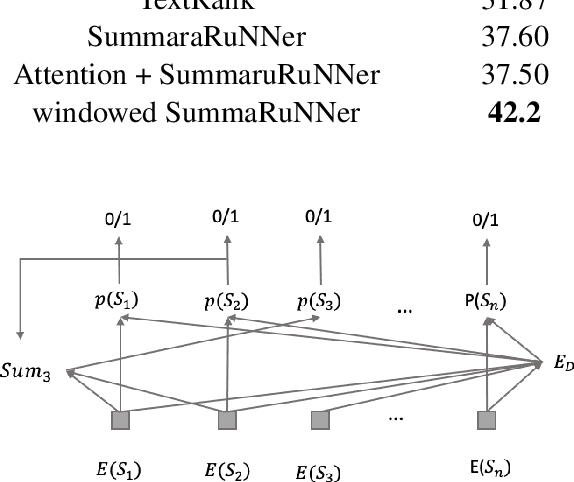
Abstract:We introduce an extractive method that will summarize long scientific papers. Our model uses presentation slides provided by the authors of the papers as the gold summary standard to label the sentences. The sentences are ranked based on their novelty and their importance as estimated by deep neural networks. Our window-based extractive labeling of sentences results in the improvement of at least 4 ROUGE1-Recall points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge