Asi Shefer
OpenAsp: A Benchmark for Multi-document Open Aspect-based Summarization
Dec 07, 2023
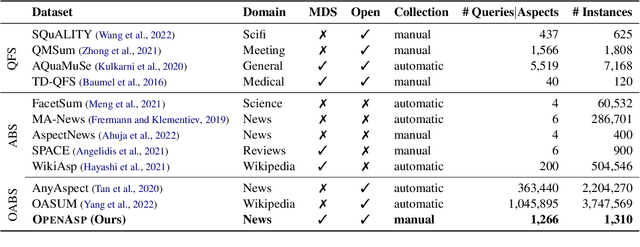
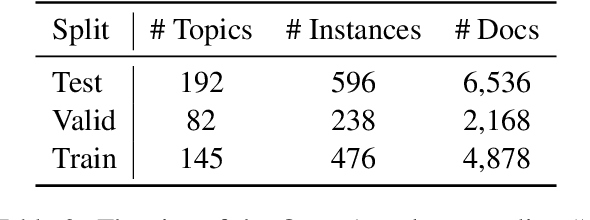
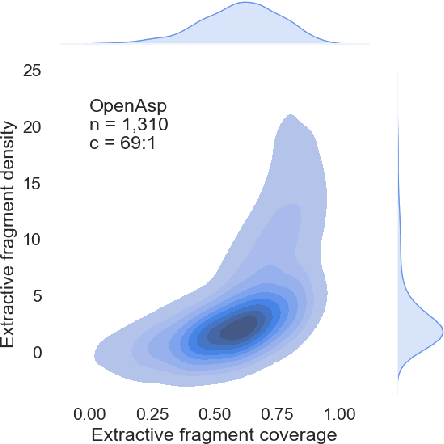
Abstract:The performance of automatic summarization models has improved dramatically in recent years. Yet, there is still a gap in meeting specific information needs of users in real-world scenarios, particularly when a targeted summary is sought, such as in the useful aspect-based summarization setting targeted in this paper. Previous datasets and studies for this setting have predominantly concentrated on a limited set of pre-defined aspects, focused solely on single document inputs, or relied on synthetic data. To advance research on more realistic scenarios, we introduce OpenAsp, a benchmark for multi-document \textit{open} aspect-based summarization. This benchmark is created using a novel and cost-effective annotation protocol, by which an open aspect dataset is derived from existing generic multi-document summarization datasets. We analyze the properties of OpenAsp showcasing its high-quality content. Further, we show that the realistic open-aspect setting realized in OpenAsp poses a challenge for current state-of-the-art summarization models, as well as for large language models.
Revisiting Sentence Union Generation as a Testbed for Text Consolidation
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Tasks involving text generation based on multiple input texts, such as multi-document summarization, long-form question answering and contemporary dialogue applications, challenge models for their ability to properly consolidate partly-overlapping multi-text information. However, these tasks entangle the consolidation phase with the often subjective and ill-defined content selection requirement, impeding proper assessment of models' consolidation capabilities. In this paper, we suggest revisiting the sentence union generation task as an effective well-defined testbed for assessing text consolidation capabilities, decoupling the consolidation challenge from subjective content selection. To support research on this task, we present refined annotation methodology and tools for crowdsourcing sentence union, create the largest union dataset to date and provide an analysis of its rich coverage of various consolidation aspects. We then propose a comprehensive evaluation protocol for union generation, including both human and automatic evaluation. Finally, as baselines, we evaluate state-of-the-art language models on the task, along with a detailed analysis of their capacity to address multi-text consolidation challenges and their limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge