Ashrya Agrawal
Pixel to policy: DQN Encoders for within & cross-game reinforcement learning
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:Reinforcement Learning can be applied to various tasks, and environments. Many of these environments have a similar shared structure, which can be exploited to improve RL performance on other tasks. Transfer learning can be used to take advantage of this shared structure, by learning policies that are transferable across different tasks and environments and can lead to more efficient learning as well as improved performance on a wide range of tasks. This work explores as well as compares the performance between RL models being trained from the scratch and on different approaches of transfer learning. Additionally, the study explores the performance of a model trained on multiple game environments, with the goal of developing a universal game-playing agent as well as transfer learning a pre-trained encoder using DQN, and training it on the same game or a different game. Our DQN model achieves a mean episode reward of 46.16 which even beats the human-level performance with merely 20k episodes which is significantly lower than deepmind's 1M episodes. The achieved mean rewards of 533.42 and 402.17 on the Assault and Space Invader environments respectively, represent noteworthy performance on these challenging environments.
Exploiting CNNs for Semantic Segmentation with Pascal VOC
May 05, 2023
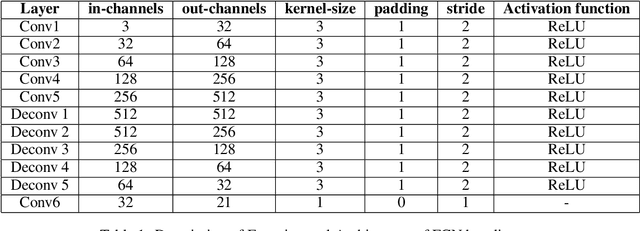
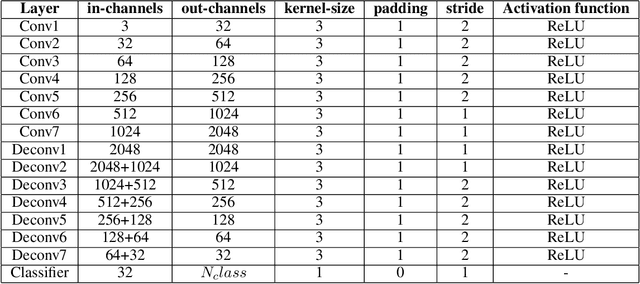
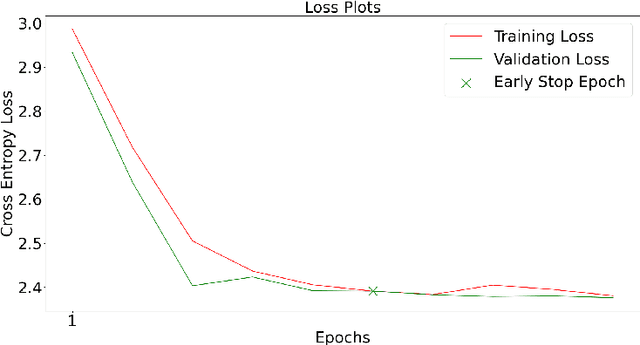
Abstract:In this paper, we present a comprehensive study on semantic segmentation with the Pascal VOC dataset. Here, we have to label each pixel with a class which in turn segments the entire image based on the objects/entities present. To tackle this, we firstly use a Fully Convolution Network (FCN) baseline which gave 71.31% pixel accuracy and 0.0527 mean IoU. We analyze its performance and working and subsequently address the issues in the baseline with three improvements: a) cosine annealing learning rate scheduler(pixel accuracy: 72.86%, IoU: 0.0529), b) data augmentation(pixel accuracy: 69.88%, IoU: 0.0585) c) class imbalance weights(pixel accuracy: 68.98%, IoU: 0.0596). Apart from these changes in training pipeline, we also explore three different architectures: a) Our proposed model -- Advanced FCN (pixel accuracy: 67.20%, IoU: 0.0602) b) Transfer Learning with ResNet (Best performance) (pixel accuracy: 71.33%, IoU: 0.0926 ) c) U-Net(pixel accuracy: 72.15%, IoU: 0.0649). We observe that the improvements help in greatly improving the performance, as reflected both, in metrics and segmentation maps. Interestingly, we observe that among the improvements, dataset augmentation has the greatest contribution. Also, note that transfer learning model performs the best on the pascal dataset. We analyse the performance of these using loss, accuracy and IoU plots along with segmentation maps, which help us draw valuable insights about the working of the models.
Debiasing classifiers: is reality at variance with expectation?
Nov 04, 2020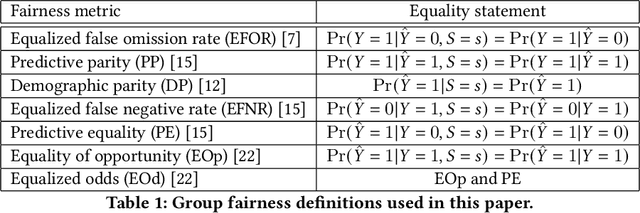

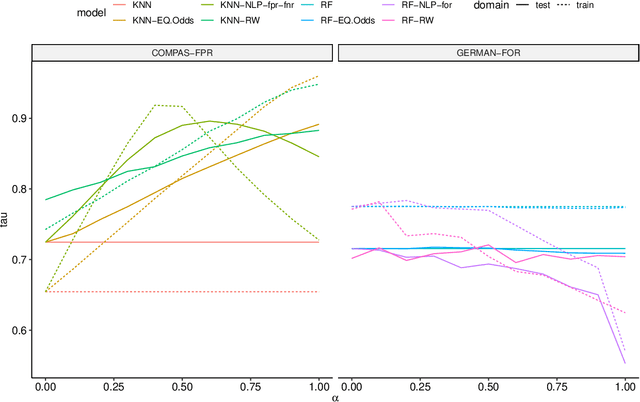
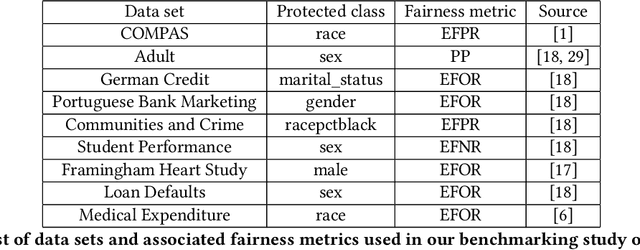
Abstract:Many methods for debiasing classifiers have been proposed, but their effectiveness in practice remains unclear. We evaluate the performance of pre-processing and post-processing debiasers for improving fairness in random forest classifiers trained on a suite of data sets. Specifically, we study how these debiasers generalize with respect to both out-of-sample test error for computing fairness -- performance and fairness -- fairness trade-offs, and on the change in other fairness metrics that were not explicitly optimised. Our results demonstrate that out-of-sample performance on fairness and performance can vary substantially and unexpectedly. Moreover, the variance in estimation arises from class imbalances with respect to both the outcome and the protected classes. Our results highlight the importance of evaluating out-of-sample performance in practical usage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge