Arkaitz Artetxe
REMoH: A Reflective Evolution of Multi-objective Heuristics approach via Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Multi-objective optimization is fundamental in complex decision-making tasks. Traditional algorithms, while effective, often demand extensive problem-specific modeling and struggle to adapt to nonlinear structures. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer enhanced explainability, adaptability, and reasoning. This work proposes Reflective Evolution of Multi-objective Heuristics (REMoH), a novel framework integrating NSGA-II with LLM-based heuristic generation. A key innovation is a reflection mechanism that uses clustering and search-space reflection to guide the creation of diverse, high-quality heuristics, improving convergence and maintaining solution diversity. The approach is evaluated on the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem (FJSSP) in-depth benchmarking against state-of-the-art methods using three instance datasets: Dauzere, Barnes, and Brandimarte. Results demonstrate that REMoH achieves competitive results compared to state-of-the-art approaches with reduced modeling effort and enhanced adaptability. These findings underscore the potential of LLMs to augment traditional optimization, offering greater flexibility, interpretability, and robustness in multi-objective scenarios.
Exploring Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Unrelated Parallel Machine Scheduling
Nov 12, 2024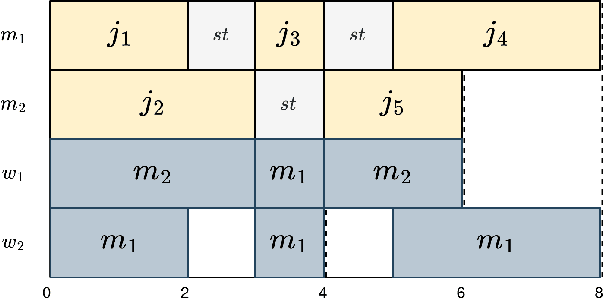



Abstract:Scheduling problems pose significant challenges in resource, industry, and operational management. This paper addresses the Unrelated Parallel Machine Scheduling Problem (UPMS) with setup times and resources using a Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) approach. The study introduces the Reinforcement Learning environment and conducts empirical analyses, comparing MARL with Single-Agent algorithms. The experiments employ various deep neural network policies for single- and Multi-Agent approaches. Results demonstrate the efficacy of the Maskable extension of the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm in Single-Agent scenarios and the Multi-Agent PPO algorithm in Multi-Agent setups. While Single-Agent algorithms perform adequately in reduced scenarios, Multi-Agent approaches reveal challenges in cooperative learning but a scalable capacity. This research contributes insights into applying MARL techniques to scheduling optimization, emphasizing the need for algorithmic sophistication balanced with scalability for intelligent scheduling solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge