Anurag Sahu
MVRackLay: Monocular Multi-View Layout Estimation for Warehouse Racks and Shelves
Nov 30, 2022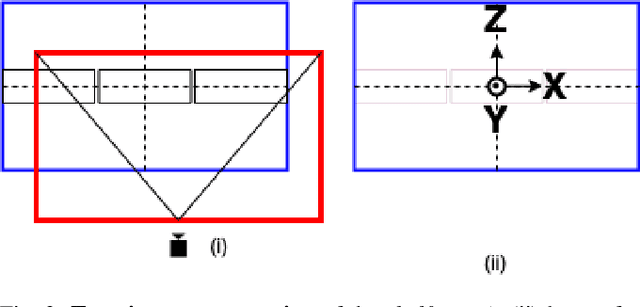
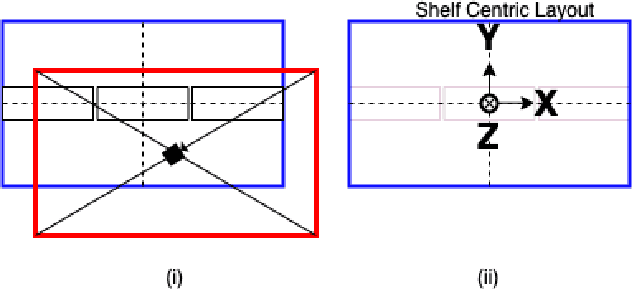
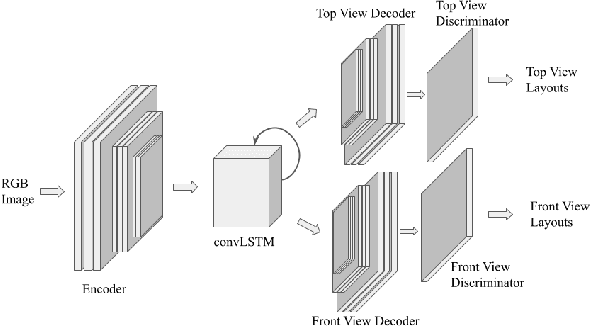
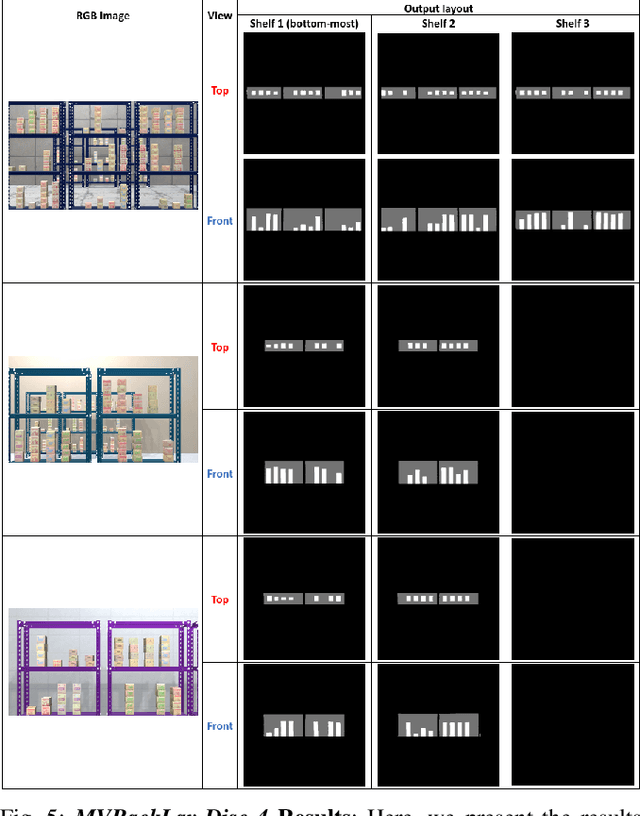
Abstract:In this paper, we propose and showcase, for the first time, monocular multi-view layout estimation for warehouse racks and shelves. Unlike typical layout estimation methods, MVRackLay estimates multi-layered layouts, wherein each layer corresponds to the layout of a shelf within a rack. Given a sequence of images of a warehouse scene, a dual-headed Convolutional-LSTM architecture outputs segmented racks, the front and the top view layout of each shelf within a rack. With minimal effort, such an output is transformed into a 3D rendering of all racks, shelves and objects on the shelves, giving an accurate 3D depiction of the entire warehouse scene in terms of racks, shelves and the number of objects on each shelf. MVRackLay generalizes to a diverse set of warehouse scenes with varying number of objects on each shelf, number of shelves and in the presence of other such racks in the background. Further, MVRackLay shows superior performance vis-a-vis its single view counterpart, RackLay, in layout accuracy, quantized in terms of the mean IoU and mAP metrics. We also showcase a multi-view stitching of the 3D layouts resulting in a representation of the warehouse scene with respect to a global reference frame akin to a rendering of the scene from a SLAM pipeline. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first such work to portray a 3D rendering of a warehouse scene in terms of its semantic components - Racks, Shelves and Objects - all from a single monocular camera.
RackLay: Multi-Layer Layout Estimation for Warehouse Racks
Mar 17, 2021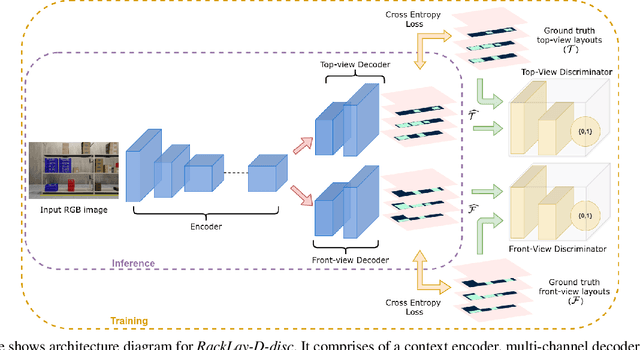

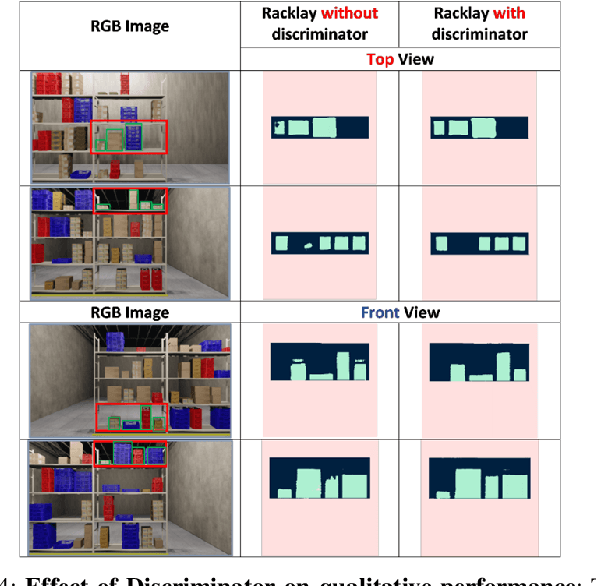
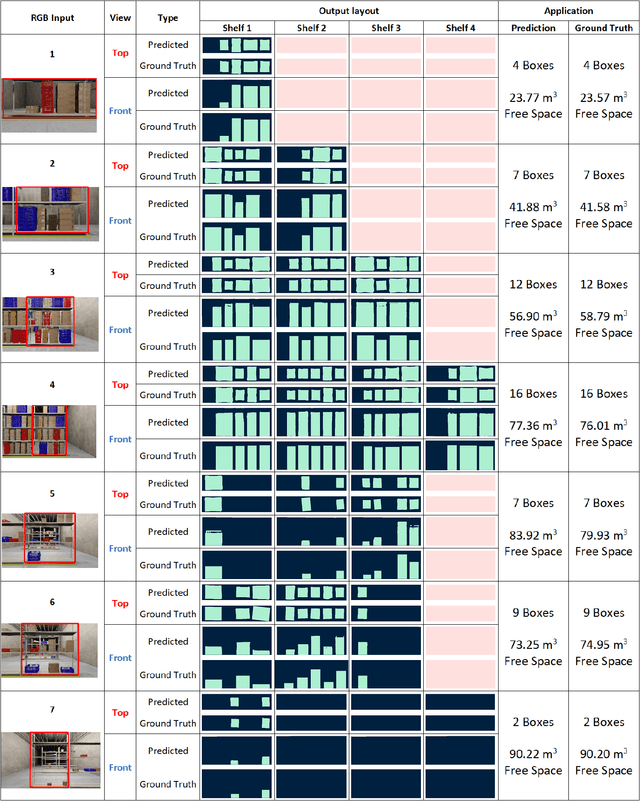
Abstract:Given a monocular colour image of a warehouse rack, we aim to predict the bird's-eye view layout for each shelf in the rack, which we term as multi-layer layout prediction. To this end, we present RackLay, a deep neural network for real-time shelf layout estimation from a single image. Unlike previous layout estimation methods, which provide a single layout for the dominant ground plane alone, RackLay estimates the top-view and front-view layout for each shelf in the considered rack populated with objects. RackLay's architecture and its variants are versatile and estimate accurate layouts for diverse scenes characterized by varying number of visible shelves in an image, large range in shelf occupancy factor and varied background clutter. Given the extreme paucity of datasets in this space and the difficulty involved in acquiring real data from warehouses, we additionally release a flexible synthetic dataset generation pipeline WareSynth which allows users to control the generation process and tailor the dataset according to contingent application. The ablations across architectural variants and comparison with strong prior baselines vindicate the efficacy of RackLay as an apt architecture for the novel problem of multi-layered layout estimation. We also show that fusing the top-view and front-view enables 3D reasoning applications such as metric free space estimation for the considered rack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge