Antal Horváth
3D Segmentation Networks for Excessive Numbers of Classes: Distinct Bone Segmentation in Upper Bodies
Oct 14, 2020



Abstract:Segmentation of distinct bones plays a crucial role in diagnosis, planning, navigation, and the assessment of bone metastasis. It supplies semantic knowledge to visualisation tools for the planning of surgical interventions and the education of health professionals. Fully supervised segmentation of 3D data using Deep Learning methods has been extensively studied for many tasks but is usually restricted to distinguishing only a handful of classes. With 125 distinct bones, our case includes many more labels than typical 3D segmentation tasks. For this reason, the direct adaptation of most established methods is not possible. This paper discusses the intricacies of training a 3D segmentation network in a many-label setting and shows necessary modifications in network architecture, loss function, and data augmentation. As a result, we demonstrate the robustness of our method by automatically segmenting over one hundred distinct bones simultaneously in an end-to-end learnt fashion from a CT-scan.
* 10 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables, accepted into MICCAI 2020 International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging
Pathology Segmentation using Distributional Differences to Images of Healthy Origin
May 25, 2018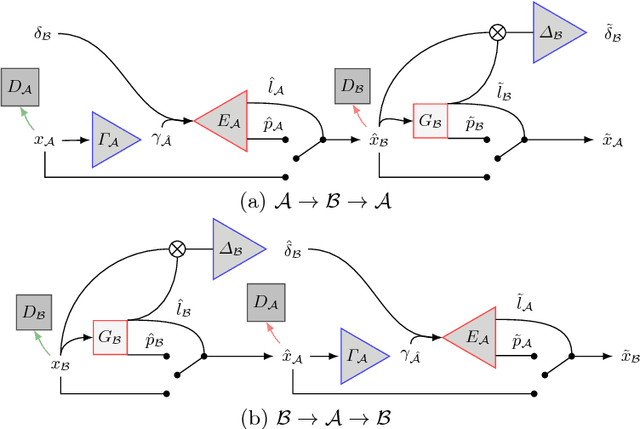
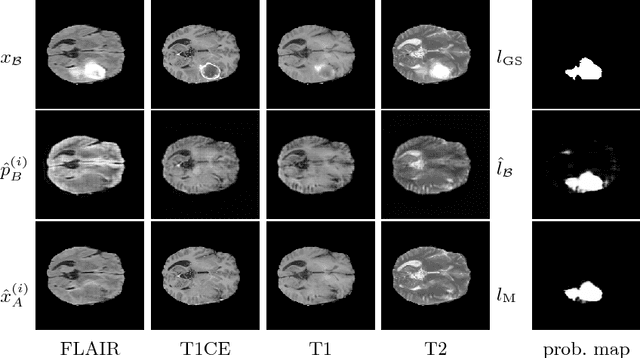
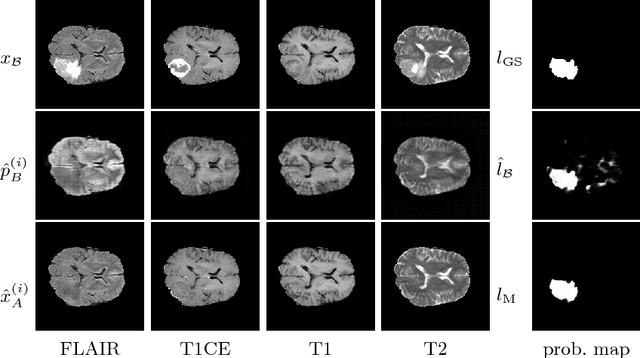
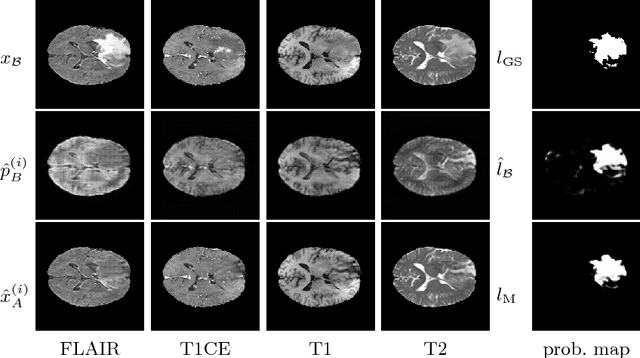
Abstract:We present a method to model pathologies in medical data, trained on data labelled on the image level as healthy or containing a visual defect. Our model not only allows us to create pixelwise semantic segmentations, it is also able to create inpaintings for the segmentations to render the pathological image healthy. Furthermore, we can draw new unseen pathology samples from this model based on the distribution in the data. We show quantitatively, that our method is able to segment pathologies with a surprising accuracy and show qualitative results of both the segmentations and inpaintings. A comparison with a supervised segmentation method indicates, that the accuracy of our proposed weakly-supervised segmentation is nevertheless quite close.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge