Ansong Li
Transition Information Enhanced Disentangled Graph Neural Networks for Session-based Recommendation
Apr 05, 2022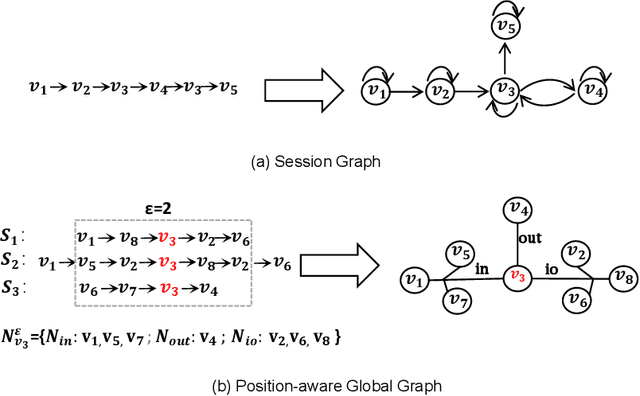
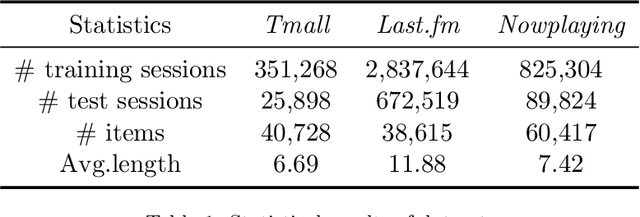
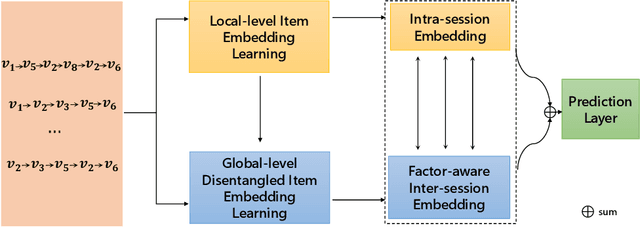
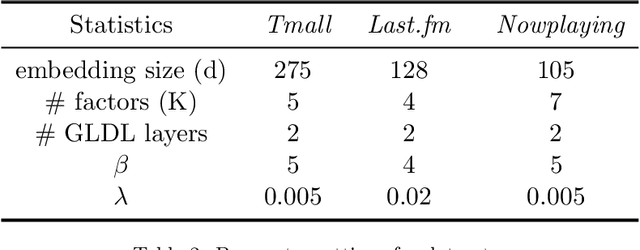
Abstract:Session-based recommendation is a practical recommendation task that predicts the next item based on an anonymous behavior sequence, and its performance relies heavily on the transition information between items in the sequence. The SOTA methods in SBR employ GNN to model neighboring item transitions from global (i.e, other sessions) and local (i.e, current session) contexts. However, most existing methods treat neighbors from different sessions equally without considering that the neighbor items from different sessions may share similar features with the target item on different aspects and may have different contributions. In other words, they have not explored finer-granularity transition information between items in the global context, leading to sub-optimal performance. In this paper, we fill this gap by proposing a novel Transition Information Enhanced Disentangled Graph Neural Network (TIE-DGNN) model to capture finer-granular transition information between items and try to interpret the reason of the transition by modeling the various factors of the item. Specifically, we propose a position-aware global graph, which utilizes the relative position information to model the neighboring item transition. Then, we slice item embeddings into blocks, each of which represents a factor, and use disentangling module to separately learn the factor embeddings over the global graph. For local context, we train item embeddings by using attention mechanisms to capture transition information from the current session. To this end, our model considers two levels of transition information. Especially in global text, we not only consider finer-granularity transition information between items but also take user intents at factor-level into account to interpret the key reason for the transition. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method over the SOTA methods.
Disentangled Graph Neural Networks for Session-based Recommendation
Jan 11, 2022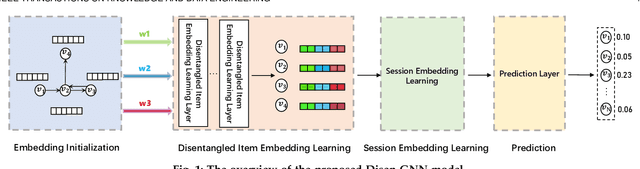


Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) has drawn increasingly research attention in recent years, due to its great practical value by only exploiting the limited user behavior history in the current session. Existing methods typically learn the session embedding at the item level, namely, aggregating the embeddings of items with or without the attention weights assigned to items. However, they ignore the fact that a user's intent on adopting an item is driven by certain factors of the item (e.g., the leading actors of an movie). In other words, they have not explored finer-granularity interests of users at the factor level to generate the session embedding, leading to sub-optimal performance. To address the problem, we propose a novel method called Disentangled Graph Neural Network (Disen-GNN) to capture the session purpose with the consideration of factor-level attention on each item. Specifically, we first employ the disentangled learning technique to cast item embeddings into the embedding of multiple factors, and then use the gated graph neural network (GGNN) to learn the embedding factor-wisely based on the item adjacent similarity matrix computed for each factor. Moreover, the distance correlation is adopted to enhance the independence between each pair of factors. After representing each item with independent factors, an attention mechanism is designed to learn user intent to different factors of each item in the session. The session embedding is then generated by aggregating the item embeddings with attention weights of each item's factors. To this end, our model takes user intents at the factor level into account to infer the user purpose in a session. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method over existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge